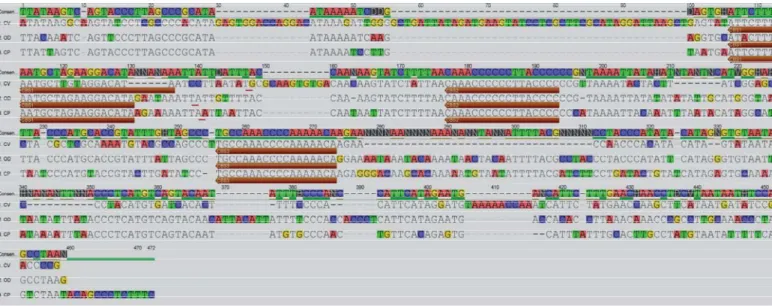
Secuencia y estructura de la regin control mitocondrial del roedor cubano Capromys pilorides (Rodentia: Capromyidae)
Texto completo
Figure




Documento similar
This study aimed to analyze the efficacy of two anxiety induction procedures in older adults and younger samples compared with a neutral mood induction control group.. We
monocytogenes in two fish products and describe inter-species competition was based on (i) the determination of the kinetic parameters of the two microbial pop- ulations
Predation was corrected for control mortality using the formula proposed by Xia et al. Functional response of each predator species was then analyzed in two steps: i)
A central role in this attenuation is played by the mitochondrial transcription termination factor (mTERF), a DNA-binding protein that protects a 28 bp region within the tRNA
(2013) as an index of parental involvement was valid in the Cuban context. The results showed that the cross-cultural validation within the Cuban context was successful, as
After constraining the SM tt normalization using a particular control region (see sec- tion 5.2), and investigating the agreement of the data and the QCD background estimate in
Observed number of species was relatively high in comparison with other studies in the Mediterranean, and we found no effects of fragment characteristics on species density,
We evaluated mitochondrial dysfunction caused by the first described case described of a mtDNA molecule harboring three LHON associated mutations in comparison with two of the