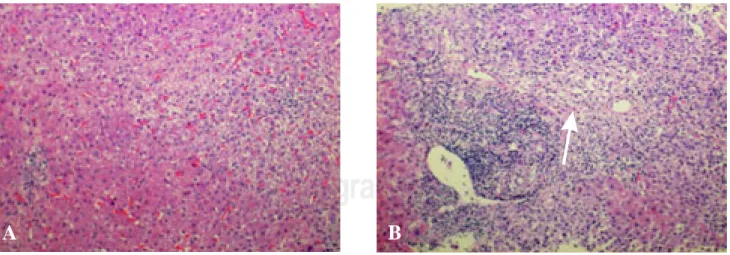
Drug induced liver injury secondary to interferon beta (IFN β) in multiple sclerosis
Texto completo
Figure

Documento similar
(a) NPs@PEG in the liver, (b) NPs@Glc in the liver and (c) NPs@Glc in the spleen at different post-administration times (72 h and four months). If in the spleen the core of
The other two studies reported that salivary progesterone levels were significantly lower in the early luteal phase in women with out-of-phase endometrial biopsy results.. One
The PLS-DA model was built using three latent variables and the top- 26 ranked variables based on the model development subset with data obtained from the metabolomic analysis of
Insulin treatment decreased liver pyruvate concentration and enhanced both liver and plasma lactate/pyruvate ratios compared with control values, whereas insulin plus
Now we also show that this upregulation occurs in H35 cells and acute liver injury, two conditions with different levels of Mat1a (minute or strongly reduced) and Mat2a expression
After the Co evaporation, the peak shifts towards to lower binding energies (-0.4eV with respect to original peak). After the Co intercalation process, C atoms will be in
We evaluated TLR2-mediated IFN-β production in peritoneal macrophages and the Raw264.7 cell line, observing that TLR2 ligands induce IFN-β although at lower levels than TLR4
Two months after challenge, hamsters immunized with HIS using the homologous strategy showed a significant parasite load reduction in the liver (Fig. 3C) but not in the