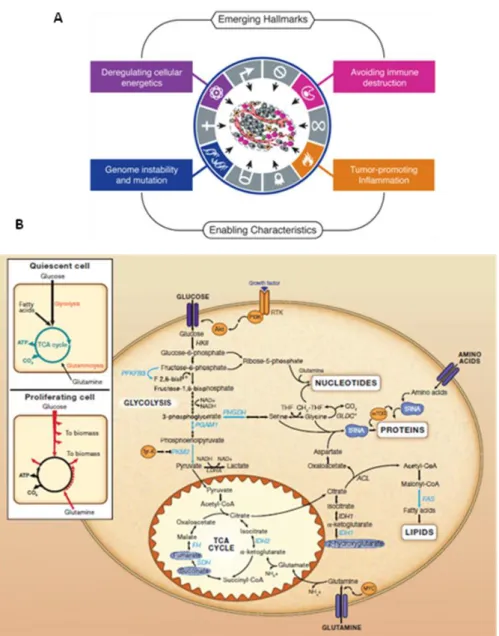
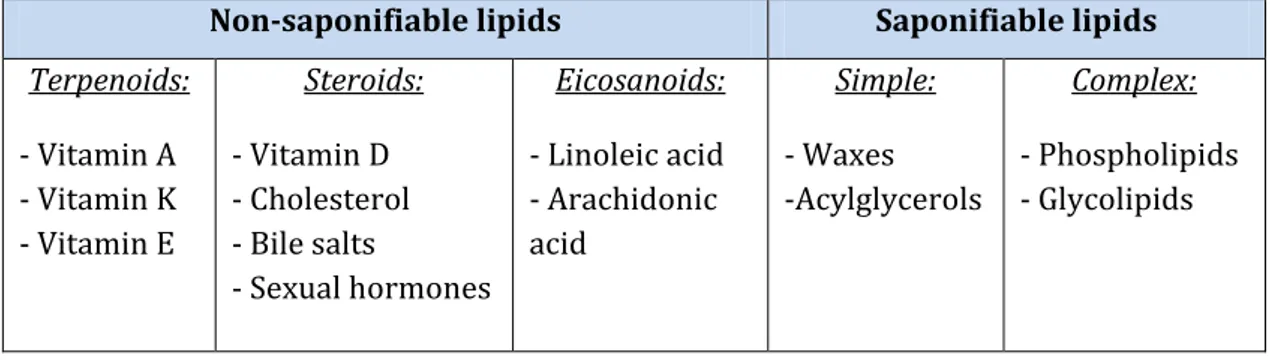
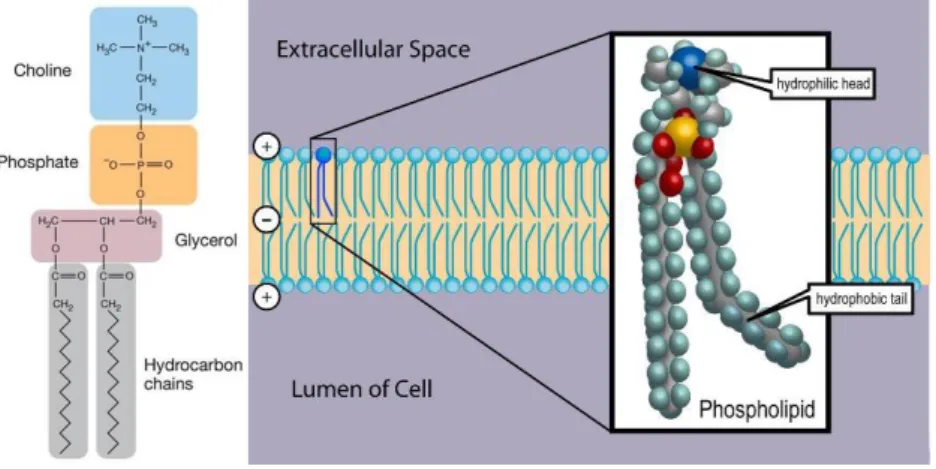
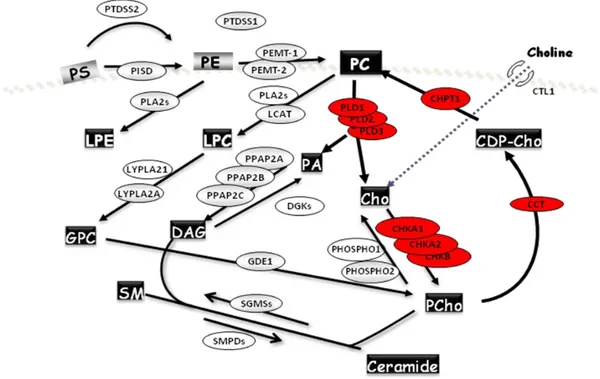
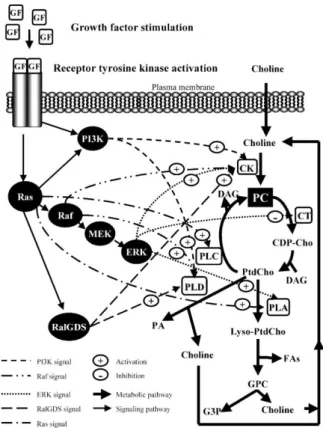
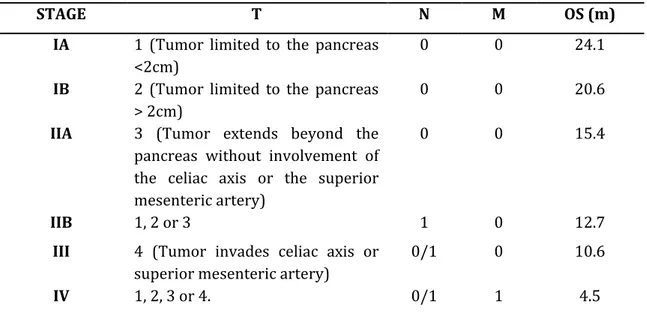
Deregulation of Choline Kinase in Pancreatic Cancer and its inhibition as a potential therapeutic strategy
Texto completo
Figure
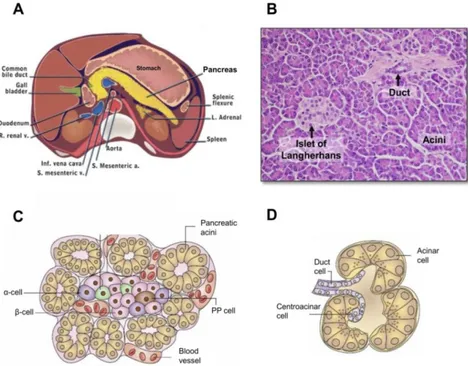
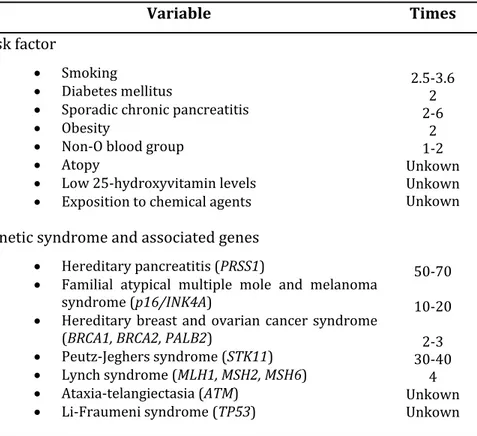
Documento similar
In addition, we define a new role for FGFR4 as regulator of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion in colorectal cancer that makes it an attractive target for
17,18 Contrary to graphene, the band gap in ML-MDS separating the valence and conduction bands is naturally large and due to the absence of inversion symmetry in ML-MDS the
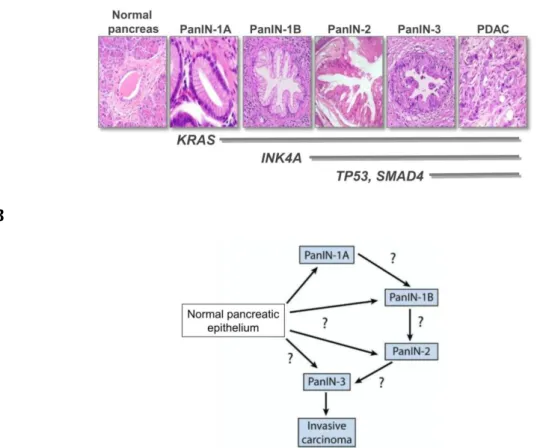
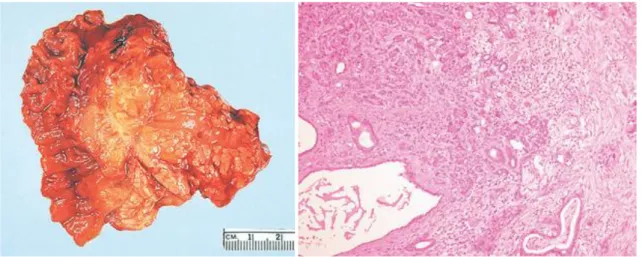
Accordingly, macrophages are the major leukocyte subpopulation present in ADM and PanINs (Clark et al., 2007) and, importantly, it has been shown that in response to
CDK4/6i have been shown to be effective in the pre-clinical treatment of huge variety of solid tumors: breat cancer, hepatoma, glioblastoma, ovarian cancer, neuroblastoma,
Second, hierarchical clustering of pancreatic cancer cell lines with primary tumours enabled the translation of drug sensitivity data from cell lines to the tumour subtypes found
This in turn invites a re-drawing of Giannobile’s catalogue (see below) to allow the possibility that the central elements are in fact the figure appearing on the obverse
In the in vivo animal experiments, Δ 9 -THCA-A successfully show a potential therapeutic effect in inflammatory diseases as we have observed in a model of
(C) lncRNAs can represent a bridge between the many layers of epigenetic gene regulation, interacting with, for example, histone modifiers or serving as ceRNAs for miRNAs; (D)