Temporal contexts: Filling the gap between episodic memory and associative learning
Texto completo
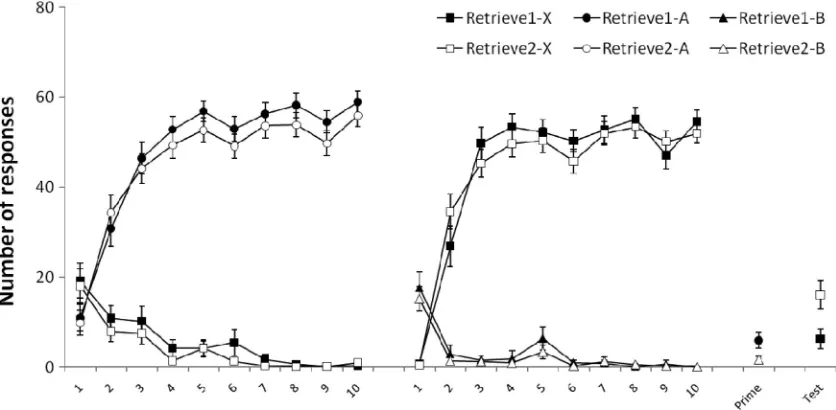
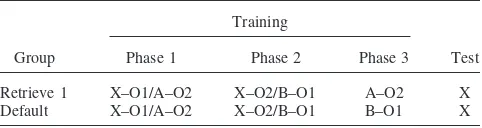
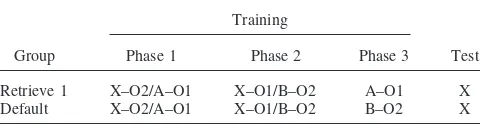
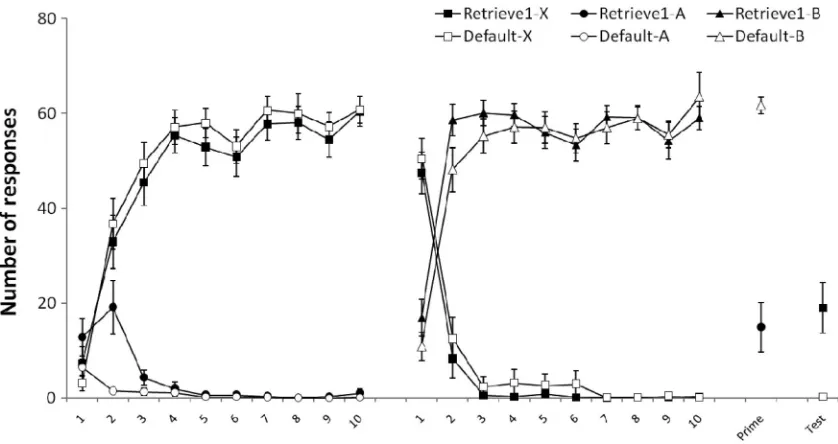
Figure

Documento similar
Our results here also indicate that the orders of integration are higher than 1 but smaller than 2 and thus, the standard approach of taking first differences does not lead to
In the “big picture” perspective of the recent years that we have described in Brazil, Spain, Portugal and Puerto Rico there are some similarities and important differences,
In the next 4 Sections of this paper, we explain the process used to create a test-set of correlated del.icio.us and flickr accounts, present the overlaps that emerge between
This paper deals with a case study exploring the way in which the integration of ICT impacts learning in the context The results of the questionnaire show that the use of these
For instance, the best overall accuracy of bagging in Breast with 20% noise is achieved using a 10% sampling ratio: The test error goes from 4.1% when no noise is injected to 3.5%
In particular, different versions of the training set for the base learners can be used, as in bagging (bootstrap sampling of training data), class-switching (noise injection in
2(b-d) show the comparison between the emission spectra collected in and out of the vicinity of the Ag NPs chain in different spectral regions. The spectra show a well
The RR values found in the VPR 2015 form’s indicators confirm that in contexts where protection of the victim is demanded based on the risk, the majority of risk indica- tors can