TítuloA 2D numerical model using finite volume method for sediment transport in rivers
Texto completo
Figure
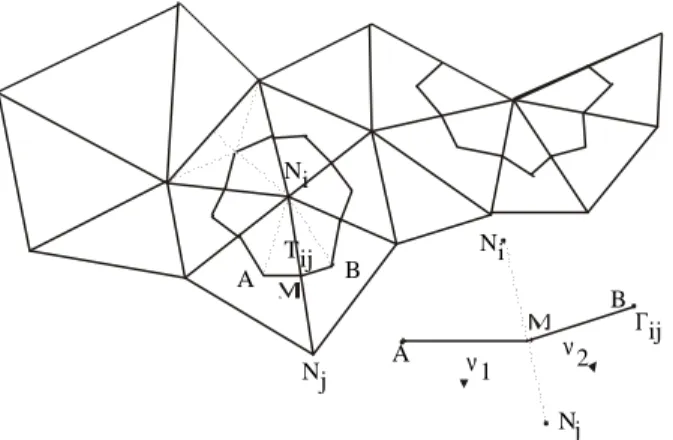
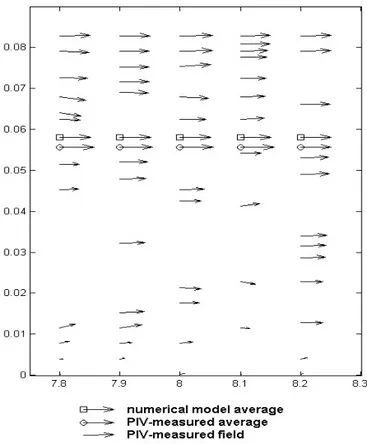
Documento similar
In this paper we analyze a finite element method applied to a continuous downscaling data assimilation algorithm for the numerical approximation of the two and three dimensional
The quality factors and coupling coefficients needed as training and testing sets for both boxes were computed using the neural network method described in Ref.. In this method,
B Analytical solutions for two dimensional problems 99 B.1 Analytical solutions of cutoff frequencies for TE and TM modes in two dimensions 99 B.2 Analytical solutions of
In this way, a powerful method following that methodology and being based on circuit theory, is the so-called Network Simulation Method (NSM), a numerical approach applied to
Numerical Simulation of Density-Driven Flow and Heat Transport Processes in Porous Media Using the Network Method.. Manuel Cánovas 1, * ID , Iván Alhama 2 , Gonzalo García 2 ,
Based on the network simulation method, a precise numerical model is designed for the 2-D groundwater flow in porous and isotropic aquifers.. If a partially pen- etrating
Numerical computing approach for solving Hunter-Saxton equation arising in liquid crystal model through sinc collocation method.. Iftikhar Ahmad a , Hira Ilyas a , Kadir Kutlu c ,
The method extends the positive definite non-oscillatory finite element algorithm (NFEM) capabilities to predict sediment transport, multiphase flow, and evolution of the