Serum adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in liver transplant recipients and the metabolic syndrome
Texto completo
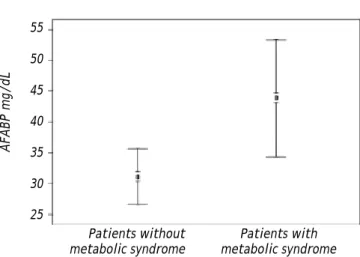
Figure


Documento similar
(a) NPs@PEG in the liver, (b) NPs@Glc in the liver and (c) NPs@Glc in the spleen at different post-administration times (72 h and four months). If in the spleen the core of
In this study, internal tissues of chicken liver samples were analysed for the presence of phages using a meta- genomics approach and the liver virome was compared with that of
It is noteworthy that only in diabetes, metabolic syn- drome, and Fatty liver disease index high do the results obtained coincide (with statistical significance) between the
Our results indicate that FLI-defined NAFLD is more prevalent in men than women, and it is associated with age, lower social class, and a dysmetabolic state charac- terized
Core tip: The Milan criteria for liver transplantation have improved survival of patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but up to 20% of patients still experience
Restless legs syndrome in patients with high serum ferritin and normal iron
A Study on the Relationship between Serum Beta 2-Microglobulin Levels, Underlying Chronic Kidney Disease, and Peripheral Arterial Disease in High-Vascular-Risk
Thirteen species of bats (order Chiroptera) were also found infected with the parasite in Mexico, employing skin, heart, liver and spleen in a PCR of kDNA and SSU [5].. The