Fatty liver and abdominal fat relationships with high C reactive protein in adults without coronary heart disease
Texto completo
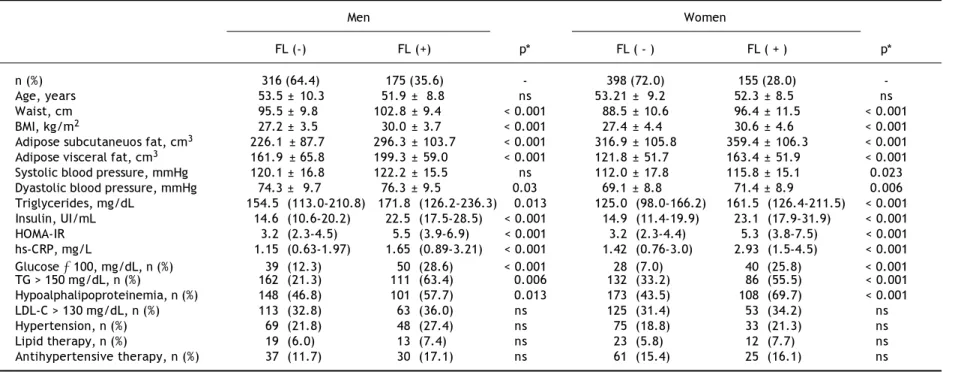
Figure

Documento similar
Besides, restrained eaters had lower triglyceride, homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), fasting insulin, blood glucose, and higher high-density
In conclusion, the circulating levels of the novel insulin- like adipokine ISM1 are significantly higher in pubertal chil- dren with obesity and are associated with BMI Z-score and fat
On the other hand, we addressed the role of GRK2 in the heart of adult (9 month) mice or of mice fed with high-fat diet, two conditions known to promote insulin resistance. In
A total of 1178 patients diagnosed with grade I-IIIa FL between January 1980 and December 2013, in the Oncology Department of 18 Spanish hospitals, were enrolled in the FL Registry,
We can use/make students use the new technologies in the classroom in different ways: by using commercially developed language programs or activities on the web; by assigning
Effects of resistance training on muscle strength, exercise capacity, and mobility in middle-aged and elderly patients with coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis.
It is noteworthy that only in diabetes, metabolic syn- drome, and Fatty liver disease index high do the results obtained coincide (with statistical significance) between the
Abstract: Background: A lifestyle with regular PA (physical activity) and Mediterranean diet has benefits on NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) and MetS (metabolic