Alternative method for concentration retrieval in differential optical absorption spectroscopy atmospheric gas pollutant measurements
Texto completo
Figure
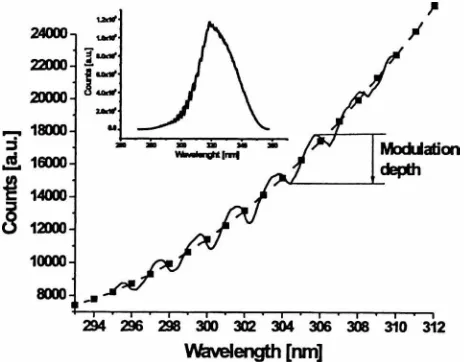
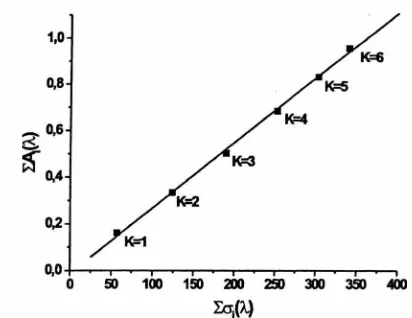
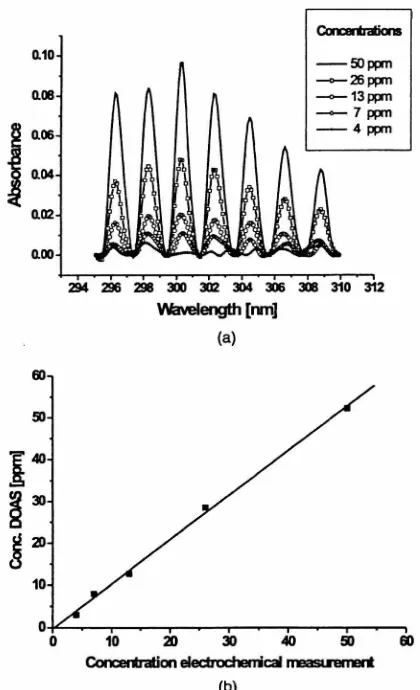

Documento similar
So, we have combined the analysis by two different techniques such as x-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS) and neutron powder diffraction (NPD) to extend our understanding on
The radiative transfer equation (RTE) and its formal solution (both in differential and integral form).. •
Here, we demonstrate attosecond transient absorption spectroscopy (ATAS) as a viable probe of the electronic and nuclear dynamics initiated in excited states of a neutral molecule by
QM/PCM approach, and absorption spectra in water computed by the full-QM, QM/MMee, and QM/MMpol approaches for pyridine with an inset zooming the first absorption feature
We have characterized the structural and magnetic properties of these platelets by Mössbauer spectroscopy, x-ray transmission microscopy (TXM), transmission electron microscopy
Figure 5 shows XAS spectra, obtained in the TEY mode at the region near the oxygen 1s absorp- tion edge, of samples grown with different plasma oxygen contents, taken at
In this contribution, an optical sensing technology using so-called non-dispersive infrared absorption (NDIR) spec- troscopy and employing a photoacoustic detector is proposed as
The method is based on the relationship between the rate of inelastic tunnelling events with energy loss hν at a bias voltage V bias and the total tunnel current at a lower bias eV