TítuloA posteriori error analysis of an augmented mixed finite element method for Darcy flow
Texto completo
Figure

Documento similar
To calculate the deformation of the structure, it was used a Finite Element Model for a specific geometry and an evaluation of the variation of the pressure field is done to
The method extends the positive definite non-oscillatory finite element algorithm (NFEM) capabilities to predict sediment transport, multiphase flow, and evolution of the
No obstante, como esta enfermedad afecta a cada persona de manera diferente, no todas las opciones de cuidado y tratamiento pueden ser apropiadas para cada individuo.. La forma
To search the preliminary information and to learn about some of the most relevant structural analysis with the Finite Element Method (FEM), such as modal analysis of
Subsequently, a finite element-based static analysis was performed in ANSYS software, to determine the mechanical behavior of an interior opening handle from a car door, based on
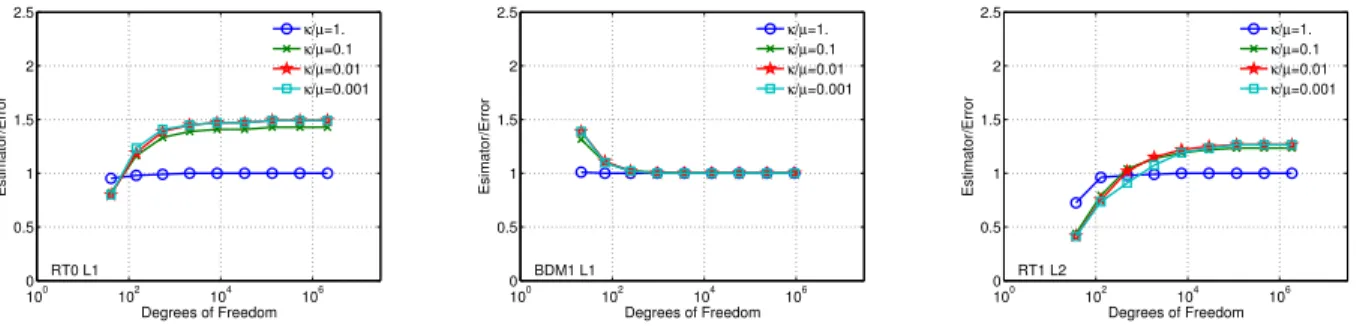
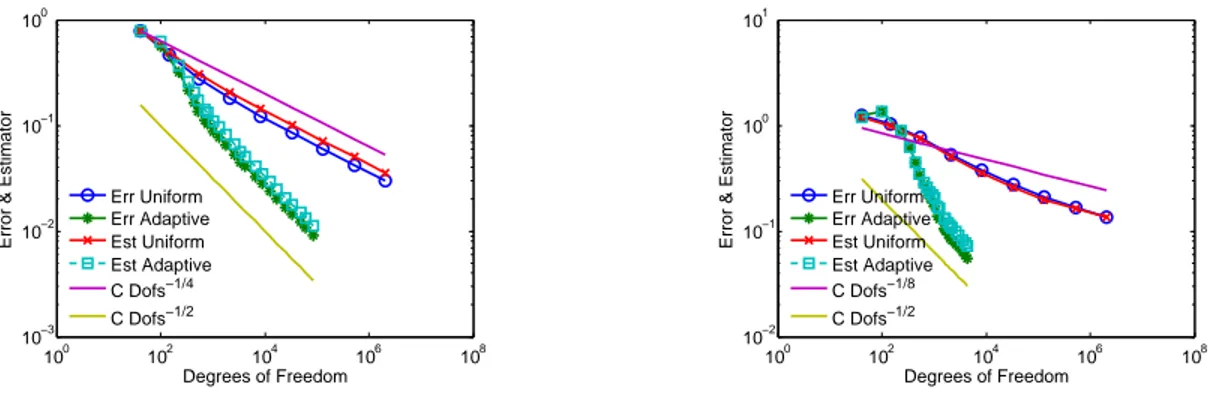
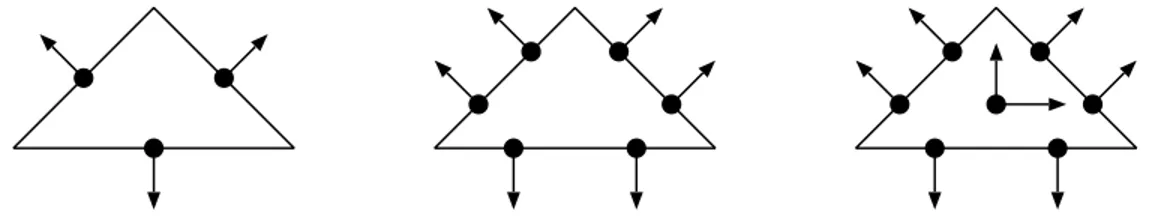
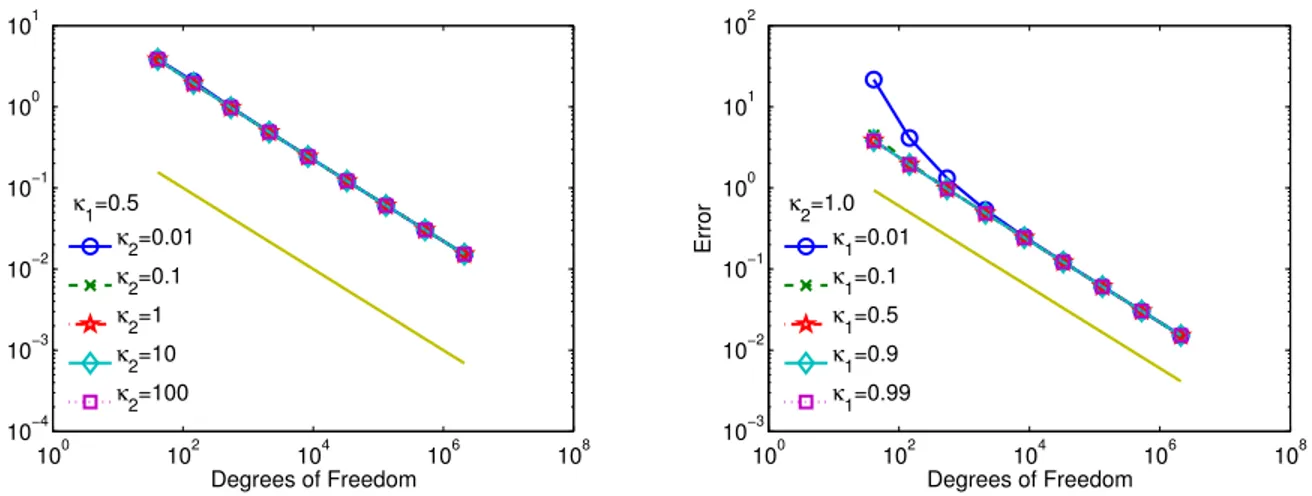
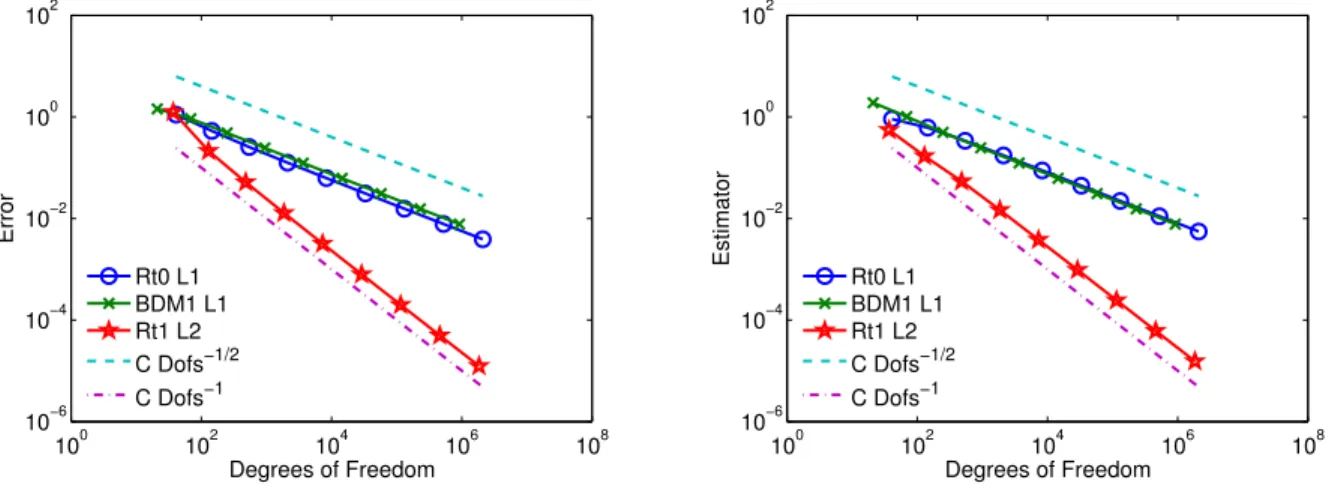
In [9] the authors prove error bounds for inf-sup stable mixed finite element approximations to the model (2) with both grad-div stabilization and local projection stabilization
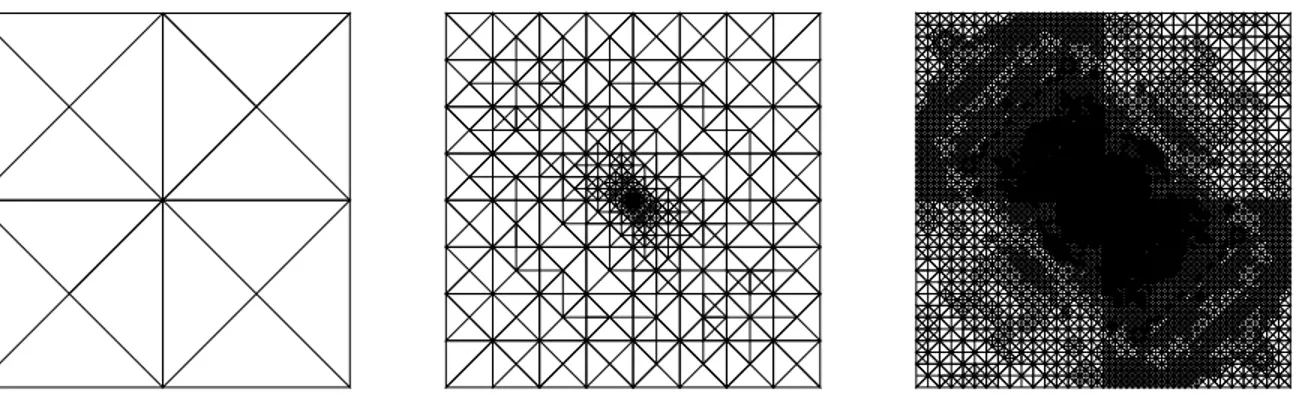
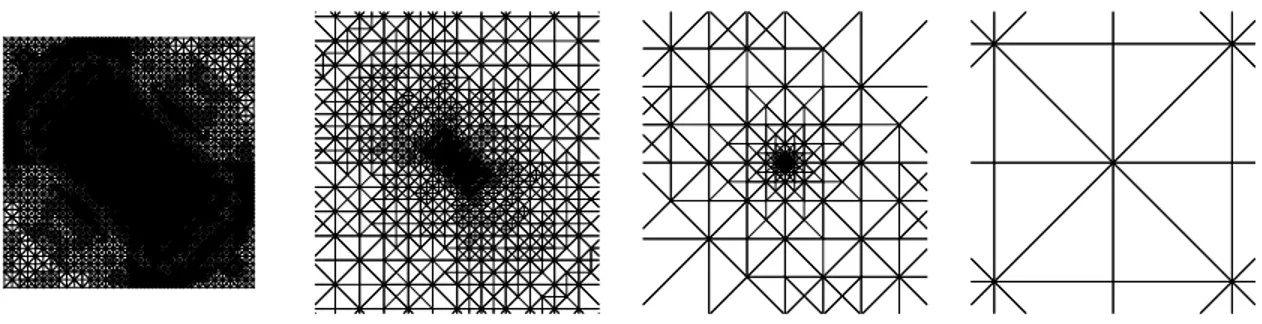
Figure 1 shows the flow diagram of a general adaptive procedure, where, at each iterative step, the problem is solved, an indication of the error for each element is obtained and
Abstract—The adaptive finite-element method (FEM) is an it- erative variant of the FEM where, in a first step, an initial mesh with few and low-order elements is generated,