Capital accumulation, trade liberalization, and rising wage inequality: the case of Argentina
Texto completo
Figure


Documento similar
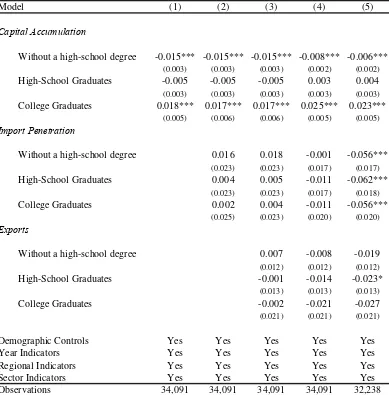
The results about wage structure (tenure and productivity payments) variables suggest that those variables are relevant in the wage-setting process, that is, the gross wage does
For a short explanation of why the committee made these recommendations and how they might affect practice, see the rationale and impact section on identifying children and young
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the
Jointly estimate this entry game with several outcome equations (fees/rates, credit limits) for bank accounts, credit cards and lines of credit. Use simulation methods to
In our sample, 2890 deals were issued by less reputable underwriters (i.e. a weighted syndication underwriting reputation share below the share of the 7 th largest underwriter
Therefore, we observe that with trade liberalization border regions result favored as a result of their improved accessibility in the world transport and trade networks, which
No significant differences were seen in leaf and root total -SH contents between the control (33Mn+0Cd) and 0Mn+0Cd treatments, whereas they increased 6 and 4.9 times in the roots
Regarding monetary consequences, our study shows the following results: 1) underqualification is penalised in wage, so this mismatch would explain wage differential between workers