Genetic engineering of the skeletal muscle to counteract insulin resistance and obesity
Texto completo
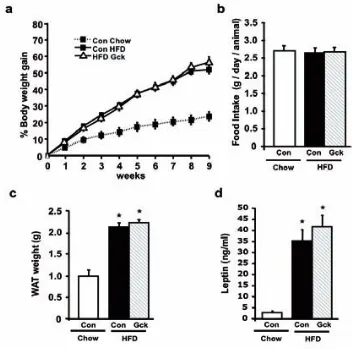
Figure




Documento similar
The characterization in amino acids, organic acids, sugars, trigonelline, volatiles compounds, fatty acids, total phenolic, carotenoids, vitamin C content, and antioxidant capacity
Pediatric patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus will have a worse fatty acid profile associated with inflammation compared with patients with Metabolic Syndrome
The fatty acid ethyl esters mixture, a fish oil residue obtained after the extraction of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty esters, has been converted into mixtures of
We can also observe in the figure the active site of the AT where the malonyl-CoA should bind to the protein to initiate the synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids.. In
In the present study, gene expression of candidate genes for fatty acid composition in muscle showed sex-dimorphism and breed effects, and gene co-expression in different
Fatty acid composition (% of total fatty acids) of oils obtained by PLE at 60ºC with 3. dichloromethane/methanol (2:1) (D:M) and ethanol (EtOH) from LOCS
Also, a very recent report demonstrates that the loss in self-renewal detected in satellite cells from aged mice can be overcome by p38α/β inhibition (Bernet and Rudnicki,
tuberculosis adaptation to a fatty acid environment, we developed an in vitro model where bacilli were grown in even-length long-chain fatty acids (LC-FAs) as the sole carbon