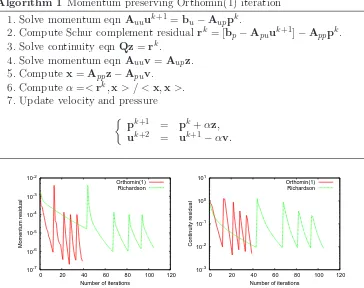
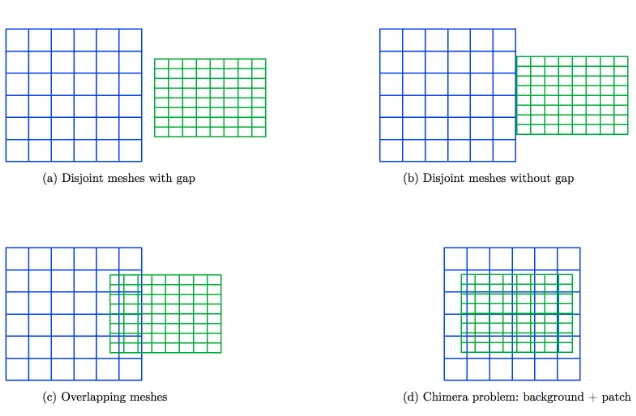
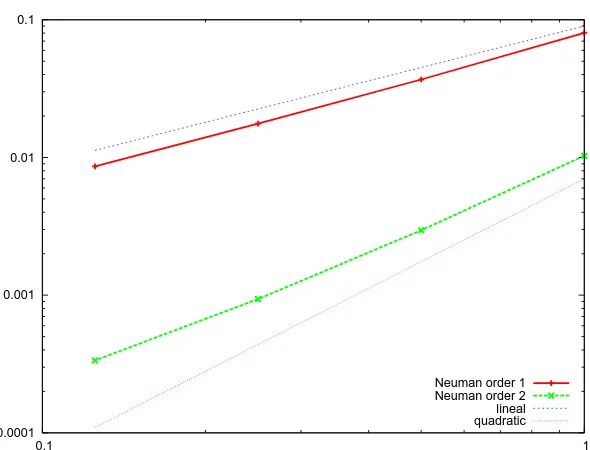
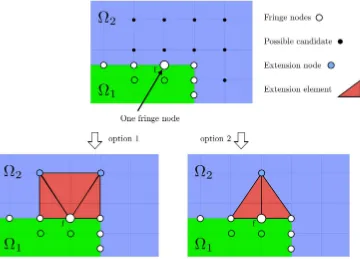
HERMESH : a geometrical domain composition method in computational mechanics
Texto completo
Figure




Documento similar
a high number of elements in the discretization of the computational domain are required to obtain an accurate numerical simulation of the
One of these problems is whether the critical coupling strength for the onset of synchronization remains finite in the thermodynamic limit for scale-free (SF) networks characterized
In the case of almost rectangular triangles, point-wise smoothers are not suitable anymore due to the anisotropy of the Voronoi mesh. By other hand, diamond smoother results in a
Therefore, while cooling of PEPs is observed, saturation of the SLR-exciton coupling sets in before condensation is reached, and the new band with weaker coupling emerges and
The interaction with the elements of the AmILab environment is possible thanks to an oral interface [4] and a graphical interface [5], by means of direct control. In the case
On the other hand, placing the biased Mo mesh between the CH 4 distribution ring and the substrate holder leads to even lower metal contents in the deposited coatings due to the
Figure 1 shows the flow diagram of a general adaptive procedure, where, at each iterative step, the problem is solved, an indication of the error for each element is obtained and
Abstract—The adaptive finite-element method (FEM) is an it- erative variant of the FEM where, in a first step, an initial mesh with few and low-order elements is generated,