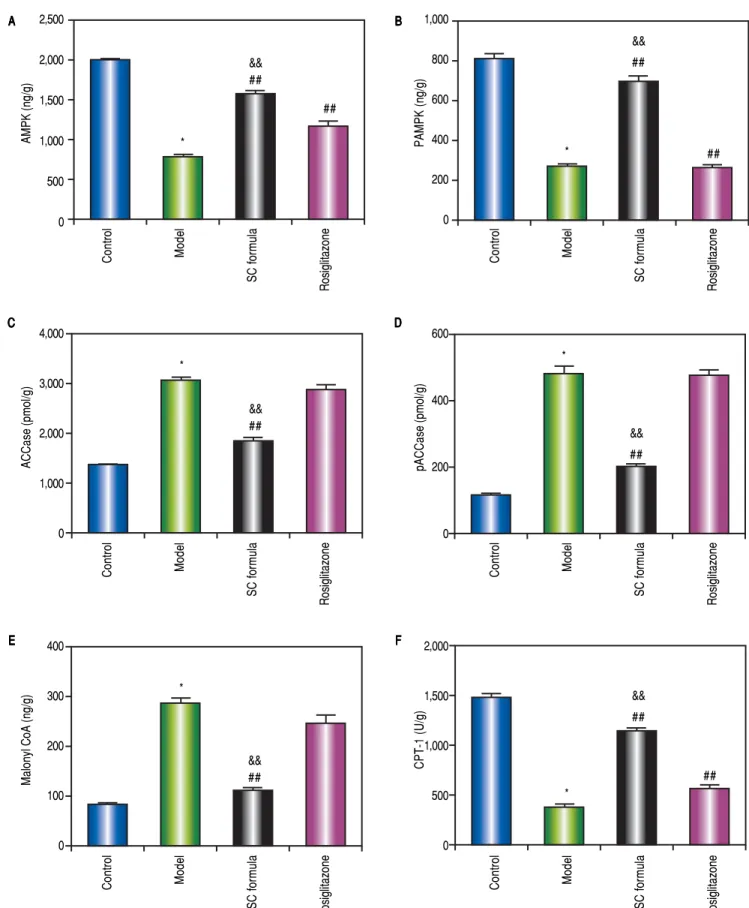
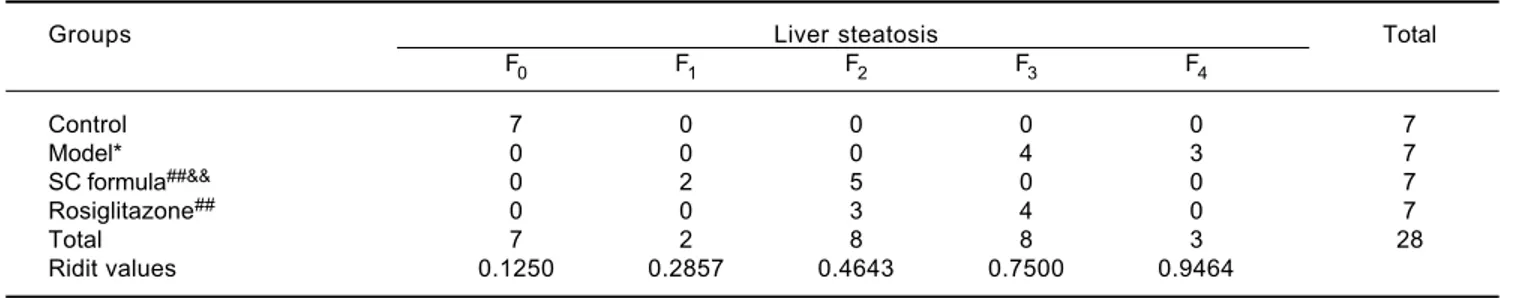
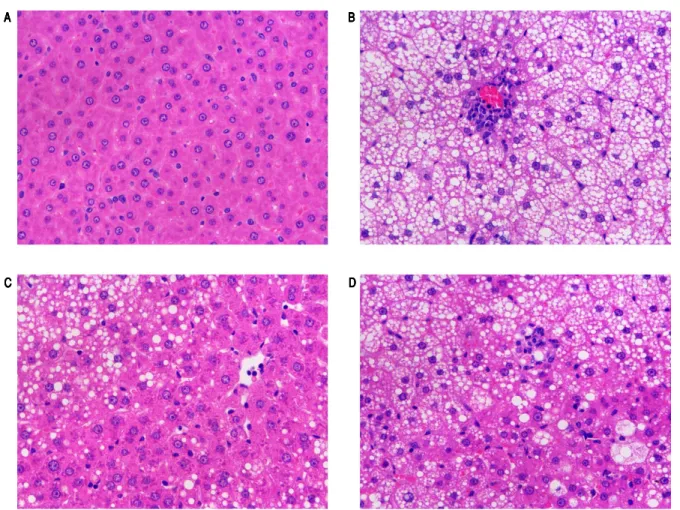
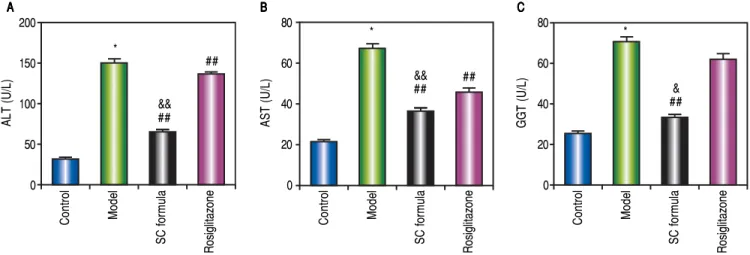
Salidroside and Curcumin Formula Prevents Liver Injury in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats
Texto completo
Figure
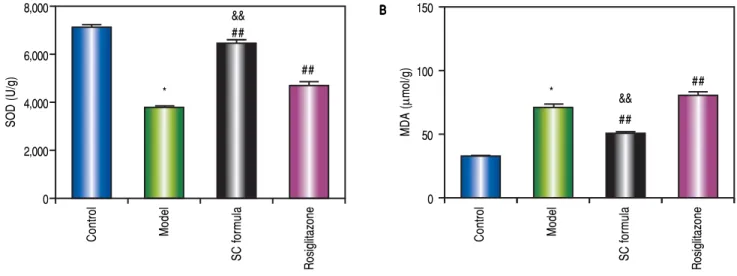
Documento similar
Average II-BW spectra obtained at three time points of the HFHS diet (1 week, 12 weeks, and 52 weeks) with three replicates of mice that: (B) were only shaved; (C) had their
Insulin treatment decreased liver pyruvate concentration and enhanced both liver and plasma lactate/pyruvate ratios compared with control values, whereas insulin plus
In this study, internal tissues of chicken liver samples were analysed for the presence of phages using a meta- genomics approach and the liver virome was compared with that of
It is noteworthy that only in diabetes, metabolic syn- drome, and Fatty liver disease index high do the results obtained coincide (with statistical significance) between the
Our results indicate that FLI-defined NAFLD is more prevalent in men than women, and it is associated with age, lower social class, and a dysmetabolic state charac- terized
In our study, admitted COVID-19 patients with CLD and abnormal admission LFTs had higher median levels of D-dimer, which could be associated with major systemic inflammation and
Magnetic Resonance Elastography vs Transient Elastography in Detection of Fibrosis and Noninvasive Measurement of Steatosis in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty
Abstract: Background: A lifestyle with regular PA (physical activity) and Mediterranean diet has benefits on NAFLD (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease) and MetS (metabolic