Reasoning with inconsistent ontologies in possibilistic defeasible logic programming
Texto completo
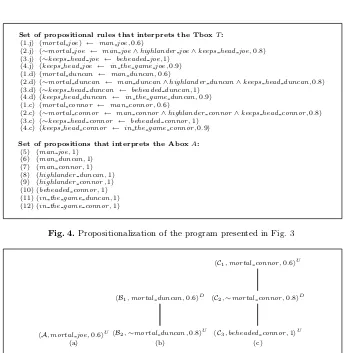
Figure



Documento similar
Keywords: Metal mining conflicts, political ecology, politics of scale, environmental justice movement, social multi-criteria evaluation, consultations, Latin
∆t p seconds where s = [0, ∞), and the index p denotes the time placement of the window measured in seconds from the beginning of the trial. For instance, in Fig. To determine whether
In Section II we review the hybrid technique based on the ex- traction of the quasi-static term to the spectral domain Green’s functions, and we show that by extracting a
In order to demonstrate the practical value of the proposed topology, we will consider the design of a bandpass filter cen- tered at the frequency of 14 GHz, and with a
Intuitively, we will use a UML/OCL consistency checking tool to find an instance of the trans- formation model satisfying the source and target meta-model well-formedness rules,
Even though the 1920s offered new employment opportunities in industries previously closed to women, often the women who took these jobs found themselves exploited.. No matter
Given a meta-model under construction (like the one in Step (3) of the figure), we can bind the role instances of the pattern instance to the meta-model elements, as shown in Step
We measured a pseudo-equivalent width (pEW) of 18±4 Å (1σ), consistent with the compilation of field L5 dwarfs ex- hibiting lithium in absorption We derived the error bars from