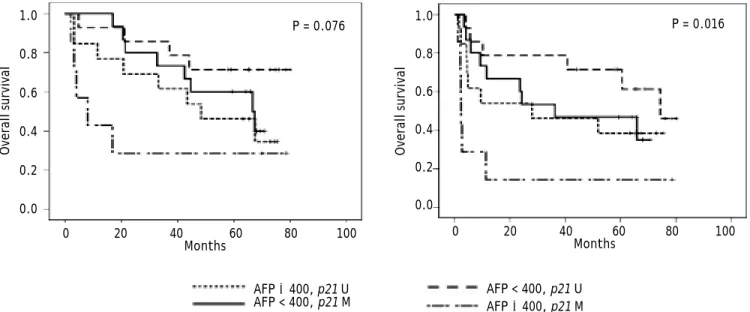
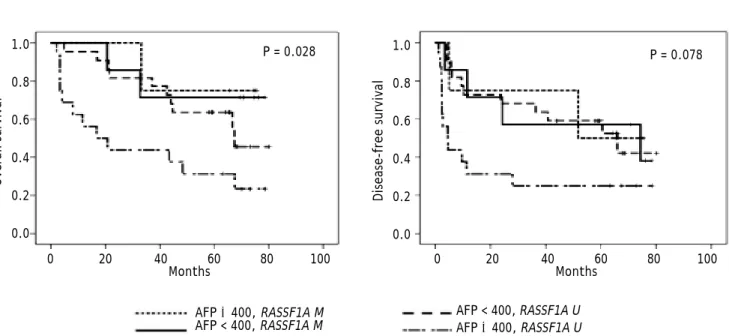
DNA methylation markers and serum α fetoprotein level are prognostic factors in hepatocellular carcinoma
Texto completo
Figure




Documento similar
tuberculosis in naive or vaccinated mice resulted in serum glycan profiles in which fucosylated and nonfucosylated glycans were detected in similar abundance, consis- tent with
Changes in serum IL-15 levels at 4 and 8 weeks as compared with baseline values were directly associated with changes in body weight, BMI, fat-free mass, and muscle mass
Restless legs syndrome in patients with high serum ferritin and normal iron
p8 is a stress induced transcription coactivator and p8 -/- mice have transiently elevated serum enzyme levels and pancreas inflammation (Vasseur et al., 2004). Mnk1 is known to
We know that patients with kidney disease have elevated serum levels of BPA and that some of the effects of BPA in laboratory ani- mals also appear in uraemic patients on
This study supports the relationship between 25(OH)D serum levels and the response of AK to MAL-PDT: VD deficient levels were found to be significantly associated to a lack of
Our main segments of tourists are rich (with high level of income) and poor people (with low level of income), tourist experiencing their first visit in Spanish
In conclusion, the circulating levels of the novel insulin- like adipokine ISM1 are significantly higher in pubertal chil- dren with obesity and are associated with BMI Z-score and fat