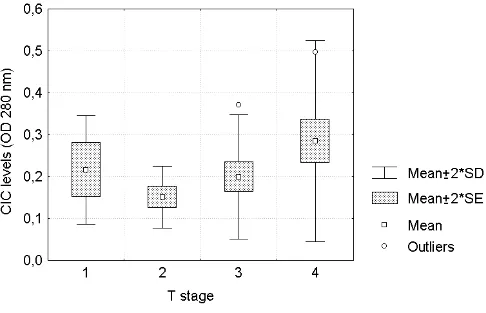
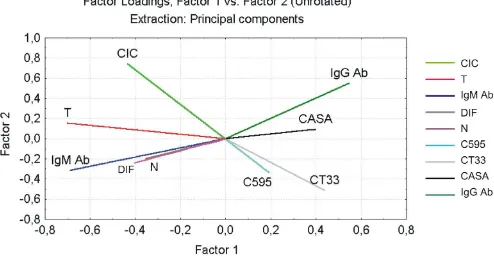
MUCI expression and anti-MUCI serum immune response in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC): A multivariate analysis
Texto completo
Figure



Documento similar
Analysis of breast cancers from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) showed that HSD17B14 expression is increased significantly in cancer compared with normal breast tissue and that it
Furthermore, a previous pilot study performed by our group showed significantly higher levels of acetate among MS patients with higher scores in the Expanded Disability Status
However, several recent cohort’s studies have reported results that suggest a modest positive association between fat intake and the risk of breast cancer (54) and more recently,
Regulation of VCAM-1 levels through a VHL-PHD-NFκB-dependent pathway and its role in the immune response against clear-cell renal cell
In this report, we demonstrate that mice treated with different indu- cible models of colon carcinogenesis developed a humoral immune response, which was similar to that observed
The regulation of more than thousand vitamin D target genes in colon carcinoma cells, normal stem cells, cancer stem cells, stromal NFs and CAFs as well as immune cells of the
In conclusion, we have shown that (i) YB-1 overexpression promotes EMT features, cell migration, and invasion in breast cancer cell lines; (ii) YB-1 knockdown partially reverts
In order to characterize whether the ISG15 antiviral activity observed in animal models is cell-type specific and to further characterize its implication in the immune response, we