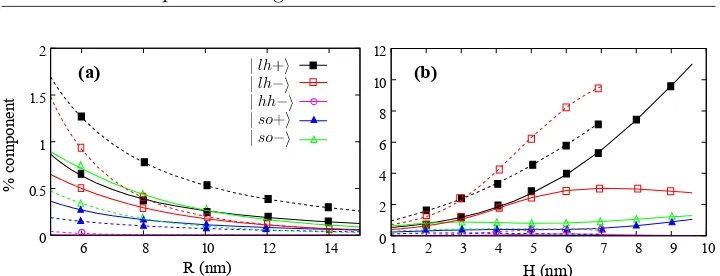
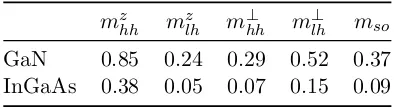
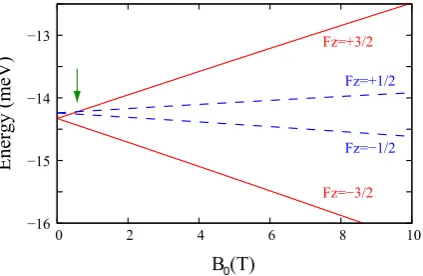
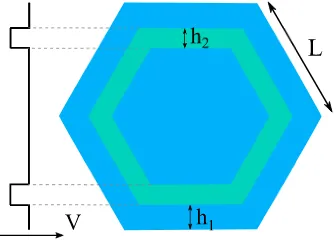
Electronic structure of quantum dots: response to the environment and externally applied fields
Texto completo
Figure
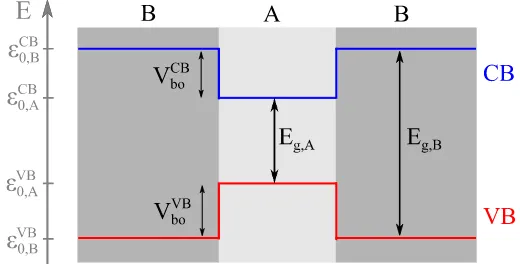
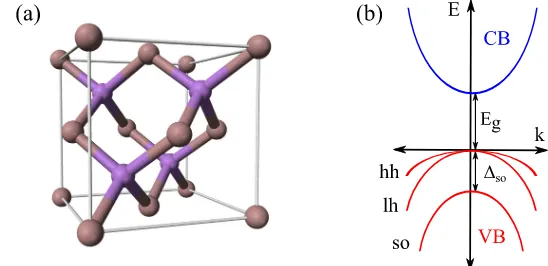
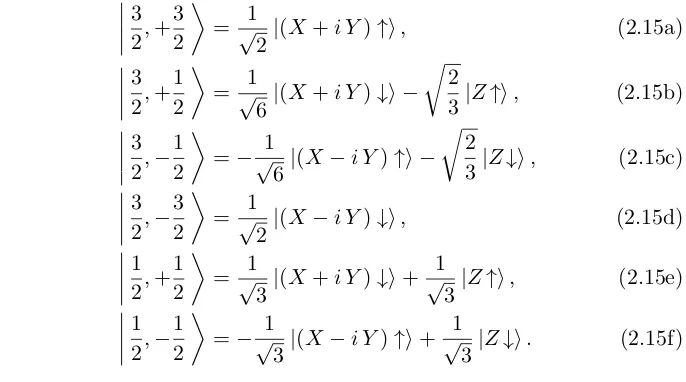
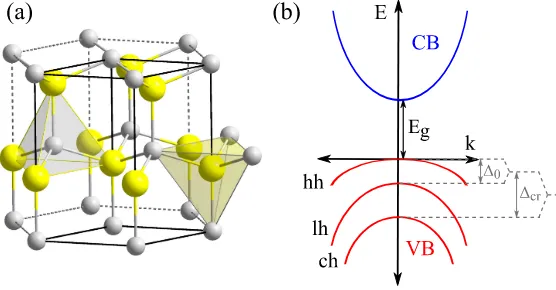
Documento similar
In this work we have been used classic and ab initio molecular dynamics simulations combined with electronic structure calculations to reproduce en- tire sequences of collisions and
While the calculated electronic structure rules out the formation of a magnetic moment around the divacancy, the generation of an electronic resonance near the Fermi level
The theory of inflation gives a fairly satisfactory explanation of the origin of these perturbations in terms of quantum fluctuations in the primordial density field, while the
The synthesis and analysis of these properties were then featured by (i) the composition, geometry, and electronic and mag- netic structure of the exposed surfaces at the
According to our group theory, MnWO 4 with a wolframite structure has 18 Raman active modes or optical phonons represented in the center of the Brillouin zone after decomposition of
20 geometry and electronic properties of Ca 10 V 6 O 25 crystal in the fundamental and excited electronic.. 21 states (singlet
The scope of this Thesis is the investigation of the optical properties of two systems based on semiconductor nanostructures: InAs/GaAs quantum rings embedded in photonic
In this Letter, we demonstrate that the quantum degeneracy of frontier electronic states of two interacting bodies forming an atomic point contact can be explored by precise
![Figure 2.4: Crystal structures and their stacking sequence for (left)ZB in the [111] direction and (right) WZ in the [0001] direction.Reprinted with permission from [46]](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/5258877.96473/33.595.201.423.145.303/crystal-structures-stacking-sequence-direction-direction-reprinted-permission.webp)