Hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic HBV HCV co infection is correlated to fibrosis and disease duration
Texto completo
Figure
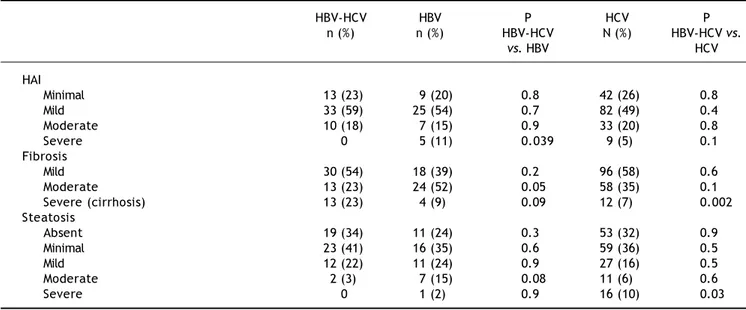
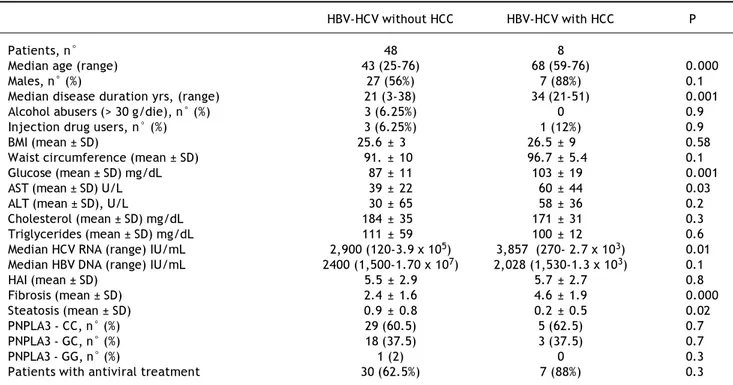
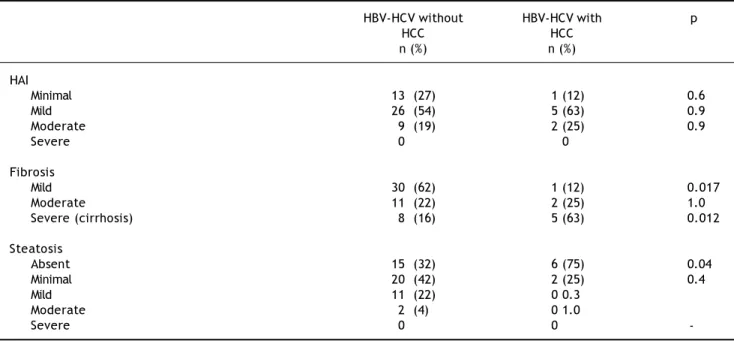
Documento similar
Therefore, the aim of this study was to compare the type and frequency of defective deletions found in the SARS-CoV-2 spike gene in patients with mild infection caused by the
The objective of the present study was to analyse the presence of PCV-3 infection (by qPCR and ISH) in for- malin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples from retrospective
The objective of this retrospective study was to evaluate whether open reduction with cerclage wire affected union rates, complications, and reoperations in patients
Introduction: The aim of this study is to evaluate results in a series of patients with chronic posterior-lateral instability of the elbow treated with reconstruction of the
The assessment of perceived health status in patients with chronic diseases is essential for measuring the impact and burden of disease, as in the case of patients with
We have studied the characteristics of HCV-nAbs through a retrospective study involving 29 HIV/HCV-coinfected patients who achieved sustained virological response (SVR) with peg-
Core tip: The Milan criteria for liver transplantation have improved survival of patients with small hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), but up to 20% of patients still experience
* Study showing the efficacy of tocilizumab in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis, a chronic inflammatory disease that in some cases may be associated with the development