HBsAg expression of liver correlates with histological activities and viral replication in chronic hepatitis B
Texto completo
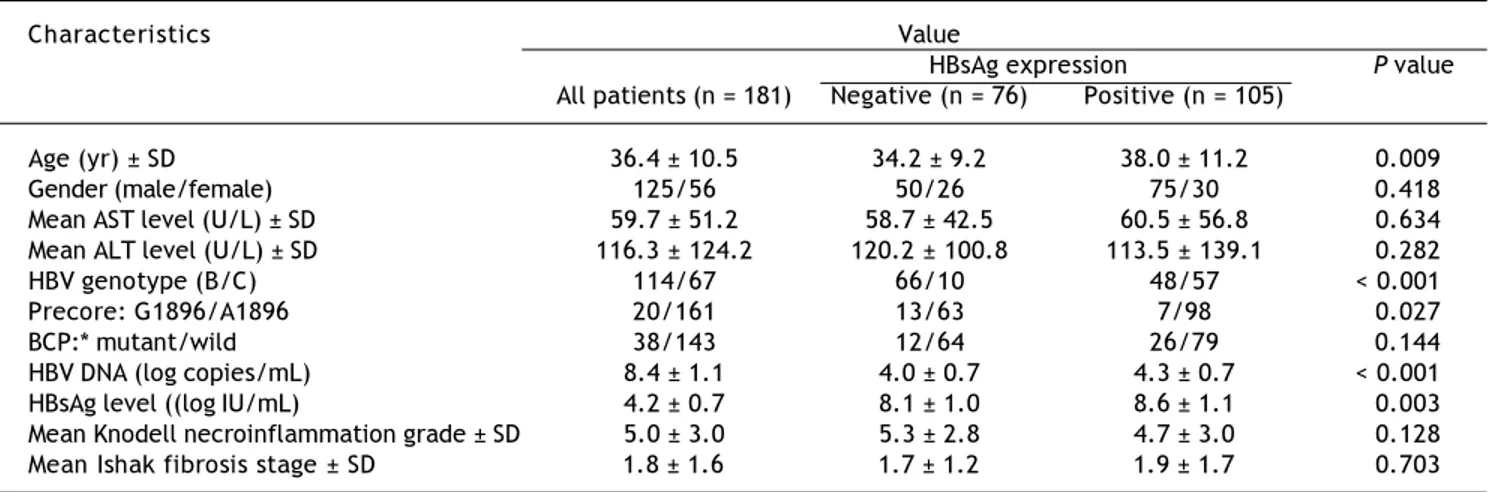
Figure



Documento similar
Prevalence, viral replication efficiency and antiviral drug susceptibility of rtQ215 polymerase mutations within the hepatitis B virus genome... Mechanistic
The higher hsCRP levels observed in children with type 1 diabetes compared with a control group with a similar BMI and lower than children with severe obesity suggest a
Complex III-deficient fibroblasts exhibited increased levels of proteins involved 14. in cell signaling processes that couple gene expression to intracellular trafficking, such
Effect of cactus seed oil, olive oil, or colza oil treatment on gene expression of the proin- flammatory markers Il-1β (A,D), iNos (B,E), and Il-6 (C,F), in the brain and
Now we also show that this upregulation occurs in H35 cells and acute liver injury, two conditions with different levels of Mat1a (minute or strongly reduced) and Mat2a expression
In summary, CD81 regulates HIV-1 early replication via direct association with SAMHD1, modulating the intracellular dNTP content through the control of SAMHD1 expression and
In agreement with the observed changes in hepatic SREBP-1c expression in liver, central leptin blunted the up- regulation of the mRNA levels of ACC, FAS, and SCD-1 elicited by the
(a) NPs@PEG in the liver, (b) NPs@Glc in the liver and (c) NPs@Glc in the spleen at different post-administration times (72 h and four months). If in the spleen the core of

