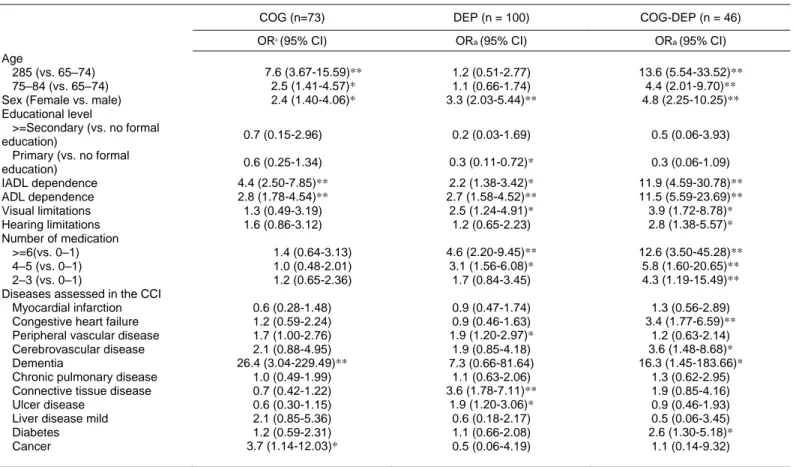
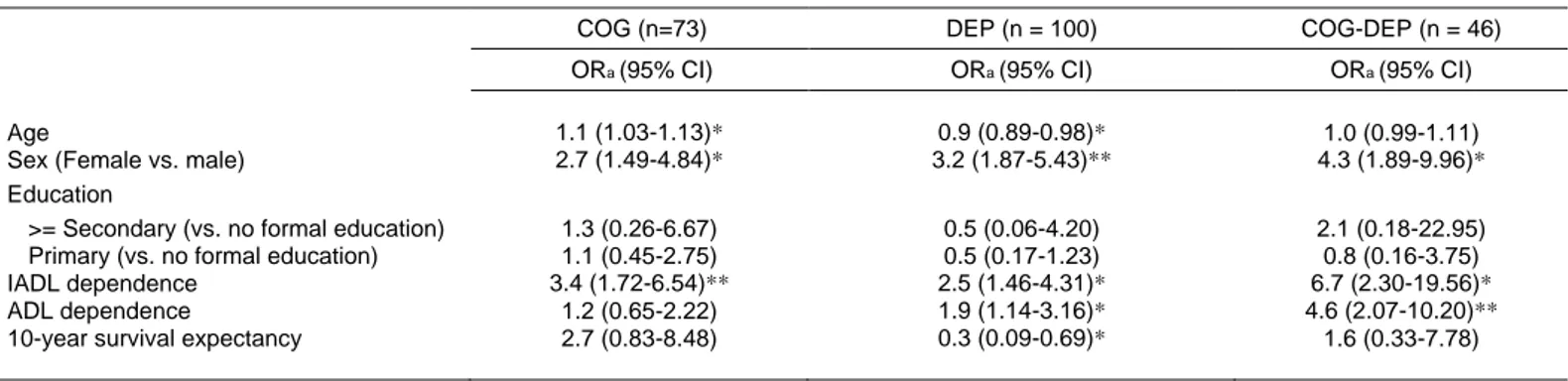
TítuloMental and psychological conditions, medical comorbidity and functional limitation: differential associations in older adults with cognitive impairment, depressive symptoms and co existence of both
Texto completo
Figure


Documento similar
In this prospective study of community-dwelling older adults, higher serum leptin concentration was associated with greater risk of impairment in mobility, agility, lower
Objectives: To study the dental status and treatment needs of institutionalized older adults with chronic mental illness compared to a non-psychiatric control sample.. Study
This study aimed to analyze the efficacy of two anxiety induction procedures in older adults and younger samples compared with a neutral mood induction control group.. We
The second study was a RCT with parallel design of three groups to compare the effectiveness of brief transdiagnostic therapy in both individual and group formats and pharmacological
Thus, the aim of the present study was to evaluate the role of various determinants on SMM, sarcopenia, and sarcopenic obesity in nine countries (China, Finland, Ghana, India, Mex-
Thus, the aim of the current study was to assess whether food insecurity is associated with MCI using data from a nationally representative sample of older adults in South
The results of the present study are similar to those obtained in previous studies and point that institutions for older adults should offer activities that encourage participation
It is against this background that we undertook a systematic review and meta-analysis with the aim of estimating the prevalence of hypertension in adults aged 50 years or older