TítuloLiver toxicity and risk of discontinuation in HIV/hepatitis C virus coinfected patients receiving an etravirine containing antiretroviral regimen: influence of liver fibrosis
Texto completo
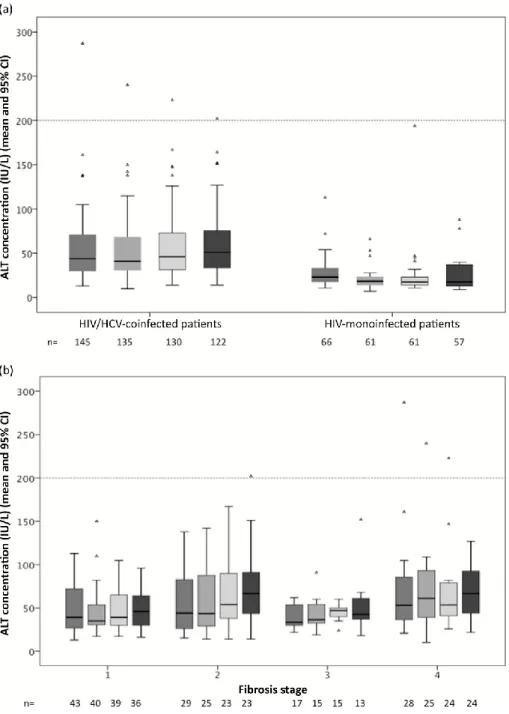
Figure

Documento similar
In this study, internal tissues of chicken liver samples were analysed for the presence of phages using a meta- genomics approach and the liver virome was compared with that of
In our study, admitted COVID-19 patients with CLD and abnormal admission LFTs had higher median levels of D-dimer, which could be associated with major systemic inflammation and
We aimed to detect the most relevant changes in peripheral immune biomarkers among HIV/HCV-coinfected patients who achieved sustained virologic response (SVR)
Of special concern for this work are outbreaks formed by the benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis (Schmidt), including several species producers of palytoxin (PLTX)-like compounds,
Serum ferritin as risk factor for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome of the liver in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1
Integrated HIV DNA was quantified by q-PCR in cross- sectional samples from different groups of patients: (1) HIV+ group: HIV-monoinfected patients that had never been in contact
This analysis showed that levels of both exhaustion and activation of effector CD4 T-cells were significantly increased in pre-DAAs HIV/HCV patients compared to HIV patients,
Subjects with liver cirrhosis, parenteral drug users, cases of prosthetic endocarditis, and patients who did not undergo surgical treatment had an increased risk of a second IE