Theoretical and Experimental Study of Cooperativity Effects in Noncovalent Interactions
Texto completo
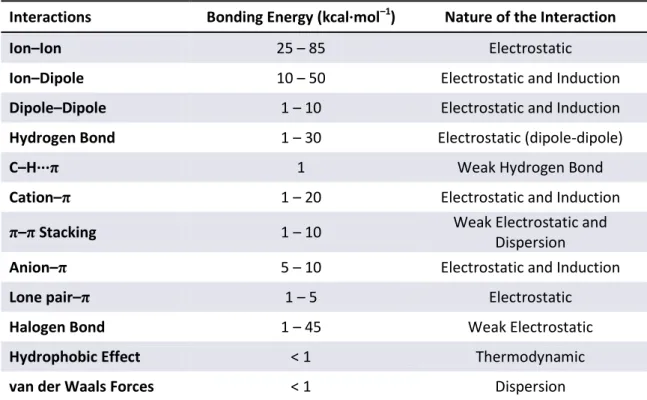
Figure


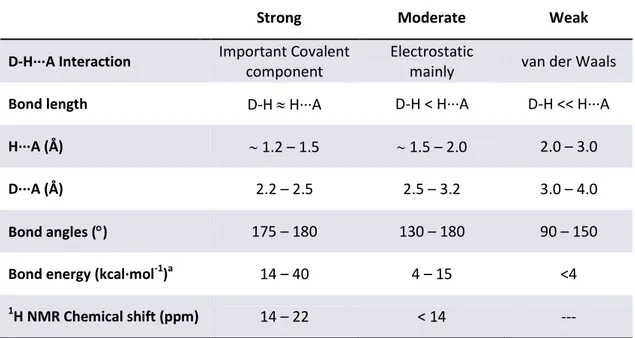

Documento similar
Experimental results have demonstrated that artificial neural networks can substantially reduce the number of model parameters and surpass the performance of previous approaches
Three different theoretical methods have been used: (i) molecular dynamics (MD) simulations in the framework of the density functional theory (DFT) and the density functional
In this investigation we have addressed (i) the study of the expression level of IF1 in different prevalent human carcinomas, (ii) the metabolic and signaling events that mediate
The thresholds at the conventional frequencies were calculated in decibels hearing level (dB HL) and the thresholds at EHFs, in dB sound pressure level (dB SPL). Results Table
Overall, the results support that a low expression level of IF1 in colon cancer cells favors metastatic disease because the operation of at least two contributing factors: (i)
Molecular electron density (MED) and electrostatic potential (MESP) critical points (CP’s) for (a) LSD, (b) zidovudine, and (c) (ZnS) 10 cluster at B3LYP/6-31 +G(d) level of
The results of the present study are similar to those obtained in previous studies and point that institutions for older adults should offer activities that encourage participation
The main objectives of this work were: (1) to compare the dynamics of fitness gains at 43 ◦ C and the fitness values that were reached at the end of the transfer series, and