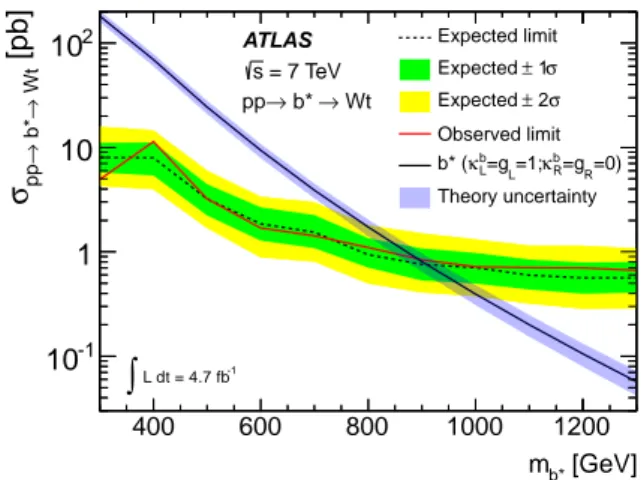
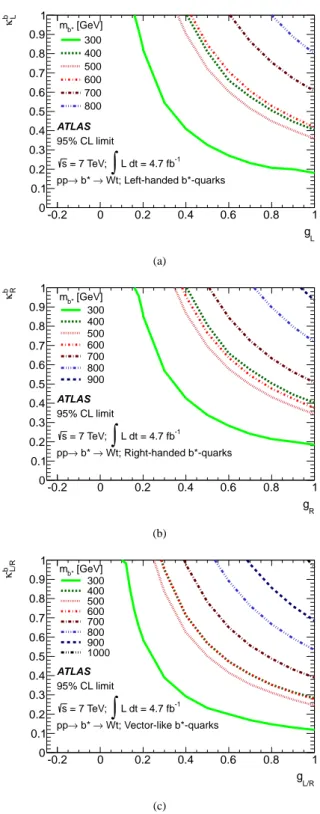
Search for single b* quark production with the ATLAS detector at root s=7 TeV
Texto completo
Figure




Documento similar
The impact of contamination due to pair produced top quarks contaminating the signal or control regions has been explicitly evaluated and is observed to be less than 5% (10%) for
Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; (c) Department
Figure 3 shows the evolution of the uncertainties in the background prediction, before the fit to the invariant mass distribution described in section 8, as a function of m γγ in
50b High Energy Physics Institute, Tbilisi State University, Tbilisi, Georgia. 51 II Physikalisches Institut, Justus-Liebig-Universita¨t Giessen,
With a total cross section to same-sign leptons equal to 0.7 pb, small with respect to the expected b ′ or same-sign top-quark production, SM diboson events are a rare but
32a Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China. 32b Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China,
33 ( a ) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; ( b ) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; ( c
33 (a) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui, China;