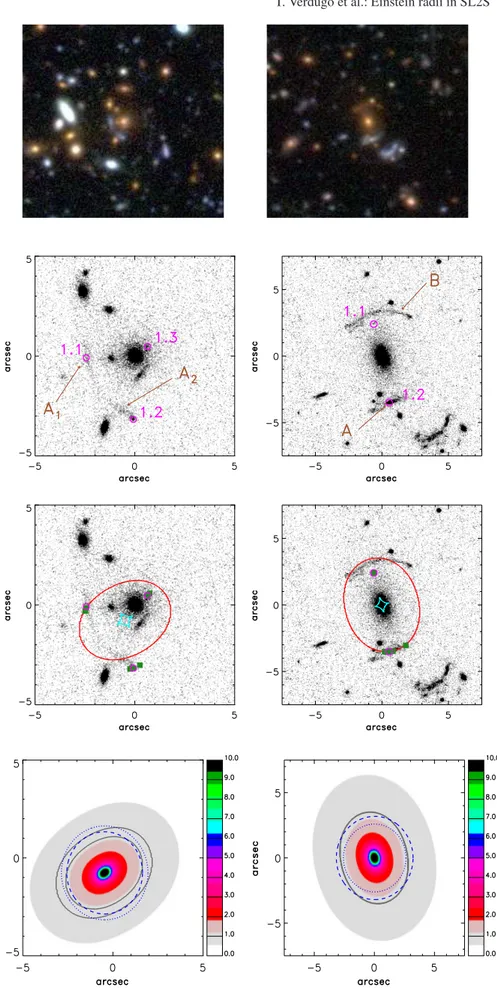
Characterizing SL2S galaxy groups using the Einstein radius
Texto completo
Figure




Documento similar
Astrometric and photometric star cata- logues derived from the ESA HIPPARCOS Space Astrometry Mission.
The photometry of the 236 238 objects detected in the reference images was grouped into the reference catalog (Table 3) 5 , which contains the object identifier, the right
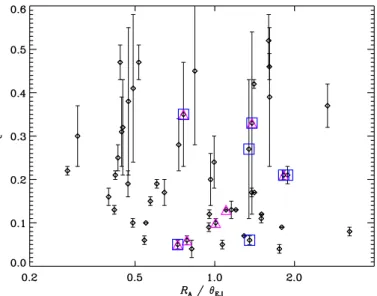
3. Estimate the physical properties of the system: mass density slope of the lens galaxy γ, projected dark matter mass fraction within the Einstein radius M dark /M lens ,
as a function of the parent galaxy stellar mass are shown in Fig. 12, in three bins of the family classes of bars. In Buta et al. It appears that for the strong bars the inner,
We study the density profiles of voids identified using the ZOBOV watershed transform algorithm in realistic mock luminous red galaxy (LRG) catalogues from the Jubilee simulation,
Relationship between the total cluster stellar mass and the photometric blue fraction for the ALHAMBRA cluster and group sample stacked into different redshift bins. The galaxy
We have then examined the performance of an approach for gene selection using random forest, and compared it to alternative approaches. Our results, using both simulated and
In this Thesis, the weak-lensing magnification has been measured using two data- sets for the Dark Energy Survey: the Science Verification (DES-SV) and the Year 1 (DES-Y1),