UNIVERSIDAD NACIONAL ABIERTA Y A DISTANCIA
UNAD
BACHELOR IN TEACHING ENGLISH AS A FOREIGN LANGUAGE ESCUELA DE CIENCIAS DE LA EDUCACION
ECEDU
The current state of education of Bachelor degree in English in Colombia
Donald Andres Tobio Lopez 1044426538
Advisor Henry Carvajal
Written Analytical Summary 1. Type of document
Monograph
2. Title of the document
The current state of education of Bachelor degree in English in Colombia 3. Author
Donald Andres Tobio Lopez. 4. Key Words
Bachelor, Degree, Teaching, English, Globalization, Curriculum, Practices, University, Technology, Purposes, Credits, Common European Framework of Reference, Virtual Education, Traditional Education.
5. Description
This monograph seeks to answer what the current state of education of the Bachelor degree in Teaching English currently offered by Higher Education Institutions nationally is, in accordance with what has been expressed and needed nationally and globally.
6. References
7. Contents
This monograph starts with different definitions and explanations about what Education is and how education is mediated in Colombia and the world. Secondly, it provides information what bachelor degrees in Colombia can be and how they are regulated through a set of guidelines. Thirdly, it shows what the curriculum is, what it must contain and how it must be regulated. Fourthly, it exposes what technology is and its relation with education. Fifthly, there is information about what globalization is and its relation with the English learning nowadays. Sixthly, there is content related to the Common European Framework Reference (CERF). Then, there is the methodology that was used to conduct the research.
Moreover, the researcher could associate the content already mentioned with the collected data about the Bachelor degree in English in regards to credits, curricular structure, practices, purposes and technological compounds. Finally, there is a set of recommendations for the universities that could not seem to meet 100% what is needed nationally and globally regarding Bachelor degree in English and conclusions.
8. Methodology
The qualitative research approach was used to conduct this monograph. Then a documentary review or research was the methodology that was applied to conduct this paper. Therefore, for this document, the researcher had to review definitions and guidelines already set up by the Ministry of National Education (MEN), and other definitions that could support the monograph. Then, the next step was visit the webpages of all the universities in Colombia that offer a Bachelor of Arts in English as a Foreign Language. Finally, the literature review leaded to disclose the current status of Bachelor degrees in English in Colombia with the conclusions and recommendations to improve that status.
9. Conclusions and recommendations
A reform in the curriculum, purposes, practices, technologies and credits is generally needed in Colombia so that all universities can fully meet the institutional projects that the MEN has established in national and global contexts.
In terms of purposes, Universidad Panamericana did not show a clear path, goals to achieve and guarantee communicative competences. Then, most of the universities in general did not all show that the student would receive training related to flexibility and interdisciplinary subjects. In general, most of the universities that met what the MEN requires in its guidelines, besides the ones that did not fully meet the institutional guidelines already set up by the MEN. This is by demonstrating interest when describing the purposes that are going to be accomplished by graduate and future students.
In regards to curriculum, it could be seen that not all universities have a flexible
curriculum, some of them either showed just a few electives, while others did not show them, they were just focused on areas linked to English training, or a seminary as an elective which is not what the MEN asks. This includes Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira, Fundacion
Universitaria Luis Amigo, Universidad Panamericana and Universidad del Amazonas. Secondly, not all the curriculums incorporated ICT and Web 2.0 tools training. This includes Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe, Universidad del Amazonas and Universidad
Panamericana. Finally, curriculums of training in cultural immersions in local and global contexts, socio-humanistic formation, and more courses related to pedagogy, virtual and traditional were not fully included by Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe, Universidad Panamericana, and Universidad del Amazonas.
In general, universities must provide more information that can be accessed and found when it is desired to review and read their offers because future readers would be able to find all what is needed when visiting their websites so the right choice can be made. Then, they would need to redesign their websites, train their own students to help them improve the webpages in
Table of Content
Introduction…...7
Justification………..………..……...…..9
Statement of the problem……….……….………….…11
Objectives………..………12
General Objective……….……….………..12
Specific Objectives……….……….12
Theoretical Framework………..13
Education in Colombia………..……….………....…...13
How education is mediated in Colombia. Education Modalities………....14
Bachelor Degrees in Colombia………..………..16
Bachelor degree in Teaching English in Colombia………..………...17
Curriculum………….……….……….……18
Technology and education………….……….……….19
Globalization and English Leaning nowadays……….………...20
The Common European Framework……….…………..……….………...22
Methodology….…...………..………. ..25
Research Line……….………...…..26
Research Paradigm……….……….27
Strategies and Data Collection Techniques……….………28
Comparative tables about the current status of education of the universities that offer Bachelor degree in English in Colombia………...29
Data results and analysis……...………...36
Conclusions and recommendation……..………...45
Conclusions……...……….………..……….…45
References…...…….………,………..………....…... 51
Annexes……….………...……..…….60
Figure Index Figure 1. Cambridge English. A range of exams to meet different needs………..…………...23
Tables Index Table 1. Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe (CECAR) ………...…….…….29
Table 2. Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira………...29
Table 3. Universidad Surcolombiana………...………....30
Table 4. Fundacion Universitaria Luis Amigo………..………... 30
Table 5. Universidad de Tolima ……….………..……...31
Table 6. Universidad ICESI……….………..……..31
Table 7. Universidad industrial de Santander (UIS)………..…..32
Table 8. Universidad Santo Tomas……….……… 32
Table 9. Universidad la Gran Colombia……….……….33
Table 10. Universidad San Buena Ventura……….………..…..….33
Table 11. Universidad Panamericana………..……… 33
Table 12. Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia (UNAD)……….…...…… 34
Table 13. Uniminuto – Corporacion Universitaria Minuto de Dios………34
Introduction
In today’s globalized era, English learning is becoming mandatoryfor all societies. Moreover, Bachelor degrees in English are offered by learning centers to fulfill that demand. Hence, reviewing if institutions should adapt their Bachelor degrees in English to today’s demands turn pertinent and appropriate. Therefore, reviewing the country’s current state of education of Bachelor degree in Teaching English programs is important to see if the majors can fulfill today’s technological, academic, practical, durational, and propositional needs coherently and appropriately.
The intention to review this topic is because the researcher took a Bachelor degree in Teaching English and a number of situations related to the major selection were realized and faced. First, he struggled when selecting a program that could offer a complete degree. Indeed, it was noticed that not all Bachelor in Teaching English programs incorporated a curriculum with a variety of credit choices, practices, research, technology usage and clear purposes. Therefore, since not all the programs reviewed seemed to be complete, this research was made.
This research begins with a chapter of definitions about education, Bachelor degrees in education and English in Colombia, a review of the importance of the English language, globalization and education, information about the Common Reference Framework for foreign languages and other concepts. Secondly, there is another chapter where the research
methodology is discussed. Then there is a third chapter with data about the Bachelor degrees in Teaching English offered in Colombia. Finally, there is a fourth chapter about the data analysis, suggestions, bibliography, etc.
Justification
In Colombia, English education must be accredited, reachable, enjoyable, and effective. Future and current English Teachers must be competitive and everybody deserves to have good choices to learn an English degree. Also, English education must be balanced, that includes including more technology, cultural elements, timing, curriculum, etc. Therefore, reviewing the country’s current state in terms of educational factors about the English degrees currently offered
is imperative. Evidently, that is the reason why this research is centralized in the status of English degrees offered nationally.
English degrees are offered by educational institutions just like other degrees.
Additionally, it has been seen that many people tend to study the degree because it opens them a lot of gates and job opportunities that are not just about teaching. Likewise, Bachelor degree in English is one of the majors that people choose nowadays. From all this, there is the importance of analyzing the current state of education for Bachelor degree in Teaching English in the
country, since eventually, due to the globalization, Bachelor Degree in Teaching English degrees will be a requested field everywhere.
This research is important because it provides readers with a current status of
Colombia’s Bachelor of Art in Teaching English degree programs, curriculum, training purposes,
Statement of the problem
Globalization has brought intercultural, technological extension and the English learning as a requirement for everybody. As a result, there is a need for all learning centers that offer a Bachelor in Teaching English to assure and supply today’s demands in terms of purposes, credits, curricular structure, pedagogical practices, internships and ICT (Information and
Communication Technologies) coherently, to reach limits and build competences. In addition, programs of Bachelor in English should provide technologies, ensure the integrity, consistency and content with objective and accurate formation in their curriculum structure, define precise indicators to control quality of the teaching processes by re-adjusting their existing offers, to assure that national and international demands of today globalized era are met.
This monograph seeks to answer this question: What is the current state of education of the Bachelor degree in Teaching English offered by Higher Education Institutions
nationally in regards to purposes, curriculum, credits, technological compounds, and
practices? Therefore, it is significant to diagnose and be conscious of the current state of
education of the Bachelor degrees in Teaching English because if their statuses meet in a
coherent way the national and international requirements of today’s era regarding purposes, etc.,
Objectives
General Objective
To identify the status of the Bachelor of Arts in Teaching English as a Foreign Language
degree currently offered in Colombian universities
Specific Objectives
To describe the current status of Bachelor degree in English currently offered in
Colombian Universities.
To determine similarities and differences among the Bachelor degree of Teaching
English in Colombia.
To present some recommendations that can help universities in Colombia improve their
Chapter I
Theoretical Framework
For this study, a theoretical review has been made. Therefore, in order to diagnosein a national and global context, the current status of education in terms of Bachelor degree in Teaching English to the national and globalized contexts, some national rules, statements, ordinances and guidelines must be reviewed. Secondly, notions that are important for this study, general concepts that are related nowadays to national and global definitions must be revised. Therefore, this would include concepts related to globalization and the Common European Reference Framework that are also important for the research.
Education in Colombia
Likewise, in accordance to Law 115 of 1994, the goals of education are the full development of the personality, acquisition of scientific, humanistic, technological, social, cultural, research and ethical elements, as well as a sense of environment conservation, and language skills, in relation with the country and world development. See Annex: Law 115 of 1994.
Therefore, based on what was quoted by Turbay (2000), the OECD and the Ministerio de Educacion Nacional, and Law 115 of 1994, it can be said that in Colombia, education is a right that must be assured by the state, everybody but especially national entities must assure it. On the other hand, it must incorporate cultural elements and prompt research, along with other elements that are important nowadays such as ethics, technology, etc., starting from childhood. Then, the researchers realized that education is a right that mustbe assured to prompt knowledge and human development and to achieve it, all the elements such as high-quality purposes,
technological varieties, complete curricular structure, etc., need to be include .
How Education is Mediated in Colombia. Education Modalities
Further, in 2010 Ministerio de Educacion Nacional said that virtual education is a learning mediation where there is no need to have a physical encounter in a classroom to learn, and in this scenario, the only difference between virtual and traditional education is the
mediation. However, what guarantee its success are the technological resources and their usage along with the pedagogies, communication and other factors.
Likewise, there is a summary of the guidelines for virtual education that were set up by the Ministerio de Educacion Nacional, and according to it (2010) in virtual education, programs have to be designed and aligned with the educational institutional project, include credits with up to 20% of synchronic activities, include self-learning to encourage responsibility and freedom to make decisions and encourage freedom to choose when to study, where to search, what to learn now and later, etc. and be based on competence construction. See Annex: Lineamientos para la Educacion Virtual en la Educacion Superior.
In terms of communication, programs must encourage interaction among peers, materials, students and teachers, include ICT and WEB 2.0 tools for those that cannot reach ICT and
Bachelor Degrees in Colombia
Bachelor degrees are available internationally, and Colombia is not the exception. Therefore, there are guidelines and regulations that have been set up by the Ministerio de
Educacion Nacional. Then according to it (2014) Bachelor degrees must be aligned with the Law 115 of 1994, in which it is said that Bachelor degree majors must be empathized with the campus of knowledge, be research oriented, diagnose local, national and international tendencies and needs. Secondly, majors must have competitive teacherswho are able to evaluate and teach. Third, in terms of quality, Bachelor degree majors must be engaged with self-evaluation and continuous improvement; they must be well-configured and they must be registered to be run by universities. See Annex: Lineamientos de Calidad para las Licenciaturas en Educacion.
Conversely, a very important component of any program is the curriculum .Then, in terms of curriculum, according to Ministerio de Educacion (2014), it must have theoretical fundaments. Secondly, it must be aligned with educational purposes where a defined profile that the student will graduate is described as well as objectives related to self and team work, critical and self- thinking, communicative competences development, and articulation with pedagogy, didactic, practices, research, disciplinary subjects and learning. Thirdly, it must have a number of credits in accordance with its duration and intensity of hours. Fourthly, it must show practices that should be available since the 3rd semester, interdisciplinary, regional and national
Equally, the previous sets of guidelines are the ones to be compared to the data to be analyzed to get the current state of education about the Bachelor degree in Teaching English in Colombia. Subsequently, in 2014, the Ministerio de Educacion mentioned other guidelines, one about Organization of Academic Activities, where the emphasis is on cultural tolerance, social projection, participation, conflict resolution, use of ICT in the activities and so on. Finally, a very important component of any educational program is the practice which is the action of executing duties related to the field of study.
In 2015, Ministerio de Educacion said that practices are requirement to graduate. Additionally, it said that practices can be in different modalities, such as practice activities, and in this scenario, the student goes to labs, does research, goes to workshops, and does social projects and so on. Whereas, the work practice is the one that is a requirement for graduation, and in this scenario, practices are not linked to the theoretical-practical credits that are internally made (practice activities), but to a national-approved institution where there is a contract or convention. See Annex: Lineamientos de Calidad para las Licenciaturas en Educacion.
Bachelor degree in Teaching English in Colombia
proficiency levels where new-graduate students must have a C1 of the CERF to be certified as English Teachers.
Curriculum
The curriculum is an important component of every university’s degrees and educational programs. According to UNESCO (1918) quoted by Bolaños and Borgantes (1990) the
curriculum can be all the activities, materials, teaching methods, and other means that are used by teachers and educators in order to reach and share education. Also, for George Beauchamp (1968) quoted by Bolaños and Borgantes (1990) the curriculum can be the set of subjects or credits that must be taught. Then, it can be said that the curriculum is present in all the degrees such as English degrees. Therefore, the curriculum is a vital part of the educational programs, without it, learning would not be achieved and programs would not be structured.
The Law115 of 1994 in its articles, 77 and 78, gives information about what the Curriculum is. Then according to it (1994), it is a set of criteria, plans, study programs, methodologies, and processes that contribute to the integral formation and the construction of national, regional and local cultural identity, including, research, cultural activities, sport
activities, permanent evaluation, human, academic and physical resources to implement policies and carry out the institutional educational project. Additionally, it is developed to guide the academic to do and should be designed flexibly to allow innovation and adaptation to the characteristics of the cultural environment where it is applied. See Annexes: Law 115 of 1994 and Lineamientos de Calidad para las Licenciaturas en Educacion.
Ministerio de Educacion Nacional (2010), in its Decreto N° 1295, academic credits are the measurement units of academic work to express all activities that are part of the curriculum to be met by students. Additionally, each credit is equivalent to 48 hours of self and tutorial work. Finally, they are expressed by whole numbers.
The previous guidelines were set up by the government in order to regulate what must be taken when presenting curriculums. Besides, the definitions about curriculum indicate that it is a set of subjects that are also known as credits in higher education. Then the program and the subjects must have specific purposes and goals that can be related to the curriculum. Finally, in that context, evaluation, research and electives must be incorporated in the curriculum and purposes for the student choice, nationally and globally, as well as cultural insights, both international, and national insights.
Technology and Education
Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) are referred to any communication appliances. According to Rouse M. 2005, ICT can be any communication device such as mobile phones, computers and so on. Likewise, besides the ICT, there are the WEB 2.0 tools that are just a set of online technologies that people use to work, to study, to publish their products, etc. In 2015, Haughn stated that WEB 2.0 tools are Wikis, social applications such as Facebook or Instagram, forums, microblogging, and so on.
their traditional classroom and teaching methods. Finally, in 2004, Ministerio de Educacion also mentioned that ICT are an added value that let the educative community explore new bounds, since ICT can be a set of sources where information can be provided and displayed in different modes, critical thinking can be further developed and cooperation can take place as well.
As for the connection between ICT and teaching English, Galindo and Moreno (2008), argue that bilingual education is a multidimensional educational process that does not only need the assistance of the government and language teachers, but also, the technological ways to improve the educational process. In the formation of a second language, it is taken into account a number of elements such as: teaching, strategies, and environment and of course the technology; these elements must be taken into account by the teacher, because of the influence of each of these variables in the process of learning. Therefore, they must be considered by universities when offering English degrees.
Globalization and English Learning nowadays
According to Al Rodhan and Stoudmann (2006), Globalization is a process that has been impacting communities, cultures, and economies for hundreds of years; it is a result of the international and inter-cultural integrations that have occurred throughout human history; and it also encompasses human activities suchas the linguistic, cultural, economic, and political aspects of human life etc.
In other words, based on what Al Rodhan and Stoudmann said in 2006 about
spread among all societies in global contexts. It has to be considered that the United States is the first-world country, and English is its official language. Therefore, since all the countries have to be linked to the USA because of economic, cultural, educational, political, businesses and other purposes, the English language is promoted and it keeps reaching all societies because of the Globalization and because the USA is the major country where the official language is English.
In terms of English learning, it has to be mentioned that in order for people to be encompassed and immersed into that process called globalization, people are required to learn English, to be competitive and to be in a level where globalization cannot leave anybody behind. Then, English learning emerges and is offered to people who are willing to teach and to learners who are willing to learn English. This can just be possible as long as Universities assure that they provide high quality components regarding practices, curricular structure etc., when offering English degrees.
Also, in terms of education, in 2003, Bellor de Arellano said education is an element to take advantage from globalization because this process makes education and research to be priorities. First, globalization is linked to human resources and technological development that are part of education. Likewise, according to Bello de Arellano (2003), setting up flexible educational systems that can be adapted to today’s globalization and demands, is mandatory.
Therefore, based on Quezada’ study, it can be said that in today’s globalized era, English educators are needed to cover that demand. Additionally, educations and institutions must take advantage from globalization to sell and provide high-quality Bachelor degree in English to make profits.
Moreover, according to Ministerio de Educacion Nacional (2006)the National Government has a fundamental commitment to creating the conditions for Colombians to develop communication skills in another language. Furthermore, having a good command of English facilitates access to employment and educational opportunities that help improve the quality of life. Thus, being proficient in another language is essential in a globalized world, which requires being able to communicate better, open borders, understanding other contexts, appropriating knowledge and circulate them, understand and be understood, play a decisive role in the country's development. Finally, being bilingual expands opportunities to be more
competent and competitive.
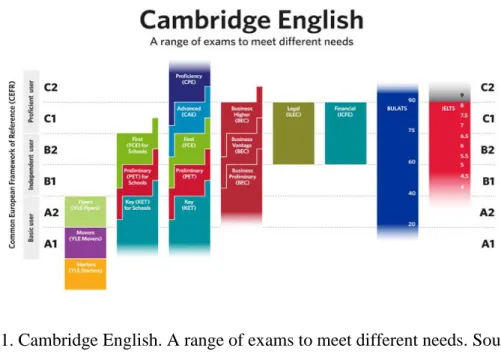
The Common European Framework.
Figure 1. Cambridge English. A range of exams to meet different needs. Source: International language standards | Cambridge English. (2016). Cambridgeenglish.org. Retrieved
from http://www.cambridgeenglish.org/exams/cefr/.
The previous diagram indicates that there are different levels of proficiency that are reached by the learner gradually. Additionally, it shows the exams that are valid to certify the learner’s level. Then, it can be interfered that the CERF encourages the evaluation to certify the student’s level, in the case of this research, a Bachelor degree in Teaching English must promote evaluation in accordance with the CERF for evaluation and certification.
Chapter II Methodology
A documentary review or research is the methodology that was be applied to conduct this paper. First, because, the researcher could go through different sources to compare and review the information that has been published there. Therefore, for this document, the researcher had to visit the webpages of all the universities in Colombia that offer a Bachelor of Arts in English as a Foreign Language. Then, additional documents were reviewed to gather the data that has to be scanned to get the research results.
According to Scott (2006) “Documentary research involves the use of texts and documents as source materials: government publications, newspapers, certificates, census publications, novels, film and video, paintings, personal photographs, diaries and innumerable other written, visual and pictorial sources in paper, electronic, or other `hard copy' form.” Therefore, to get the current state of education of the Bachelor of Arts in English as a Foreign Language currently offered in Colombia, a set of documents and sources were necessaryto be analyzed to determine the answers for the research question.
offer English degrees were classified by region, they were reviewed separately, by researching and gathering data from their websites or additional search that can be useful for this research.
On the other hand, it is vital to mention that to make this research, the hermeneutic was needed, according to Calles, Moreno de Tovar, and Arraez, (2006) the term hermeneutics, derived from the corresponding Greek as herméneutique and from Latin as interpretari which is the art of interpreting texts, especially sacred, to fix its true sense, and according to Dicccionario Hispanico Universal (1961) quoted by Calles, Moreno de Tovar, and Arraez (2006) it is referred in latin as sermo that indicates the efficacy of the linguistic expression. Consequently, the interpretation is to identify with the understanding of all text whose meaning is not immediately evident and is a problem, pointed for some distance (historical, psychological, linguistic, etc.) that is between us and the document.
The previous statement is a complete definition of what hermeneutic is. Then in can be inferred, based on the previous paragraph that the hermeneutic could help the researcher decode and interpret different texts, bibliographies, online sources and documents that gave an insight of the current status of Education of Bachelor degree in Teaching English in Colombia.
Additionally, monographs are usually a research in which there is pure literature review. Finally, without the hermeneutic, and literature review, the needed results could not be obtained.
Research Line
Education and Human Development, that seeks to understand the relationship between human development and education. Moreover, it seeks to study the culture of educational institutions that promote human development. Then, it seeks to generate new knowledge about teaching and learning for human development. Therefore, since this research was made to see if Bachelor degree in English offered nationally meet coherently what the country and the world need in terms of human development and education, this research has been made.
Research Paradigm
In this research, the type of study that was used is the descriptive qualitative research because it allowed the study of the variables such as data to connect it with the current state of Bachelor degrees in English. Likewise, in 2008 Monsen said that descriptive research is an efficient path to get information used in arranging hypotheses and proposing associations; this type of study usually displays an important but non-quantified topic involving a well-focused research question. Further, as all the variables could be reviewed and connected, and since the descriptive research studies and describes the relationship between variables, cause- and effects, descriptive research could be used.
The descriptive research approach is used in this paper to provide the current status of education of Bachelor degree in Teaching English, to see if the degrees that are offered nationally meet in a coherent way, the needs that are sought nationally and internationally in terms of English education and English requirements nowadays. Then, after scanning the data, the information could be processed by comparing all the elements to get the main result which was to see if Bachelor degree in Teaching English meet what is nationally and globally needed. Therefore, a documentary review had to be made.
Strategies and data collection techniques
CHAPTER III
Comparative tables about the current status of education of the universities that offer Bachelor degree in English in Colombia
This research seeks to scan the current state of education about Bachelor Degree in Teaching English in Colombia. Then a review of aspects such as purposes, curricular structure, number of credits, practices, technological compounds, in order to validate the current status of the degrees being offered by universities in Colombia by comparing the aspects with the information discussed in the theoretical framework later on.
Table 1. Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe (CECAR) REGIÓN CARIBBEAN AXIS
Purposes Student is to master the language proficiently, get and have tools to transfer his knowledge to others; domain didactics in different formative levels; be trained with integrity, social leadership; have an enterprising spirit; execute and advise in different projects related to English teaching and be committed to planning, executing and evaluating English learning and his own performance.
Curricular Structure
There are English courses from the first until the last semester; there are research subjects, workshops, basic courses such as Ethic; courses for the training field such as Curriculum, Evaluation, Pedagogy and Epistemology etc., and there are electives.)
Total of Credits
Total of credits are 122 for 8 semesters.
Technological Compounds
The university has a platform so students can access to their courses: https://aulavirtual.cecar.edu.co/virtual/login/
On the other hand, they have other servers, and technologies like RACK DELL PowerEdge R720 with Windows Server Core 2012 R2, Renata Research Network, Moodle, Microsoft Programs, and Gmail account for all students, Dropbox, Digital modules that can be read and downloaded, online chat to get support, etc.
Practices It can be seen in the curricular plan that professional practices are offered in the 7th and 8th semester, they last 2 semesters,
they are also taken as a subject of 3 credits, and the university or student must establish a connection with an institution so students can complete the practice, if the student works, he can choose the work place to do his practice if it is socio-pedagogical.
The student must participate, make observations, and know his performance. Likewise, there are also research practices and practices must be planned along with the activities, justify absenteeism, behave well, and students must be monitored by a Teacher Leader who can be his tutor during the process. See Annex:
Taken from: Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe CECAR (2016); Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe CECAR (2013); Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe CECAR (2016).
Table 2. Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira Region COFFEE AXIS (RISARALDA-PEREIRA)
Purposes Be internationally and nationally projected regarding ICT, research and humanistic plus continuous preparation of their graduates so they can lead in many fields of the English language development.
Prepare Teachers with values, ethics, responsibility,
Develop different projects and connections nationally and globally. Conduct research and train teachers for today.
Curricular Structure
English courses, and linguistic courses are offered to develop the foreign language skills; no electives are offered; research courses, pedagogical practice, and courses related to cultural and national development are offered; courses to develop disciplinary skills such as Educational Management, Curricular Design, Sports, etc. are offered and also courses to develop humanistic skills, such as Anthropology, Psychology of Learning, and Ethic are offered.
Total of Credits 152 credits. Technological
compounds
The university has computer rooms, television, and radio.
Practices They take place in the last 2 semesters; they make a total of 11 credits and they take place in private and public institutions that have agreement with the university. Additionally, practices can be social and in this case the student can develop it as a degree mode; they can be interinstitutional if they are made to resolve an institutional issue and a degree project is made; they can be made overseas and a virtual tutor is needed; and they can be pedagogical so they take place in learning centers. No more information about the practices mediations, durability and control could be found.
Take from: Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira (2009); Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira (2012).; Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira (2016).
Table 3. Universidad Surcolombiana Region COFFEE AXIS (NEIVA-HUILA)
Purposes To develop citizenship skills that can be played in different social roles for human fulfillment.
To reach and advance level of communicative competence of English in a mastery way of all language skills and functioning of languages at all levels (phonetic, phonological, morphological, syntactic, semantic, pragmatic and discourse) but also use language as a means of communication.
To acquire knowledge and management of information systems and communication in the field of ICT, to serve as support for their teaching and research work.
Curricular Structure
English courses are offered from the first until the last semester; elective courses are offered; courses focused on ICT are offered; basic courses that develop socio-cultural skills such as Ethic, Psychology of Learning, Political Construction; courses that are offered to build professional field such as Epistemology, Curriculum, Pedagogy, Research courses, etc.
Total of Credits
165 credits.
Technological compounds
No relevant information about ICT mediation could be found, however, there is a platform so students can access to relevant information about their programs.
Practices They take place in the last 2 semesters and are taken as credits that are equivalent to 8 credits in total and according to Resolution 008 (2016) quoted by Universidad Surcolombiana (2016), they are made at the university or in any other institution such as private or public sectors; They are 4 to 8 hours per week, there is an introduction to the practice; a small wage could be provided to the student; he/she must be enrolled to Work Insurance.
Taken from: Universidad Surcolombiana (2016); Universidad Surcolombiana (2013); Universidad Surclombiana (2016).
Table 4. Fundacion Universitaria Luis Amigo Region COFFEE AXIS (ANTIOQUIA-MEDELLIN)
Purposes To train professionals who are capable of designing, develop, apply ICT, evaluate, research, resolve and execute teaching.
To train professionals with a C1 of the CERF.
To train Teachers who have socio-cultural perspectives in a national and international reality.
To train Competitive Teachers with didactic, pedagogical, humanistic, research skills. Curriular
Structure
Specific training field courses such as English courses, English literature and culture, practice courses are offered. Then, socio-humanistic courses like Anthropology and Ethic are offered; courses focused on technology training, elective, and pedagogical courses like evaluation and theoretical courses are offered.
Total of credits 144 Credits.
Technological Compounds
According to Arboleda (2009), the Technological mediations used to mediate learning are:
Practices Pedagogical practices last 4 semesters; they can be made in public or private institutions (practice I, II and II), geriatric centers, orphanages, foundations; they are equivalent to 12 credits and correspond to 8 hours per week. Likewise, students must have a B1 of the CERF; be available 128 hours x semester; First 6 English courses must have been approved. Finally, practices can be overseas, in research fields, socially, at the student’s work place and have an improving performance plan Procedure:
At the end of the sixth semester, the student will have made choice of agency, which shall be in writing in the format created for that; this will generate a commitment to it. Only Coordination Practice is authorized to send resumes to agencies and once finished the selection process, issues an institutional authorization letter to be sent to the agency where he was.
Once the student is enrolled in the seventh semester, the Coordination of practices will assign a consultant. After the start of this, the counselor and the student will make practice connection with the cooperating teacher at the agency. Fifteen days, later, the student must begin to present the products required in the process practice, after coordination with his advisor.
Taken from : Fundacion Universitaria Luis Amigo (2016); Arboleda H (2009); Fundacion Universitaria Luis Amigo (2014).
Table 5. Universidad de Tolima Region COFFEE AXIS (TOLIMA-IBAGUE)
Purposes To prepare a degree in English, which is a comprehensive professional, autonomous, innovative, excellent academic standards in teaching and discipline, to guide the teaching of foreign languages taking into account the social function of language; comprising the educational reality Colombian and inquire about it and carry out their conscious pedagogical work of its ethical mission as a change agent and former abiding citizens that contribute to sustainable development.
Curricular Structure
English courses, elective courses, socio-humanistic courses, research and practice courses are offered.
Total of Credits
175 credits for 10 semesters.
Technological Compounds
Just a virtual platform could be found
Practices Internships can occur in the last four semesters and can be made in local institutions, and students must have a B 2 of the CERF.
Taken from: Universidad de Tolima (2016); Universidad de Tolima (2012).
Table 6. Universidad ICESI
Region COFFEE AXIS (VALLE DEL CAUCA-CALI)
Purposes To develop professionals with passion for the craft and interest in developing the full potential of the student depending on their needs and abilities; with high sensitivity and understanding of their social function against equality, justice, equity and integration, proficient in the English; formed through the permanent practice and able to self-assess their learning and working with others.
Curricular Structure
English courses, electives, pedagogical courses, humanistic courses, ICT formation course, are offered.
Total of credits
171 Credits for 10 semesters.
Technological components
E-books, forums, blogs, web-conferences, computer rooms, other ICT and WEB 2.0 tools are offered. See (Annex 8)
Practices Professional Practices are taken in the last semesters; they must be made in connection with an organization and there are meetings and organizational processes to control and coordinate them
Table 7. Universidad Industrial de Santander (UIS) Region COFFEE AXIS (SANTANDER-BUCARAMANGA)
Purposes To provide teachers a solid humanistic and scientific training aimed at contributing to the improvement of educational processes.
To train teachers with advanced communicative competence in the English language.
To provide teachers pedagogical training perspective that allows perform properly in the area of English in the middle and at the corresponding level assumed.
To develop in future teachers an academic discipline that prepares them for permanent intellectual development, independent study and research.
To enable teachers to proper performance in the workplace both for their own benefit and that of society in general. To encourage graduates in an attitude that contributes to the development of their ethical and political judgment. Curricular
Structure
Electives, pedagogical practices, English courses, research courses, ICT training course etc., are offered.
Total of credits 170 Credits for 10 semesters. Technological
components
Sony Handycam camcorder Camera TRV 65 Panasonic recorders for magnetic tapes or cassettes. Video or video projector-beam Sanyo.
Players Samsung DVD-VHS video formats. DVD to VHS video format.
Sony recorders for CDs and cassettes. Type recorders Sony journalist.
1 Camera Sony camcorder to VHS format.
Multimedia Laboratory with 19 computers Dell Optiplex GX 620 and its corresponding software Windows XP. Audio concert.
Laboratory audio equipment 21 cabins with sound recording and reproduction.
1 Living video with up to 35 people. It fits at the time of use with a video projector, TV and DVD, computer speakers or recorder.
Audio materials with CD, headphones and video platers.
Center of bibliographical documentation
Practices Based on the curricular structure, the internship are made in the last 2 semesters, as credits and there is theory of that in the 8th and 9th semester.
Taken from: Universidad Industrial de Santander (2016); Universidad Industrial de Santander (2007).
Table 8. Universidad Santo Tomas Region BOGOTA
Purposes To make professionals who can
Be able to contribute to the transformation of the social and cultural realities through a solid humanistic training, and high skills in the field and discipline research.
Identify problems of educational type in the English teaching-learning process, to design, adapt and evaluate teaching materials and resources allocated for this purpose.
Have expertise in the domain of foreign language and the Spanish language, to interact and understand national and global educational contexts.
Curricular Structure
English training courses, humanistic courses, electives, research courses, practice courses and pedagogical courses are offered.
Total of credits 157 credits and 10 semesters.
Technological components
All ICT and WEB 2.0 Tools, it includes forum, Wikis, blogs, digital portfolios, web-conferences, audio, etc.
Practices They are made in the last 2 semesters, and can be made in institutions where the student Works or where there are connections. Also, the practices are regulated by a tutor and the student must bring results as followed in the guidelines.
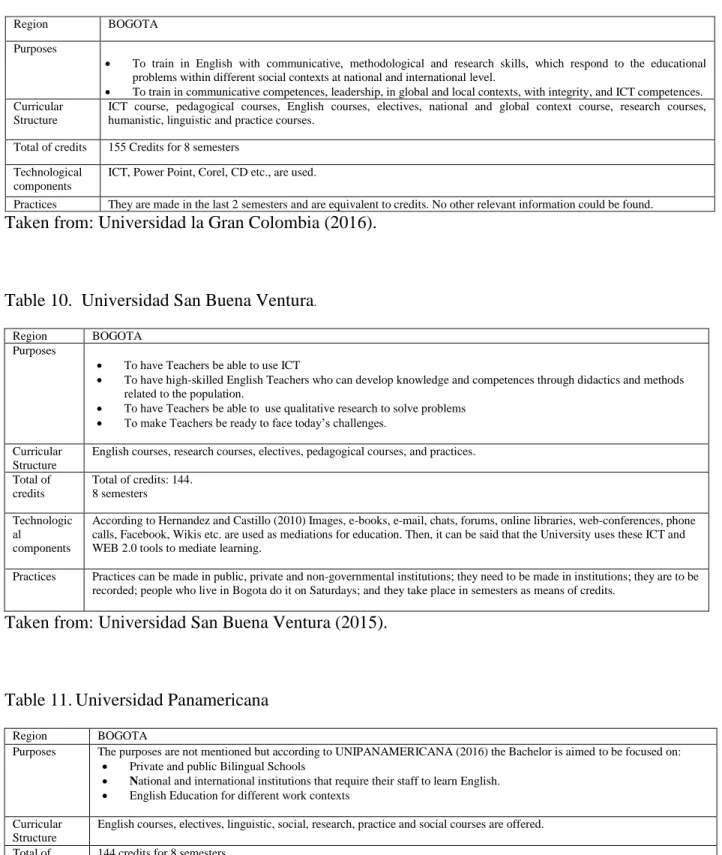
Table 9. Universidad la Gran Colombia
Taken from: Universidad la Gran Colombia (2016).
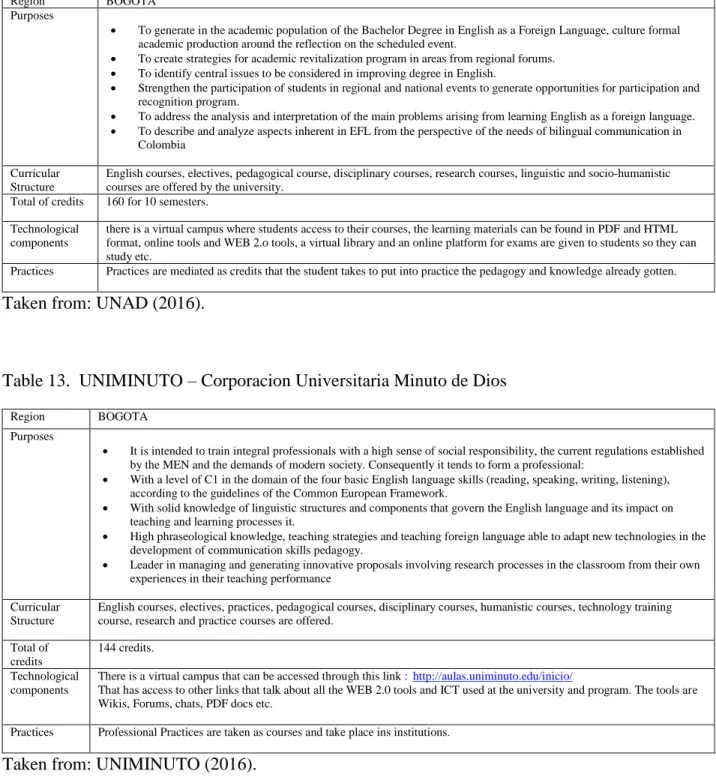
Table 10. Universidad San Buena Ventura. Region BOGOTA
Purposes
To have Teachers be able to use ICT
To have high-skilled English Teachers who can develop knowledge and competences through didactics and methods related to the population.
To have Teachers be able to use qualitative research to solve problems To make Teachers be ready to face today’s challenges.
Curricular Structure
English courses, research courses, electives, pedagogical courses, and practices.
Total of credits
Total of credits: 144. 8 semesters
Technologic al components
According to Hernandez and Castillo (2010) Images, e-books, e-mail, chats, forums, online libraries, web-conferences, phone calls, Facebook, Wikis etc. are used as mediations for education. Then, it can be said that the University uses these ICT and WEB 2.0 tools to mediate learning.
Practices Practices can be made in public, private and non-governmental institutions; they need to be made in institutions; they are to be recorded; people who live in Bogota do it on Saturdays; and they take place in semesters as means of credits.
Taken from: Universidad San Buena Ventura (2015).
Table 11. Universidad Panamericana Region BOGOTA
Purposes The purposes are not mentioned but according to UNIPANAMERICANA (2016) the Bachelor is aimed to be focused on: Private and public Bilingual Schools
National and international institutions that require their staff to learn English. English Education for different work contexts
Curricular Structure
English courses, electives, linguistic, social, research, practice and social courses are offered.
Total of credits
144 credits for 8 semesters.
Technological components
No information was found
Practices Practices are taken as credits and can last from 6 months and no more than 2 years. They are controlled and verified by the university and a track of them must be made.
Region BOGOTA
Purposes
To train in English with communicative, methodological and research skills, which respond to the educational problems within different social contexts at national and international level.
To train in communicative competences, leadership, in global and local contexts, with integrity, and ICT competences. Curricular
Structure
ICT course, pedagogical courses, English courses, electives, national and global context course, research courses, humanistic, linguistic and practice courses.
Total of credits 155 Credits for 8 semesters
Technological components
ICT, Power Point, Corel, CD etc., are used.
Taken from: Universidad Panamericana (2016), Universidad Panamericana (2015)
Table 12. Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia (UNAD) Region BOGOTA
Purposes
To generate in the academic population of the Bachelor Degree in English as a Foreign Language, culture formal academic production around the reflection on the scheduled event.
To create strategies for academic revitalization program in areas from regional forums. To identify central issues to be considered in improving degree in English.
Strengthen the participation of students in regional and national events to generate opportunities for participation and recognition program.
To address the analysis and interpretation of the main problems arising from learning English as a foreign language. To describe and analyze aspects inherent in EFL from the perspective of the needs of bilingual communication in
Colombia
Curricular Structure
English courses, electives, pedagogical course, disciplinary courses, research courses, linguistic and socio-humanistic courses are offered by the university.
Total of credits 160 for 10 semesters.
Technological components
there is a virtual campus where students access to their courses, the learning materials can be found in PDF and HTML format, online tools and WEB 2.o tools, a virtual library and an online platform for exams are given to students so they can study etc.
Practices Practices are mediated as credits that the student takes to put into practice the pedagogy and knowledge already gotten.
Taken from: UNAD (2016).
Table 13. UNIMINUTO – Corporacion Universitaria Minuto de Dios Region BOGOTA
Purposes
It is intended to train integral professionals with a high sense of social responsibility, the current regulations established by the MEN and the demands of modern society. Consequently it tends to form a professional:
With a level of C1 in the domain of the four basic English language skills (reading, speaking, writing, listening), according to the guidelines of the Common European Framework.
With solid knowledge of linguistic structures and components that govern the English language and its impact on teaching and learning processes it.
High phraseological knowledge, teaching strategies and teaching foreign language able to adapt new technologies in the development of communication skills pedagogy.
Leader in managing and generating innovative proposals involving research processes in the classroom from their own experiences in their teaching performance
Curricular Structure
English courses, electives, practices, pedagogical courses, disciplinary courses, humanistic courses, technology training course, research and practice courses are offered.
Total of credits
144 credits.
Technological components
There is a virtual campus that can be accessed through this link :http://aulas.uniminuto.edu/inicio/
That has access to other links that talk about all the WEB 2.0 tools and ICT used at the university and program. The tools are Wikis, Forums, chats, PDF docs etc.
Practices Professional Practices are taken as courses and take place ins institutions.
Table 14. Universidad de la Amazonia Region AMAZONAS
Purposes To train teachers with high levels of proficiency in their communication and teaching skills that promote the qualification of the teaching and learning of English in the regional and national context. Teachers will meet international levels of proficiency and educational performance which corresponds to a strong background in all implicit and explicit in the acquisition processes and teaching English factors.
The program's degree in English from the University of the Amazon aims to become an academic comprehensive training of English teachers with similar levels of competition to international standards and efficiency levels that promote language learning according to the contexts regional and national.
Curricular Structure
Cultural courses, English courses, linguistic courses, research courses, pedagogical courses, and socio humanistic courses are offered.
Total of credits
122 Credits for 9 semesters.
Technological components
The university offers computer rooms, and rooms for web-conferences, See following link:
http://www.udla.edu.co/v10/index.php/2013-08-14-20-35-02.html . No more information could be found.
Practices Practices are made as subjects or credits. At the same time, they have a tutor who guides the student thorough the process, they last during all the program, but are made in institutions in the last 2 semesters .They are evaluated.
CHAPTER IV Data results and analysis
It could be seen that not all universities totally meet the institutional projects set up by the MEN and the global needs nationally and internationally when offering the program of Bachelor degree in English. Then, the following, is the data results and analysis with information about the items that could be totally met by universities in Colombia that offer Bachelor degree in English in regards to credits, purposes, technological compounds, curricular structure and practices already mentioned by the nation, specifically the MEN in a global and local context.
a. Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe (CECAR)
are workshops to develop practices. Finally, it is evident that the curriculum does not include technology training, while it is a global requirement and the MEN demands it.
b. Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira. (UTP)
Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira (UTP) covers most the compounds that were set up by the MEN. First, in terms of credits, the amount of credits is an average amount for the program duration. Secondly, in terms of Technological compounds, ICT and WEB 2.0 tools are used for mediation and different purposes such as support. Thirdly, in terms of practices, they are taken just in the last semesters as the MEN said; they are made in labor places; they are equivalent to credits, and they are gotten by the student or through connections that the university has with other places. A plus is that they can be made overseas, then, it prompts globalism and cultural exchange. Fourthly, regarding purposes, they are complete by including the ethical, linguistic, research, technological and methodological compounds that are required by the MEN. Finally, the only issue that could be found was that Universidad Technological de Pereira does not present electives in its curriculum, which is the opposite of what the MEN established in its guidelines.
c. Universidad Surcolombiana
curriculum, English courses and elective courses are offered from the first until the last semester, courses focused on ICT are included; basic courses that develop socio-cultural skills such as Ethic, Psychology of Learning, Political Construction; courses that are offered to build
professional field such as Epistemology, Curriculum, Pedagogy, Research courses, etc., as well as electives, then it is flexible. Thirdly, terms of credits, there is a good amount of credits and incorporates what is needed for the student’s formation. Fourthly, the practice, which duration is of 1 to 2 semesters and the description about how they are operated matches what the MEN demands. Finally, the only gap that could be found was related to technological compounds, because there was no source that could provide the researcher knowledge about which ICT are to be used for learning and pursuing the major.
d. Fundacion Universitaria Luis Amigo
Fundacion Universitaria Luis Amigo is partially adjusted to the national projects, guidelines and international needs. First, in regards to purposes, they are aligned to what
linguistically, socially, technologically, etc., is needed today, in addition, its purposes match with the credits that are listed in the curricular structure. Secondly, in terms of technological
e. Universidad del Tolima
Universidad Del Tolima is partially adjusted to the requirements set up by the MEN and globally First, in terms of credits, the program lasts 10 semesters and the credits are 175, besides, they are well distributed among the semesters so based on what the MEN needs, the program is 100% good with credits. Secondly, its purposes are aligned to what is expected by the MEN in regards to social, pedagogical, research and linguistic goals. Additionally, the purposes match with the credits that are named in the curriculum. Thirdly, its curriculum incorporates English courses, social, disciplinary and professional courses, technology training and it is flexible because it offers electives in different fields of knowledge. Fourthly, in regards to technological compounds, information related to which technologies are to be used for learning and interacting with teachers, could not be found. Finally, the practice are offered as credits and can be made in local institutions.
f. Universidad ICESI
Universidad ICESI is adjusted to the national and MEN institutional projects, and global needs by covering all the elements that were reviewed. First, in terms of technological
compounds, both, ICT and WEB 2.0 tools are included and provided for students. Secondly, its purposes match with the credits that are offered in the curricular structure and they are aimed to what the MEN requires in regards to theoretical and practical training, language training, school management, and disciplinary training. Thirdly, the credit numbers match with the 10 semesters of the program duration. Fourthly, practices are offered as credits, they must be made in
and coordinate them. Finally, its curricular structure has all the elements that are needed
nationally and internationally in terms of English course, electives, cultural and ICT formation.
g. Universidad Industrial de Santander (UIS)
h. Universidad Santo Tomas
Universidad Santo Tomas is totally adjusted to the global and local institutional
guidelines regarding Bachelor degree in English. First, in terms of purposes, they all match with what is needed nationally and internationally, regarding research purposes, goals oriented to local and global needs, English competences, research, humanistic and curricular training goals. Secondly, its Curricular Structure includes pedagogical, humanistic, technology- orientation, investigative, linguistic-disciplinary courses and electives, which shows flexibility. Thirdly, the technological compounds, as ICT and WEB 2.0 tools are included. Fourthly, the practices that are made in institutions, are taken as credits and can last from 1 to 2 semesters, and they are well coordinated. Finally, its number of credits matches with the program duration.
i. Universidad la Gran Colombia
Universidad la Gran Colombia is fully attached to the institutional guideline .First of all, the program purposes and curricular structure are compatible. Additionally, a defined profile that the student will graduate is described as well as objectives related implied items such as self and team work, critical and self- thinking, communicative competences development and articulation with pedagogy, didactic, practices, research, disciplinary subjects and learning. Secondly, the curricular structure shows flexibility by including electives, linguistic, technological, humanistic, disciplinary, and investigative- oriented courses are included. Thirdly, the amount of credits is articulated with the program duration. Fourthly, WEB 2.0 tools and ICT are used by the
j. Universidad San Buena Ventura
Universidad San Buena Ventura totally meets the institutional guidelines set up by the MEN, by the nation and globally. First, the total of credits is related to the program duration of 8 semesters. Secondly, the technological compounds include ICT and WEB 2.0 tools that are needed locally and abroad, to mediate learning. Thirdly, the practices last and are well coordinated for a program that is virtually taken, but the weekly intensity of hours was not
specified. Fourthly, its purposes match what is asked by the MEN and nationally in terms of ICT, English training, critical thinking social and pedagogical goals. Finally, its curricular structure has all the subjects that are needed according to the MEN.
k. Universidad Panamericana
Universidad Panamericana covers just some of the national components set up by the MEN. First, in regards to total of credits that are related to the program duration of 8 semesters already mentioned by the MEN. Secondly, further information about practices, technological compounds, and purposes could not be found as in order to access and get more information, a form had to be filled in and most of the times, people do not pay fill in forms to get more
l. Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia (UNAD).
Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia (UNAD) meets in a totality all the guidelines and institutional projects in regards to purposes, practices, curricular structure, number of credits and technological compounds that the country, the MEN and the world need. First, because its curriculum is flexible and offers credits to train students in pedagogical, linguistic, social, cultural, humanistic, research and practice fields. Secondly, its offer has a balanced amount of credits in relation to the program duration. Thirdly, all ICT and WEB 2.0 tools are prompted to be used and there is training for it. Finally, its practices are taken as credits and must be made in an institution where there is a connection with.
m. Corporacion Universitaria Minuto de Dios
Corporacion Universitaria Minuto de Dios meets in a totality the requirements that are established by the MEN in accordance with the globalized context. First, its purposes match with the curricular structure since it is aimed to language construction in accordance with the CERF; it is aimed to boost linguistic, technological, occupational, and social training. Secondly, its curricular structure includes electives, so it is flexible; it includes language training courses, linguistic language courses and training courses; it includes pedagogical and humanistic courses, research, practices and cultural immersion. Thirdly, the total of credits match with the 9
n. Universidad de la Amazonia.
Universidad de la Amazonia meets a few elements that are needed in the country about institutional projects set up by the MEN in accordance with the globalized contexts. First, in terms of purposes, they are related to self and team work, critical and self- thinking,
communicative competences development, and it is articulated with pedagogy, didactic,
practices, research, disciplinary subjects and learning. Secondly, in regards of practices, they last 2 semesters; they are equivalent to credits, they aremade in labor institutions, andthey are coordinated with a tutor. Thirdly, there was no more information related to technological
Conclusions and recommendations
In regards to the current status of education of Bachelor degree in English in Colombia, it could be concluded that not all universities seem to review and comply with the MEN’s
regulations and guidelines, just 50 % of the population do it. Therefore, a reform in the
curriculum, purposes, practices, technologies and credits is generally needed in Colombia so that all universities can fully meet the institutional projects that the MEN has established in national and global contexts.Additionally, more control by the MEN is needed so institutions can
accomplish what it dictated in its guidelines. Finally, all controls and reforms have to consider national and international needs such as technological immersion in learning, which would cover both, ICT and WEB 2.0 tools, curricular flexibility and variability, purposes that are global, complete and clear, and so on.
Conclusions
In regards to curriculum, it could be seen that not all universities have a flexible curriculum, some of them either showed just a few electives, while others did not show them, they were just focused on areas linked to English training, or a seminary as an elective which is not what the MEN asks. This includes Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira, Fundacion
Universitaria Luis Amigo, Universidad Panamericana and Universidad del Amazonas. Secondly, not all the curriculums incorporated ICT and Web 2.0 tools training. This includes Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe, Universidad de la Amazonia and Universidad Panamericana. Finally, curriculums of training in cultural immersions in local and global contexts, socio-humanistic formation, and more courses related to pedagogy, virtual and traditional were not fully included by Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe, Universidad Panamericana, and Universidad del Amazonas.
Moreover, the conclusion is that by not having a flexible curriculum, the professional who graduates will not realize that there are other areas of knowledge in which he could pursue a master degree on; he will not be fully trained and flexible for other areas of knowledge, and he will just be more traditionally oriented when teaching.
able to handle technologies when having a job. Therefore, the lackof technological competence will be transmitted to learners and at the end people will not be competitive in ITC and will have hard times when trying to use technologies.
Furthermore, in terms of credits, it could be seen that even though most of the number of credits tailor the number of semesters, it is precise to say that some universities did not include more number of credits. This case would apply for Universidad UNIMINUTO, Universidad Panamericana, Universidad San Buena Ventura, Universidad La Gran Colombia, Universidad Tecnologica de Pereira and Corporacion Universitaria del Caribe CECAR. Thus, there were programs which credits were just offered to train the student in the English courses and practice courses while credits related to electives and humanistic training were just a few. Therefore, this would give fewer options for people, to be able to enroll more credits and get more knowledge.
Recommendations
In general, universities must provide more information that can be accessed and found when it is desired to review and read their offers because future readers would be able to find all what is needed when visiting their websites so the right choice can be made. Then, they would need to redesign their websites, train their own students to help them improve the webpages in cooperation with the Teachers. Additionally, a very clear offer that includes and shows all the elements that are to be included in a program is needed because that is going to make their offers more approachable to future students and anyone who reads the program purposes will
communicate that to others.
Additionally, in regards to the credit numbers, purposes and curricular structure should match with the purposes that have tobe clear and wide. Therefore, universities must redesign their curricular structure and include a variety of electives linked to other areas of knowledge, since that will increase the students’ choices to be trained in specificsubjects and fields. Also, in the programs, courses related to virtual and traditional education have to be included; this must be covered by the universities that offer the degree virtually and traditionally. Finally, credits and the curriculum must include a strong cultural formation so that students can be more open to other culture, and include workshop credits that student can take and do overseas if possible.
ICT, it is necessary that it should be used by all universities as a strategy to reach knowledge because this will also increase their accreditation, and they will be more routed to the global needs, rather than just the MEN and the local needs.
Then, universities that offer the degree traditionally should invest some money to incorporate technologies and train their teachers for ICT usage and universities that offer the degree online, must train and hire Teachers to use and apply ICT in the teaching practice because that would be transferred to students.
The other recommendations are that in regards to practices, universities must include and describe a clear route and guidelines that can be accessible to future learners, and readers that may be interested in pursuing the Bachelor degree in English. First, because the future student who works expects to make decisions about switching from his job if it is not related to his field and the practice must be the opportunity enrich the student’s career plans. Therefore, for this, universities must review all MEN guidelines to apply them in the practices as written. Moreover, it would be required for the MEN and universities to dictate courses about that so it can be applied.
and universities that do not fully MET its institutional and international projects, by periodically visiting them, reviewing them, giving feedback and set up actions plans that universities can do by themselves to be more accredited in all levels.
Regarding the CERF, the recommendation is that all universities should describe and mention in their program offers, which language certification test is to be applied. Likewise, it is recommended that all universities should include and mention in their proposals, English