TítuloPath coefficient analysis, a different approach to identify soil quality indicators
Texto completo
Figure
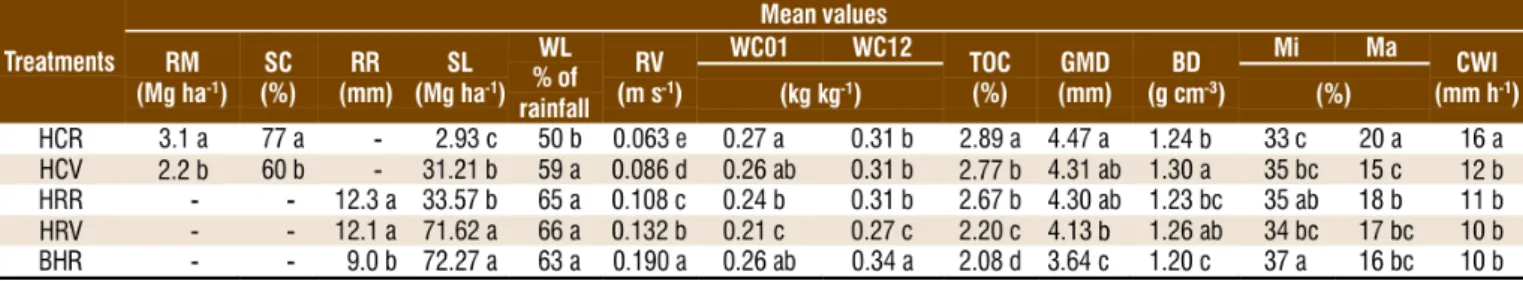
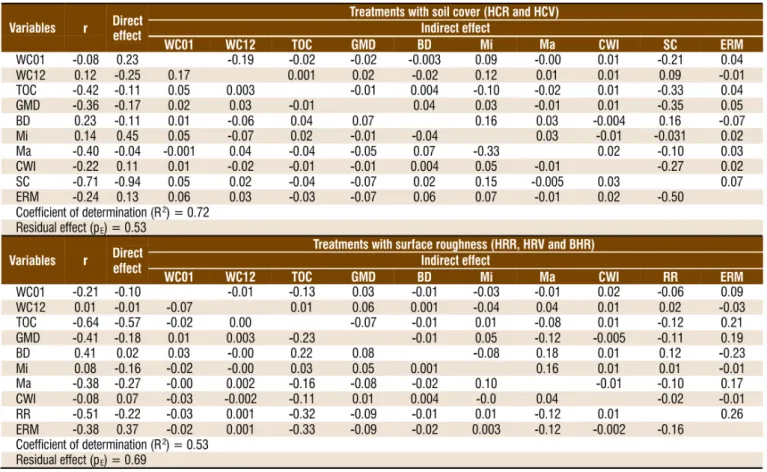


Documento similar
Groundcovers; Soil organic carbon; aggregate stability; soil porosity; soil quality.. uses, Mediterranean vineyards undergo a series of soil degradation processes: soil
An employee who sleeps 8 hours per night may still have poor sleep quality, preventing the individual from showing up for work at peak performance.. Additionally, sleep hygiene
The selection included two supporting ecosystem properties (soil conditions, composed of soil formation and soil stability, and habitat quality), four regulating services
Impacts of soil management practices on crop productivity, on indicators for climate change mitigation, and on the chemical, physical and biological quality of
Since forest variables (forest productivity and for- est biomass) and abiotic factors (climate variables, soil texture and nu- trients, and soil topography) were only calculated at
The aim of this research is to study the impact of each above-mentioned factor on N 2 O emissions during three growing seasons in a maize field, considering three nitrogen
The general objective of this dissertation was to identify spatial and temporal hydrological patterns using intensive soil erosion and water content measurements, and to
Changes in soil bulk density, soil organic carbon and water holding capacity are analysed in soils currently tilled, and after five to fifteen years of abandonment in order to