The fractional Fourier transform and quadratic field magnetic resonance imaging
Texto completo
Figure
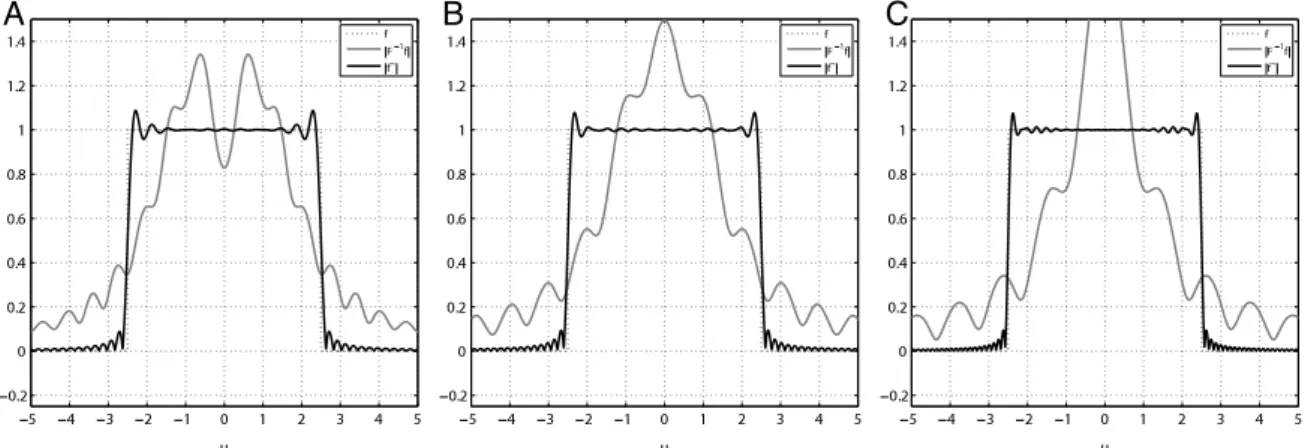
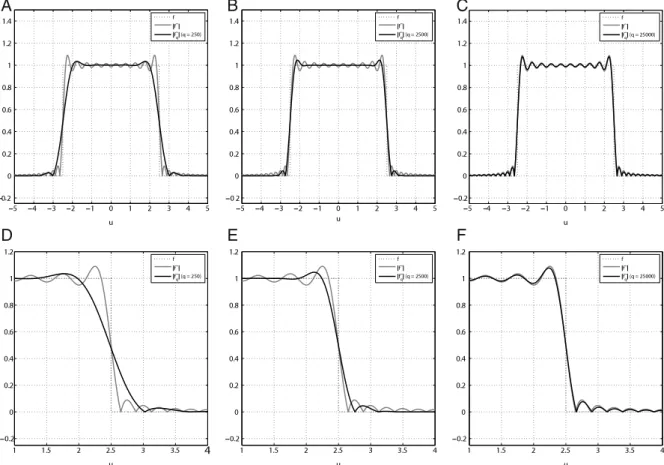
Documento similar
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the
Jointly estimate this entry game with several outcome equations (fees/rates, credit limits) for bank accounts, credit cards and lines of credit. Use simulation methods to
Phys.. Back, “Fourier transform imaging of spin vortex eigenmodes,” Phys. Zaspel, “Magnon modes for thin circular vortex-state magnetic dots,” Appl. Kim, “Dynamic origin
The guide includes a comparison to the windowed Fourier transform, the choice of an appropriate wavelet basis function, edge effects due to finite-length time series, and
The algorithm uses a parametrical model to generate the synthetic Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) of the trajectory signals, which are then refined in the time domain and completed
A simple method to alleviate this problem consists of multiplying the pro- jection Fourier transform by the sign of the CTF (this approach is named phase flipping (Frank, 1996,
In this paper we analyze a finite element method applied to a continuous downscaling data assimilation algorithm for the numerical approximation of the two and three dimensional
firstly we can take advantage of the either diagonal or circulant structure of resolution and overlapping kernel operators, respectively, to provide explicit inversion formulas