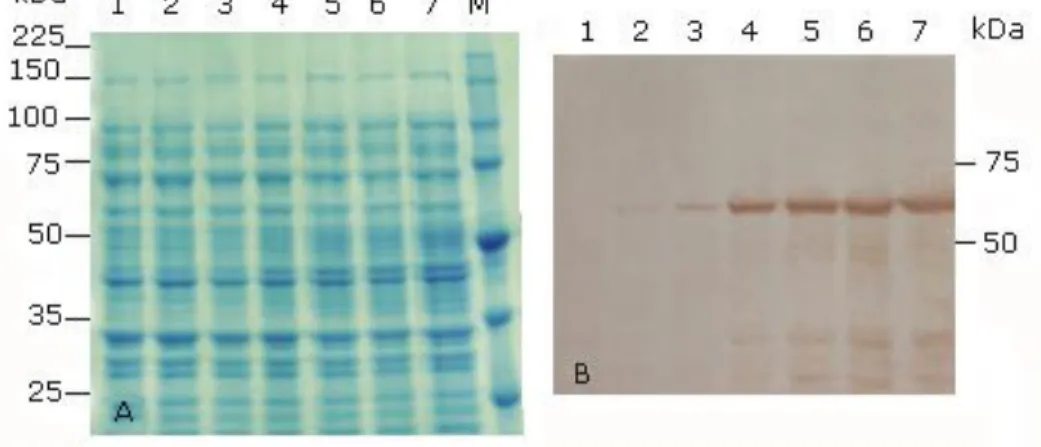
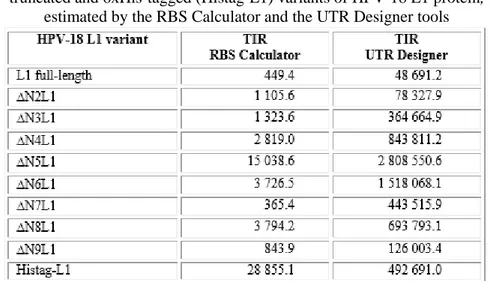
Clonacin y expresin en Escherichia coli de un gen L1 completo del virus del papiloma humano 18 aislado de una paciente cubana y variantes delecionadas
Texto completo
Figure


Documento similar
GO:0019866 - organelle inner membrane; GO_process: GO:0006464 - protein modification process 1 11 fused sensory histidine kinase in two-component regulatory system with KdpE:
organelle inner membrane; GO_function: GO:0015662 - ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of ions, phosphorylative mechanism 1 11 potassium translocating ATPase, subunit
GO:0009310 - amine catabolic process 1 11 spermidine/putrescine ABC transporter periplasmic binding protein AAC74207.1.. SAMPLE QUAL FILTER DP RPB AF1 AC1 DP4 MQ FQ PV4 VDB IS
membrane; GO_function: GO:0042280 - cell surface antigen activity, host-interacting; GO_process: GO:0009243 - O antigen biosynthetic process 1 11 putative polisoprenol-linked
process 1 11 penicillin-insensitive murein repair transglycosylase; inactive transpeptidase domain protein AAC75572.1 2.4.1.-. SAMPLE QUAL FILTER DP RPB AF1 AC1 DP4 MQ FQ PV4 VDB
Non synonimous mutations found in sample: CIM5N. FILTERS: (ANN contains MODERATE
In our work the infection of human duodenal biopsies by the effector mutant EPEC strains revealed that, although EPEC2 and EPEC1 strains were able to induce actin-pedestals in
La presente investigación tuvo por objetivo determinar el efecto antibacteriano de las diferentes concentraciones de nanopartículas Core@Shell Ag@ZnO sobre Escherichia coli

