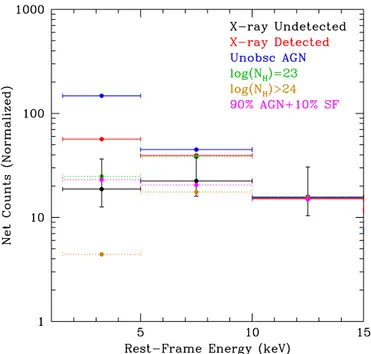
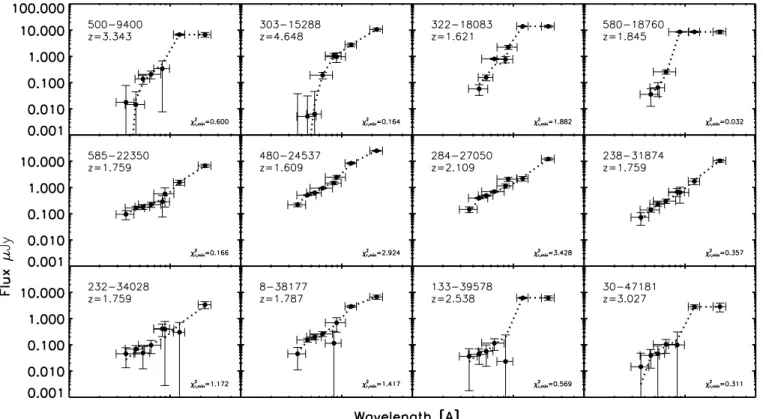
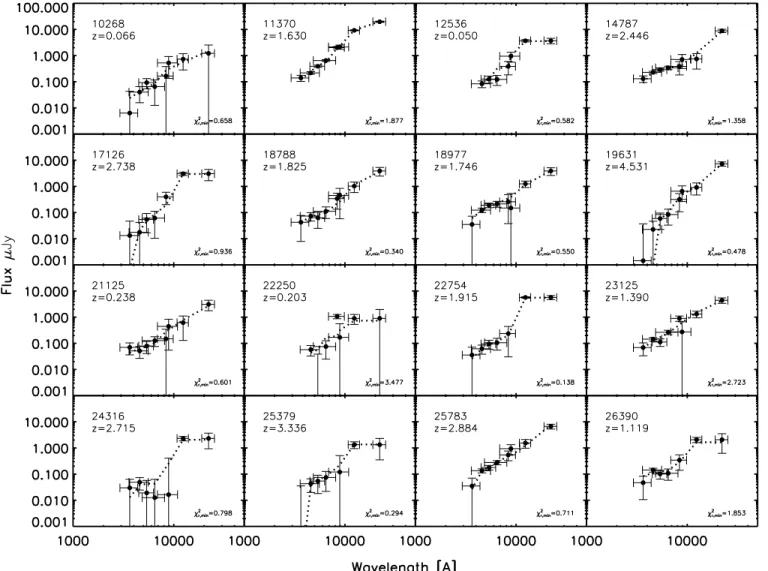
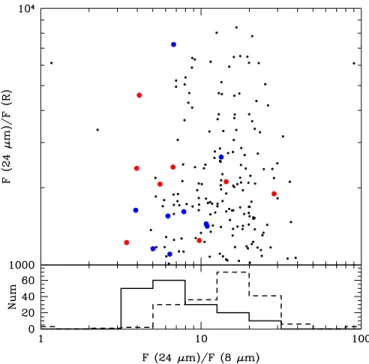
Heavily Obscured AGN in Star Forming Galaxies at z sime 2
Texto completo
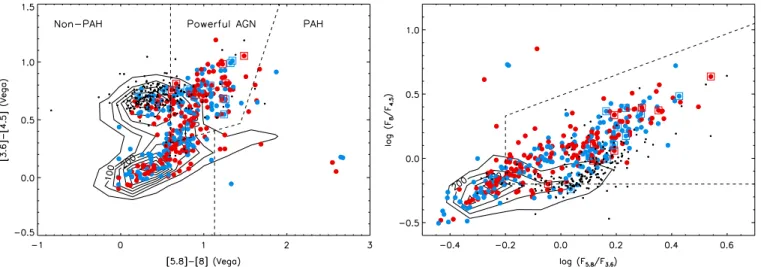
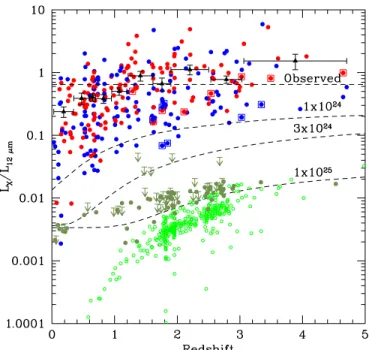
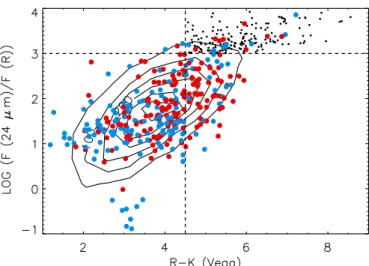
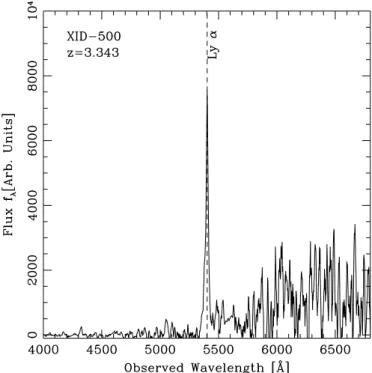
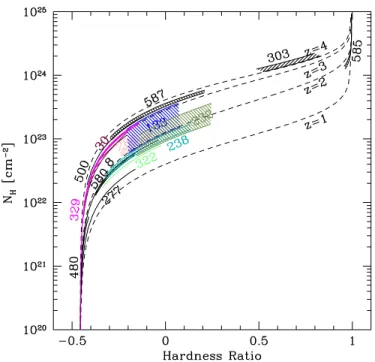
Figure

Documento similar
Measuring the concentration–mass relation and its redshift evolution in a subsample of MUSIC-2 halos that reproduces the distribution of X-ray regularity parameters of the clusters
The time selection for the following sources is based entirely on their X-ray behaviour, by taking into account the disk-jet coupling just described. Only periods of hard X-ray
Finally, the IMF of a stellar sample mainly com- posed of discy YSOs from MC09 combined with some additional X-ray stars is utilized to estimate the total number of stars inside
• Analysis of long-term variability of high-energy sources in the optical and X-ray bands, using INTEGRAL observations from IBIS (the gamma-ray imager), JEM-X (the X-ray monitor)
✴ WEAVE , IFU mode (fov = 2 sq. arcmin, with 1-2.5 arcsec/sparxel) to trace the stellar population of galaxies beyond 3 HLR in a large sample of galaxies covering all
A comparison between the radio and X-ray populations in Orion shows that the radio detections so far have been strongly biased to the brighter X-ray stars. This supports the
As a first step in our study, we characterized the mid-IR high-ionization emission lines produced by AGN and star-formation for a large sample of local galaxies, includ- ing
As a first step to reach our objectives, in Chapter §3 we have performed a detailed analysis of all data taken by the XMM-Newton satellite of UGC 11763 to characterize the