Angiotensin II induced pro fibrotic effects require p38MAPK activity and transforming growth factor beta 1 expression in skeletal muscle cells
Texto completo
Figure

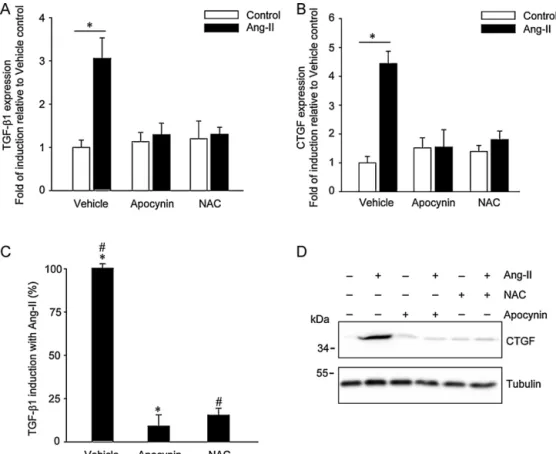

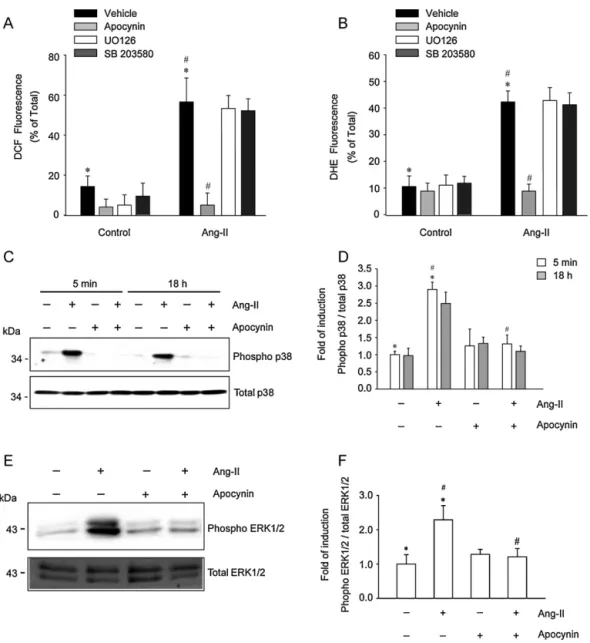
Documento similar
1. HuR is involved in the stabilization of COX-2 mRNA in cancer cells and AngII is able to increase COX-2 mRNA stability in vascular cells. In the first part of the PhD Thesis,
Direct protective effects of metformin on cardiac cells Since both sitagliptin and metformin similarly reduced fibrosis in the GK heart, and GLP-1 triggered anti-fibrotic
Also, a very recent report demonstrates that the loss in self-renewal detected in satellite cells from aged mice can be overcome by p38α/β inhibition (Bernet and Rudnicki,
Treatment of AngII-infused mice with anti-TLR4 antibody improved these structural parameters (Figure 2A-D); the treatment also improved the reduced number of smooth
Specifically, ERK1/2 can participate in HuR phosphorylation, modifying its activity in a lung cancer cell line (Yang et al., 2004) or HuR cytoplasmic location in hepatic
OSKM expression has two mutually exclusive outcomes: in some cells it induces dedifferentiation to form induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, in other cells it
Conversely, the evaluation of mRNA levels of genes encoding pro-in flammatory cytokines [interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 b ), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF a ), and transforming
Growth regulation of human colon cancer cells by epidermal growth factor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 is mediated by mutual modulation of receptor expression. The down-regulation

