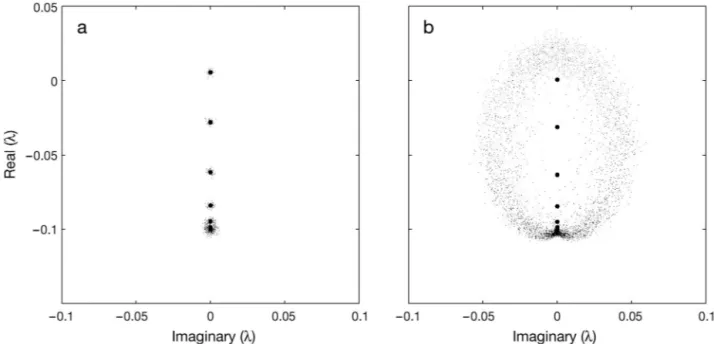
Environmental fluctuations and asymmetrical dispersal: generalized stability theory for studying metapopulation persistence and marine protected areas
Texto completo
Figure
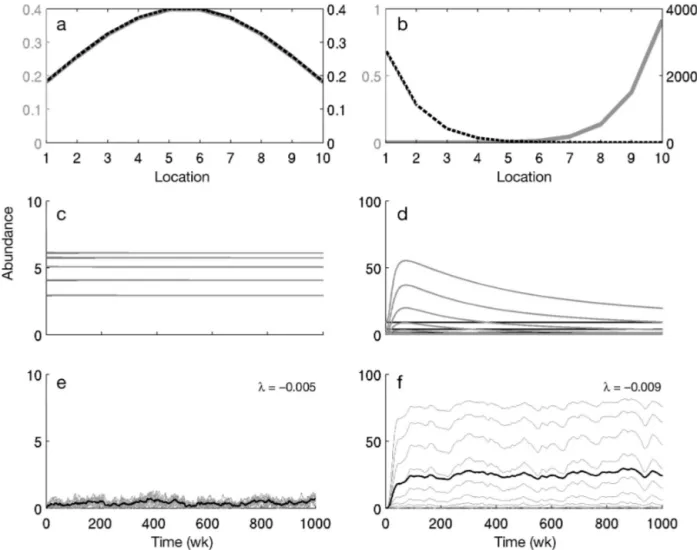
Documento similar
These dispersal ranges were similar to that expected by the general model for stream resident brown trout estimated with fishmove package, which calculates a mean movement distance
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the
Jointly estimate this entry game with several outcome equations (fees/rates, credit limits) for bank accounts, credit cards and lines of credit. Use simulation methods to
In our sample, 2890 deals were issued by less reputable underwriters (i.e. a weighted syndication underwriting reputation share below the share of the 7 th largest underwriter
Franco, 2020) we analyze the effect of cities' sustainability pillars, social, economic and environmental, in order to determine their rela- tive importance for city reputation..
Recently, modeling approaches have focused on wind dispersal (Nathan et al. 2002) and dispersal in feces (Pakeman 2001); however, these processes cannot produce sufficiently
Of special concern for this work are outbreaks formed by the benthic dinoflagellate Ostreopsis (Schmidt), including several species producers of palytoxin (PLTX)-like compounds,
One should also recall the passive dispersal m odels either through floating objects (see STEINECK et al. 1990, for deep-sea xylophile ostracods; DANIELOPOL and BONADUCE 1990,