Measurement with the ATLAS detector of multi particle azimuthal correlations in p plus Pb collisions at root s(NN)=5 02 TeV
Texto completo
Figure

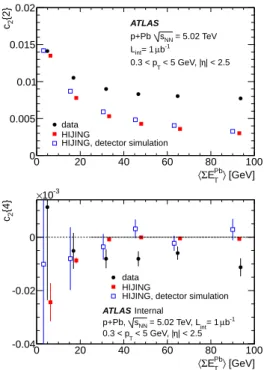
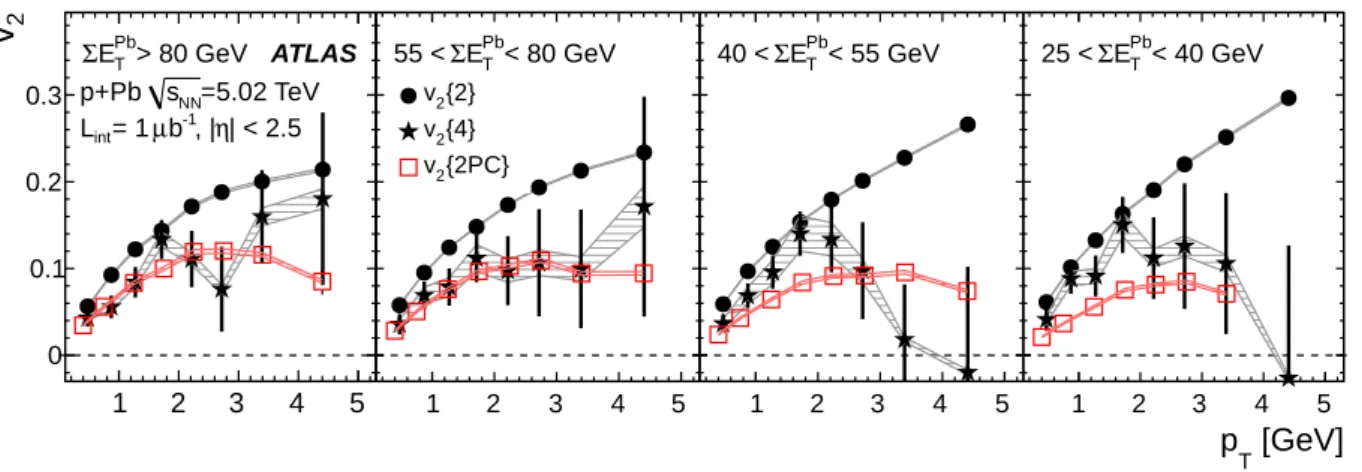
Documento similar
33 (a) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; (c) Department
35 ( a ) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; ( b ) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; ( c
33 (a) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; (c) Department
Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; (c) Department
4 (a) Department of Physics, Ankara University, Ankara, Turkey; (b) Istanbul Aydin University, Istanbul, Turkey; (c) Division of Physics, TOBB University of Economics and
35 (a) Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; (c) Department
Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; (c) Department
Institute of High Energy Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing; (b) Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Anhui; (c) Department