Texture Characterization of Fine Particles Released During Thermal Shock and Combustion Processes by Fractional Brownian Motion Analysis
Texto completo
Figure
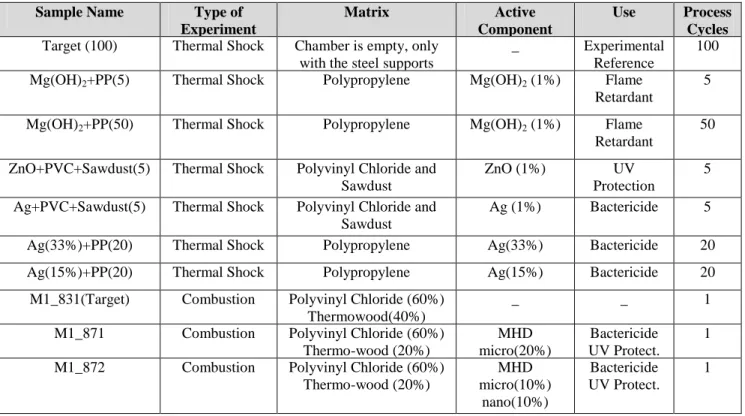


![Table 2. Analyzed samples parameters: mean values of fractal parameter H, standard deviation (SD) and variation coefficient [VC = (σ s /H)100]](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/7449728.398341/6.918.193.731.389.668/analyzed-samples-parameters-parameter-standard-deviation-variation-coefficient.webp)
Documento similar
The Brownian dynamical analysis based on the information ex- tracted from optical forces and torques on a particle in an optical tweezer, the analysis of the fulfillment of actio
Once features were extracted by quantitative texture analysis from cervical ultrasound images, a model of gestational age was developed following the next three steps: data
Hydrogeological characterization ... Thermal anomaly origin ... Permeability from fractures ... The main aquifers ... The hydrogeological functioning ... Thermal conductivity
Characterization of the thermal contacts between heat exchangers and a thermoelectric module by impedance spectroscopy (under
GCLc characterization in MLEC and lung fibroblasts isolated from Gclc(f/f) and Gclc(e/+) mice. A) Western blot analysis (left) and quantification (right) of GCLc and GCLm in MLEC
The growth of III-N ternary layers without Ga incorporation is commonly affected by several difficulties during their growth due to the large differences between AlN and InN
The proposed model was applied to predict the transient evolution of lab-scale turbulent combustion sequences of mixtures of hydrogen, air and graphite particles under low
The analysis of spatiotemporal properties and organization of cortical vi- sual neurons, together with the indications given by experimental results on visual spatial and

