Spatial and temporal characterization of fish assemblages in a tropical coastal system influenced by freshwater inputs: northwestern Yucatan peninsula
Texto completo
Figure
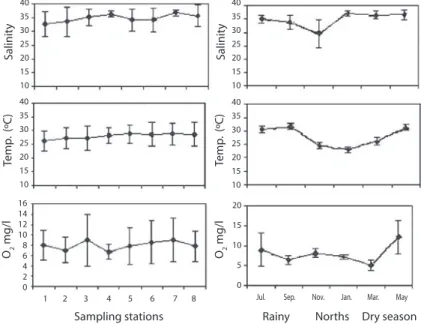

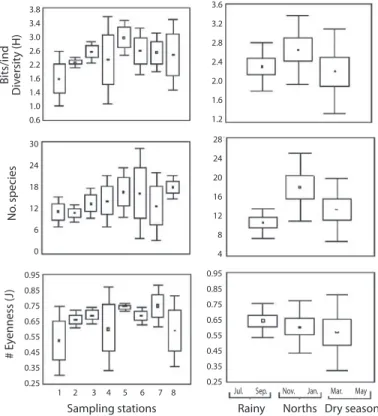
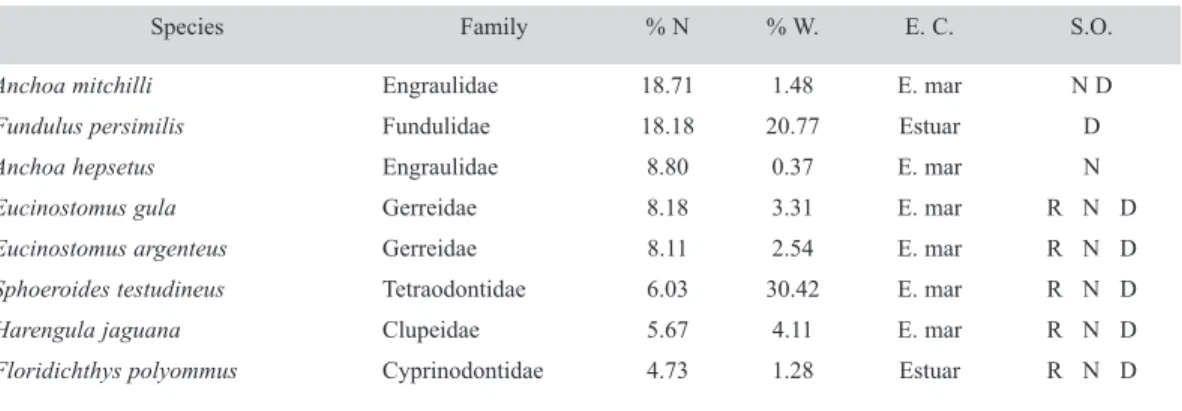
Documento similar
(2014) Isolation and Characterization of 26 Microsatellite Loci for the Shortfin Silverside Fish Chirostoma humboldtianum Valenciennes 1835 (Atherinopsidae: Menidiinae) Derived
In this cross-sectional analysis of the PREDIMED-Plus trial, we observed a non-linear inverse association only for between moderate levels of fish consumption (particularly fatty
Proline is capable of accumulating in some species like citrus [18,141,142] y in the presence of certain abiotic stresses, i.e., salinity, drought, waterlogging and temperature
Figure 1 aCGH and FISH results in the proband and the mother. a) Proband aCGH results showing 16p13.11 duplication. b-c) Proband FISH results with probe NDE1-MYH11 (red) showing
• To study the diversity, distribution and temporal dynamics of mesophilic planktonic archaeal communities in different temperate stratified freshwater lakes characterised
4) Restoration activities led to a significant positive change in the benthic community in terms of spatial and temporal variability. 5) Only the 1-GOLD metric had the capacity
Significant differences in cardiometabolic, renal, and anthropometric parameters among choline/betaine consumption quartiles at baseline were compared by 1-factor ANCOVA test
Our results, using freshwater fish cell lines and a set of relevant cytotoxicity endpoints including cell viability, oxidative stress, and DNA damage, provide additional mechanistic