Effects of unstable shoes on trunk muscle activity in patients with chronic low back pain / Pablo Salvador Coloma [et al ]
Texto completo
Figure
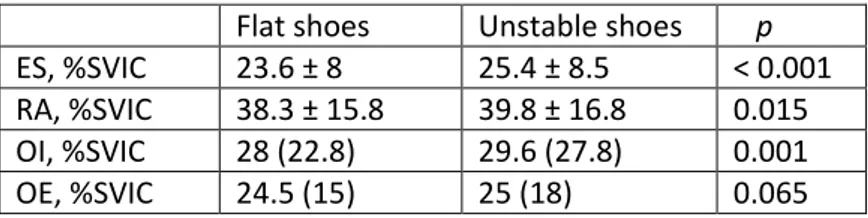
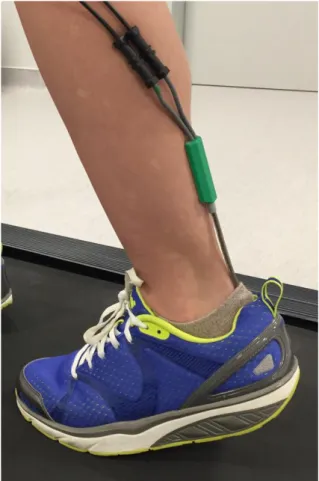
Documento similar
A web-based biopsychosocial pain education intervention for patients with chronic low back pain proved to be more beneficial than conventional care provided by
The main findings of this review indicate that (I) there is good quality evidence from studies regarding the reliability of trunk strength assessment in patients
No obstante, como esta enfermedad afecta a cada persona de manera diferente, no todas las opciones de cuidado y tratamiento pueden ser apropiadas para cada individuo.. La forma
The purpose of the present study was to compare the accelerometer-measured physical activity and sedentary behavior during the whole day, in-school time, out-of-school time,
In the preparation of this report, the Venice Commission has relied on the comments of its rapporteurs; its recently adopted Report on Respect for Democracy, Human Rights and the Rule
This work is the study of the chemical complexity and the physical conditions of the molecular gas in three galaxies with different type of activity, in our sample we have a
The objective of this project is to find out if the treatment of chronic pain with virtual reality and augmented reality obtains significantly positive results in the
Popular models of pain, such as the fear-avoidance and the psychological model of pain, have hypothesized that functional limitations in patients with chronic pain are influenced by