Extreme climatic events change the dynamics and invasibility of semi arid annual plant communities
Texto completo
Figure

Documento similar
From the very beginning the Annual Conference of the Sociedad Mexicana de Ciencia y Tecnología de Superficies y Materiales (SMCTSM, Mexican Society of Science and Technology
Void fraction rates, free surface undulation pattern, phase-change detection frequency, mean velocities near the bot- tom, and Sauter mean bubble diameter have been analyzed in
This study aims to estimate the impact of the land cover change from shrubs to oil palm plantation on mammal species richness, evenness, and composition and estimate the amount
Monthly number of days exceeding the daily EU PM10 limit value (50µg/m 3 ) during African and non-African episodes in MONAGREGA rural site.. Monthly number of days exceeding the
In this chapter, we evaluated species richness and the taxonomic diversity of the reptile communities from arid and semiarid environments in the state of Hidalgo, México; and we
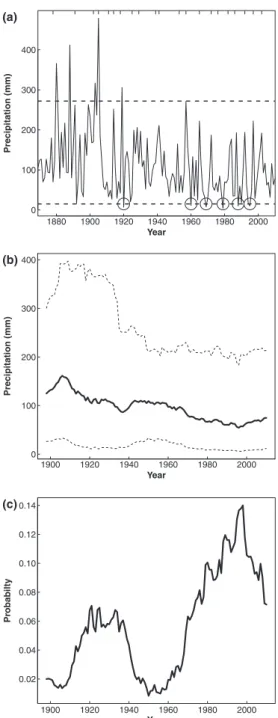
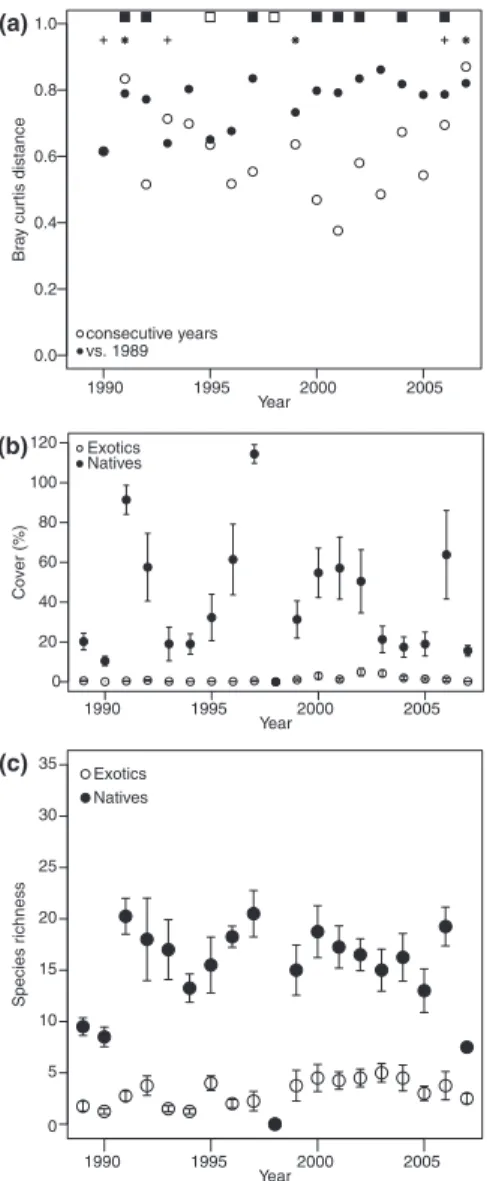
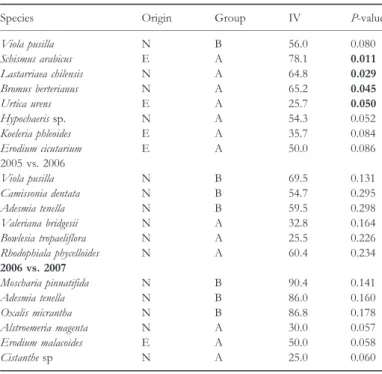
information is required from these regions to understand the effects of exotic species in these climates. Studies focusing on the effects of exotic species in arid climates are
In section 3 we consider continuous changes of variables and their generators in the context of general ordinary differential equations, whereas in sections 4 and 5 we apply
The concept of breakdown probability profile is useful to describe the break- down properties of any estimate obtained through resampling, not just the bagged median or the