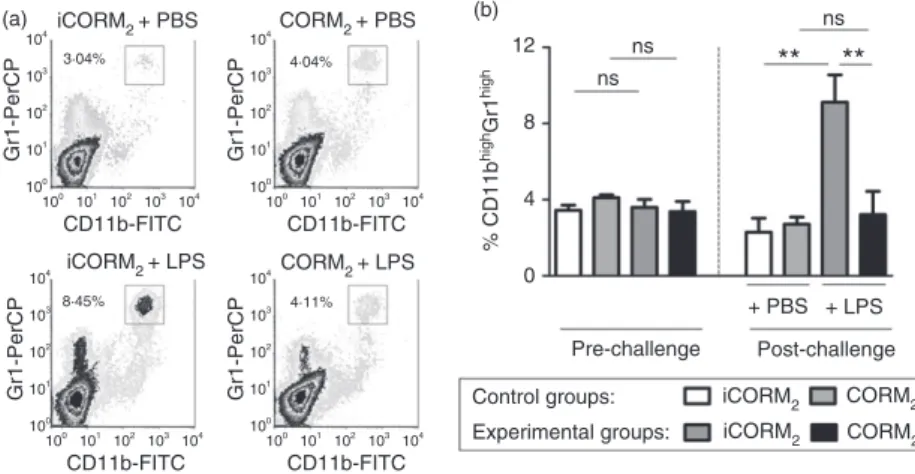
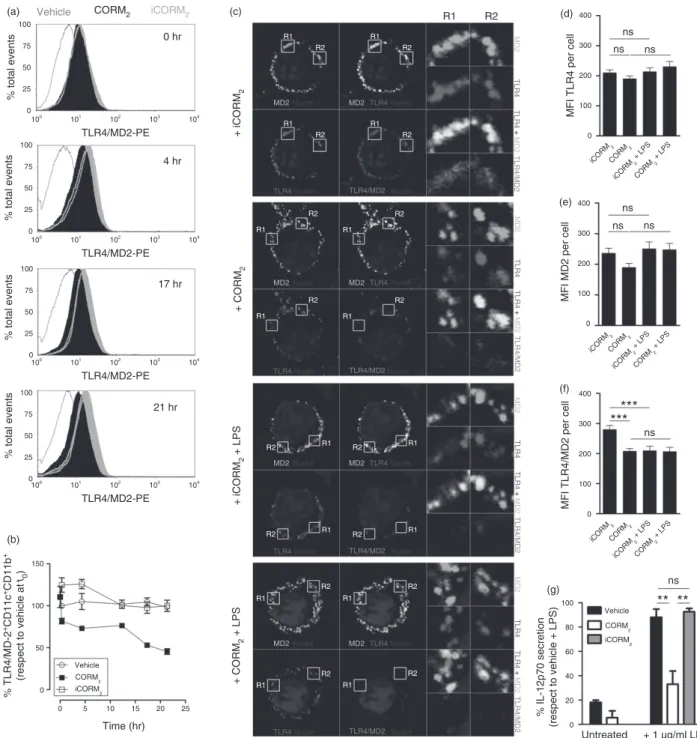
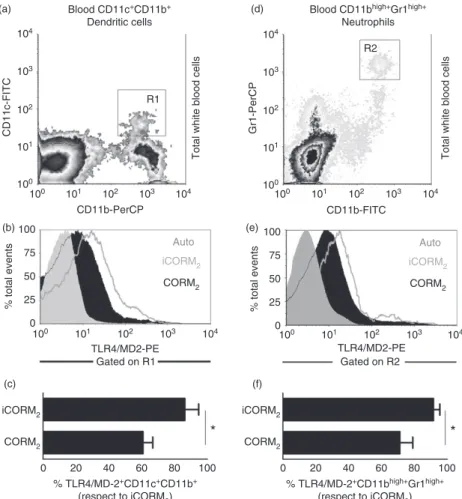
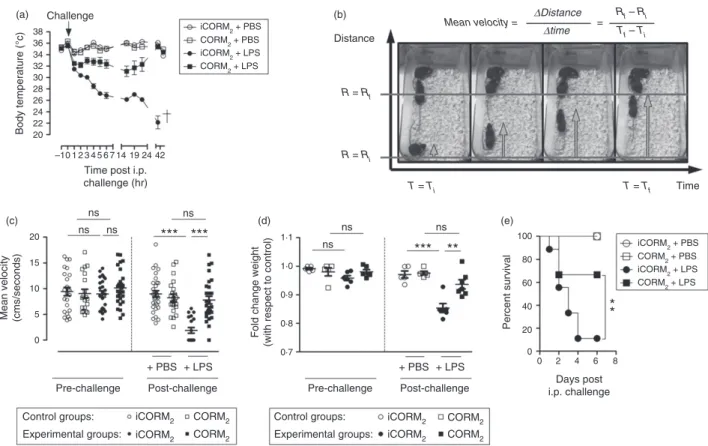
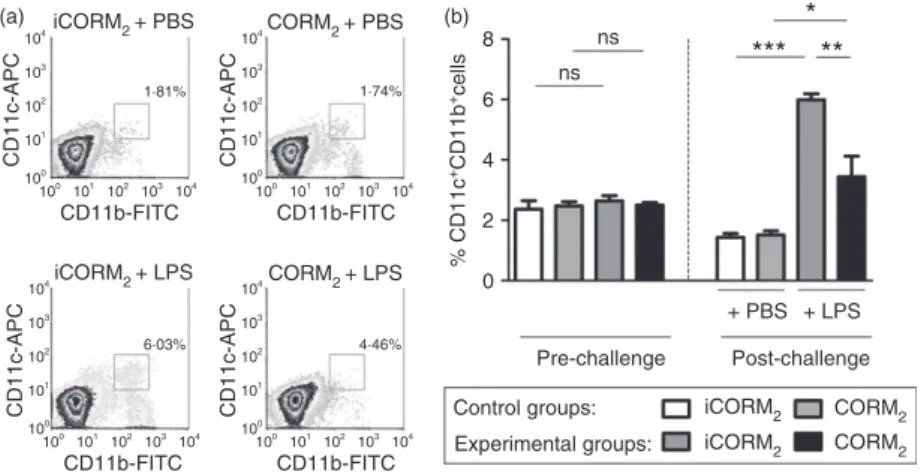
Carbon monoxide down modulates Toll like receptor 4/MD2 expression on innate immune cells and reduces endotoxic shock susceptibility
Texto completo
Figure
Documento similar
Abstract: Transepidermal water-loss (TEWL), stratum-corneum hydration (SCH), erythema, elas- ticity, pH and melanin, are parameters of the epidermal barrier function and
This effect could be explained by an increase in the concentration of carnosic acid observed in the SR extracts, which was around 10-20% greater than the
In addition we will to present our result of the effect in the magnetoresist- ance of an organic molecule such as the Manganese Phthalocyanine (MnPc), a high magnetic spin
Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) signaling augments chemokine- induced neutrophil migration by modulating cell surface expression of chemokine receptors. Overexpression of G
Chagas’ disease caused by the intracellular protozoan Trypanosoma cruzi is the most important parasitic infection in Latin America affecting several million persons. None-
Neurons, astrocytes, microglial or endothelial cells are susceptible to α-Syn aggregates (i.e., by phagocytosis, endocytosis, Toll-like receptor (TLR) stimulation, etc.), which
Growth regulation of human colon cancer cells by epidermal growth factor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 is mediated by mutual modulation of receptor expression. The down-regulation
These results suggest that unconjugated ISG15 is responsible for counteracting the development of an exacerbated inflammatory response after a high dose of VV⌬E3L virus. To analyze