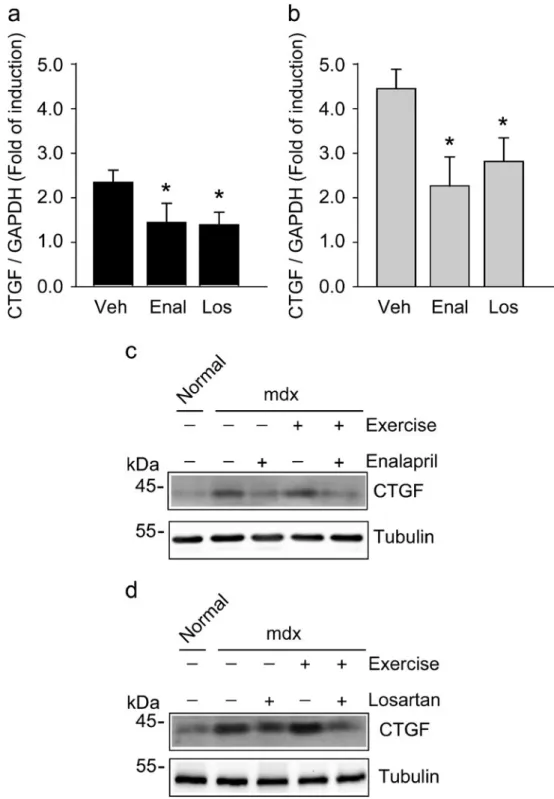
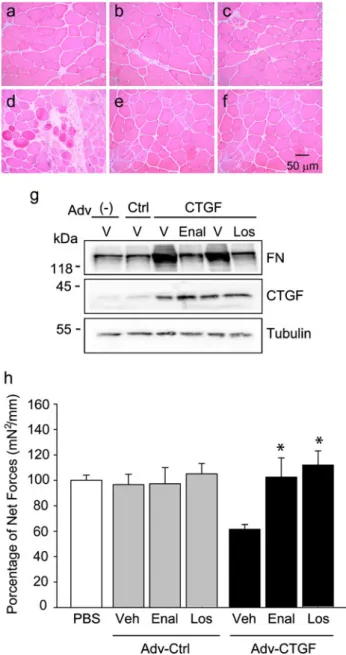
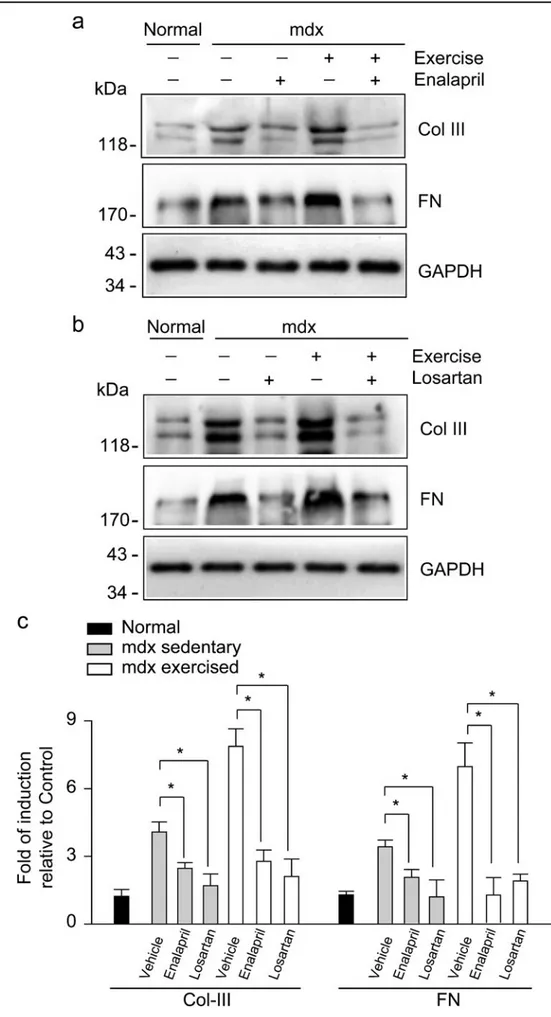
Inhibition of the angiotensin converting enzyme decreases skeletal muscle fibrosis in dystrophic mice by a diminution in the expression and activity of connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN 2)
Texto completo
Figure



Documento similar
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the
Modulation of miRNA expression in mice have revealed the great influence of those in multiple aspects of the heart physiology, from controlling myocyte growth to
At the same time, ZEB1 can switch from a transcriptional repressor to an activator by binding to p300/CBP suggesting another potential mechanism by which ZEB1 regulates
Abbreviations: ACE, angiotensin converting enzyme; Ang II, angiotensin II, ARB, angiotensin receptor blockers; ARE, antioxidant responsive element; AT1R, angiotensin II receptor type
In addition, in db/db mice, inhibition of TLR4/NF-κB signaling prevented the decreased kidney PGC-1α expression, mitochondrial dysfunction and deformation, and ROS accumulation,
AAV9-CnAβ1 decreases the expression of genes associated with heart failure and fibrosis in the remote myocardium post MI – AAV9-CnAβ1 administration at a dose of 3.5e10 VP,
More recently, we have described that over-expression of IF1 in cells with negligible content of the protein results in the inhibition of the ATP synthetic activity of the H +
Growth regulation of human colon cancer cells by epidermal growth factor and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D 3 is mediated by mutual modulation of receptor expression. The down-regulation