Problem Understanding through Landscape Theory
Texto completo
Figure
![Figure 2: Expectation E[f(M p (x))] for a function with three elementary components.](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/6341261.782531/6.892.530.778.244.495/figure-expectation-e-f-m-function-elementary-components.webp)

Documento similar
The Dwellers in the Garden of Allah 109... The Dwellers in the Garden of Allah
The generalized operators implanted in programmable logical devices (PLDs) can be applied in the solution of problems or in systems that operate with binary components without the
III we show that the magneto-optical contribution in the dressed polarizability (driving the magneto-optical dipole) can be enhanced through the interaction with a flat surface,
The gain of state space decomposition techniques with respect to the classical exact solution algorithm (solution of the underlying CTMC of the original model) is in both memory
We also prove formally (Appendix A) that the two problems are related; in particular, the proposed problem can be derived from the LP-max problem and the optimal value of the
This setup is then used to show that the existence of the Dwyer-Wilkerson centralizer decomposition with respect to the family of elementary abelian p-subgroups of a p-compact group
In this section we complete the proof that Crandall-Rabinowitz’s theorem can be applied to show that bifurcation is possible at simple eigenvalues associated with frequencies m ≥
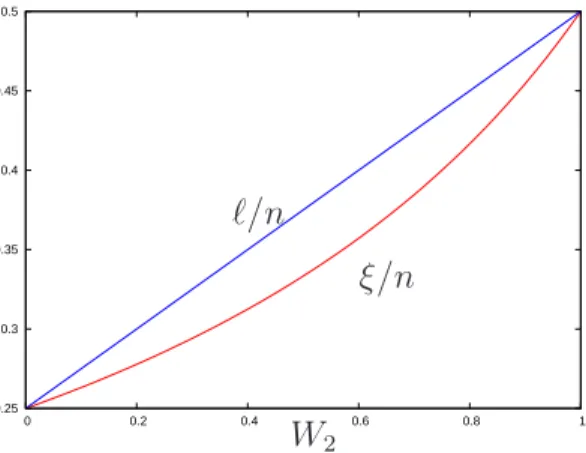
In the case of uniform distribution, i.e. Note that if k = N we obtain the solution of the coupon collector’s problem in the case of uniform distribution. When the probabilities p k