Selective cytoprotective effect of histamine on doxorubicin induced hepatic and cardiac toxicity in animal models
Texto completo
Figure
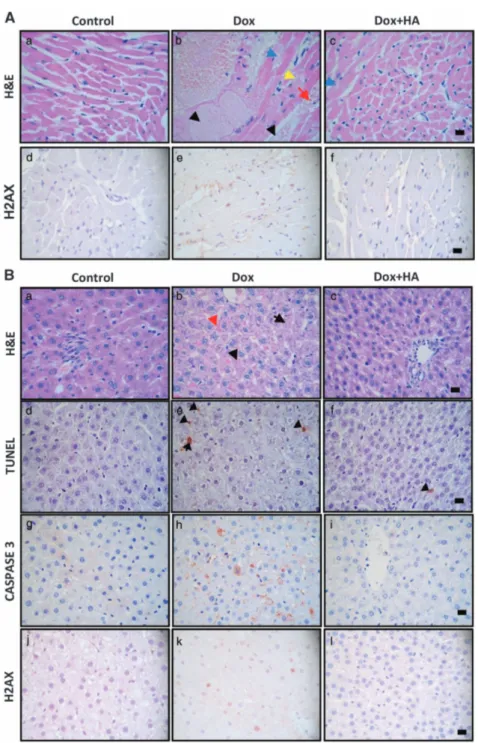

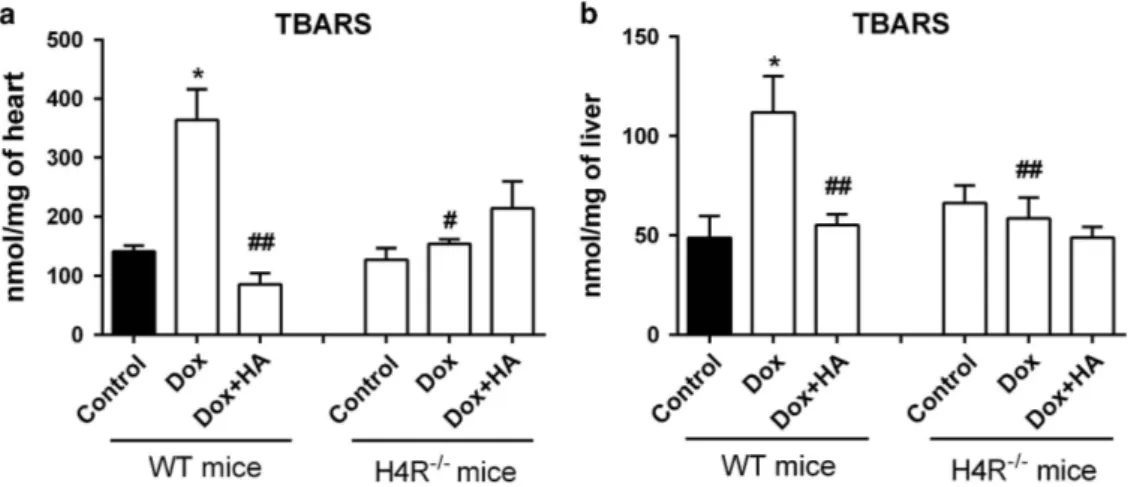
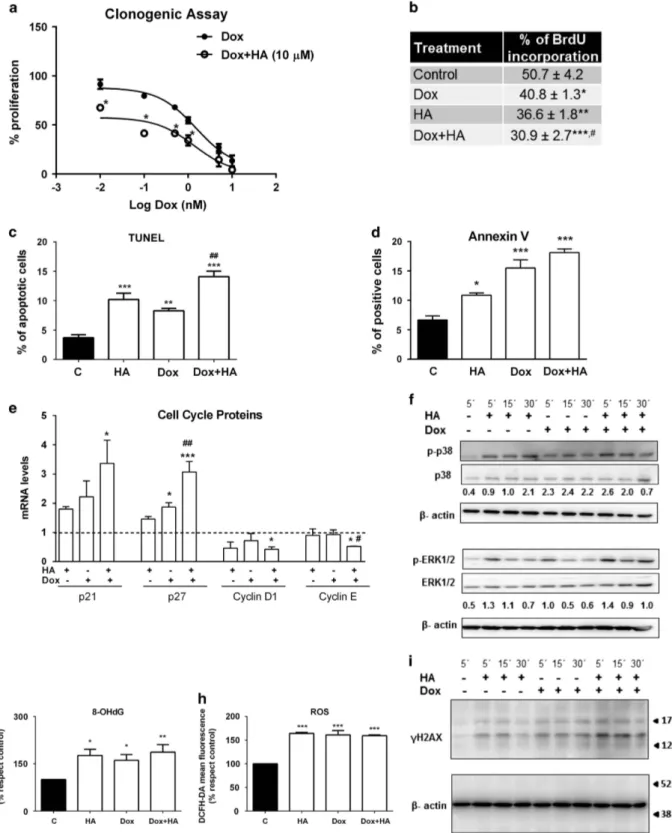
Documento similar
In the same figure, it can be observed that SKNSH, MCF-7, and C33-A cells lines did not show significant changes in cell viability with the different lectin concentrations, which
To evaluate quantitatively, the cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in a dose-dependent manner in control and hypertrophic cardiac cells.. To synthesize
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the
Jointly estimate this entry game with several outcome equations (fees/rates, credit limits) for bank accounts, credit cards and lines of credit. Use simulation methods to
In our sample, 2890 deals were issued by less reputable underwriters (i.e. a weighted syndication underwriting reputation share below the share of the 7 th largest underwriter
Moreover, CPT1C silencing increased cell survival against doxorubicin (DOX) treatment in different BC cells due to reduced drug uptake.. These findings, further complemented by
Direct protective effects of metformin on cardiac cells Since both sitagliptin and metformin similarly reduced fibrosis in the GK heart, and GLP-1 triggered anti-fibrotic
Similar to the results obtained in the genetic model, we observed a time- dependent decrease of the CD133+ cell fraction in ATR siRNA-treated cells along with a

