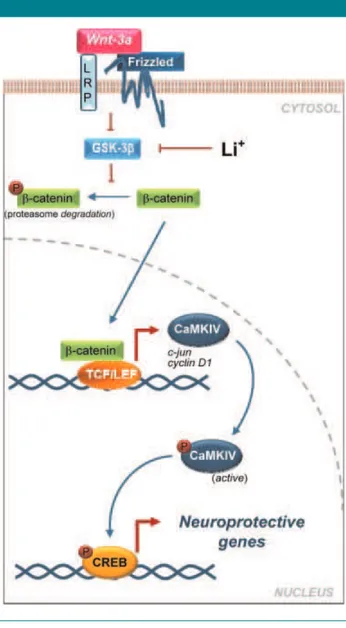
Calcium/Calmodulin Dependent Protein Kinase Type IV Is a Target Gene of the Wnt/beta Catenin Signaling Pathway
Texto completo
Figure




Documento similar
The purpose of this paper is to apply the same model to the calculation of photo and electroproduction amplitudes of the Roper, the aim being to check whether it is possible or
The lifetime signed impact parameter probability dis- tribution was determined as a function of the tau lifetime as follows: impact parameter distributions, for di erent lifetimes,
The above analysis leads to an experimental scenario characterized by precise mea-.. Figure 4: The allowed region of Soffer determined from the experimental data at 4GeV 2 ,
Taken together, these results demonstrated that the global impact of miR-17~92 on its target gene mRNA levels is subtle, that only a subset of functionally relevant target genes
On the other hand at Alalakh Level VII and at Mari, which are the sites in the Semitic world with the closest affinities to Minoan Crete, the language used was Old Babylonian,
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) is a negative regulator of insulin signaling and a therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes (T2DM). In this study, we have evaluated the role
URI specifically localizes and inhibits WNT/ catenin signaling pathway in stem-cell-like label retaining (LR) cells, essential for organ regeneration following IR
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved nutrient-sensing protein kinase that regulates cell growth and metabolism