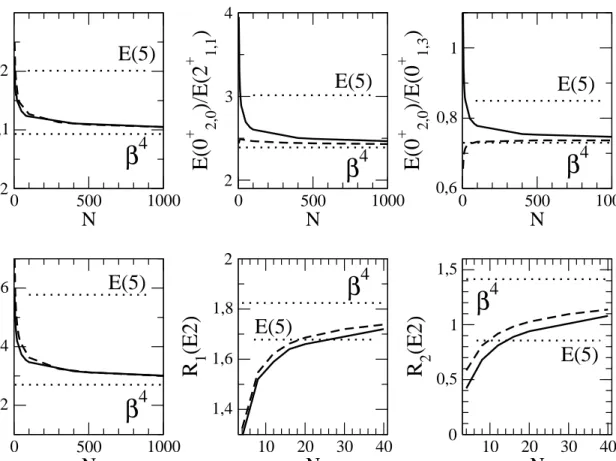
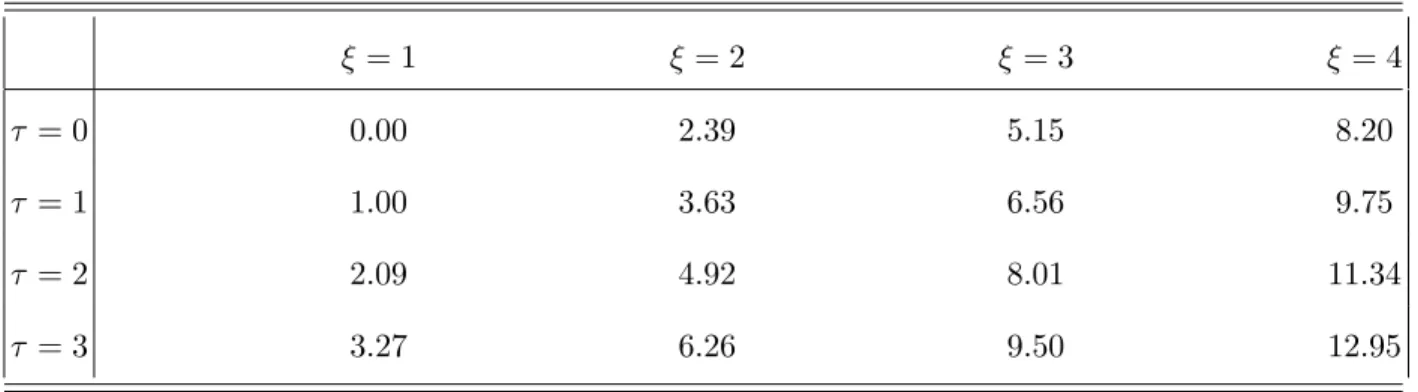
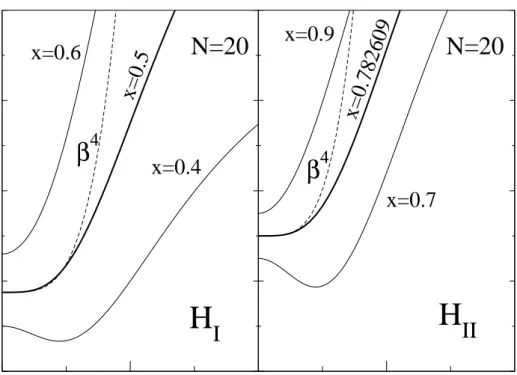
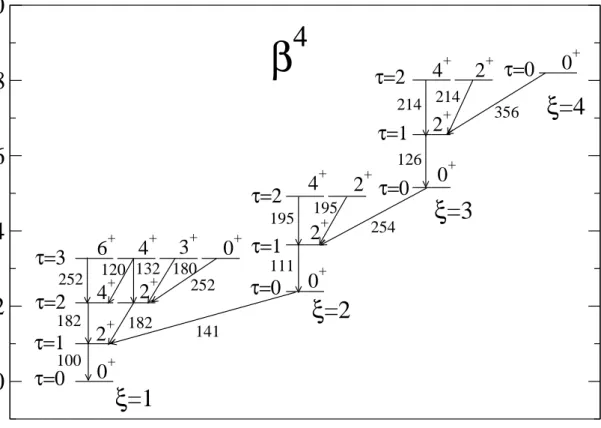
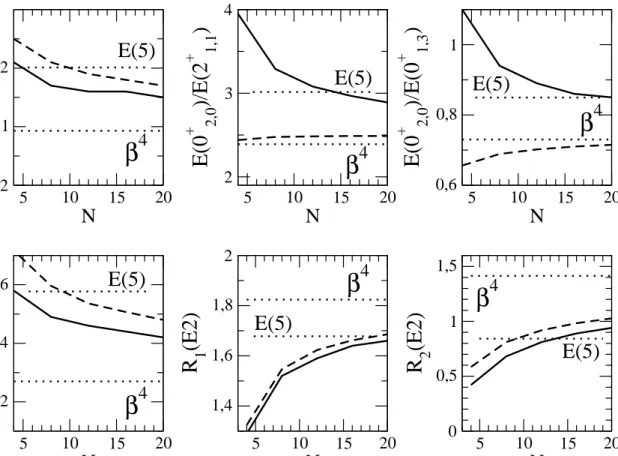
The U(5)–O(6) transition in the Interacting Boson Model and the E(5) critical point symmetry
Texto completo
Figure
Documento similar
MD simulations in this and previous work has allowed us to propose a relation between the nature of the interactions at the interface and the observed properties of nanofluids:
Government policy varies between nations and this guidance sets out the need for balanced decision-making about ways of working, and the ongoing safety considerations
The expansionary monetary policy measures have had a negative impact on net interest margins both via the reduction in interest rates and –less powerfully- the flattening of the
We classified all the objects of the 10 pc sample in five cat- egories (OBJ_CAT 5 in Table A.1): stars (K and earlier spectral types), low-mass stars (M and early-L types),
* Experiment 2. Sets of two Madam Vinous sweet orange plants were simultaneously co- inoculated with any of the 15 mild isolates indicated in Table 2 and the severe isolate T388.
The spatially-resolved information provided by these observations are allowing us to test and extend the previous body of results from small-sample studies, while at the same time
(hundreds of kHz). Resolution problems are directly related to the resulting accuracy of the computation, as it was seen in [18], so 32-bit floating point may not be appropriate
Results show that both HFP-based and fixed-point arithmetic achieve a simulation step around 10 ns for a full-bridge converter model.. A comparison regarding resolution and accuracy