TítuloEffects of severe hypoxia on bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells differentiation potential
Texto completo
Figure

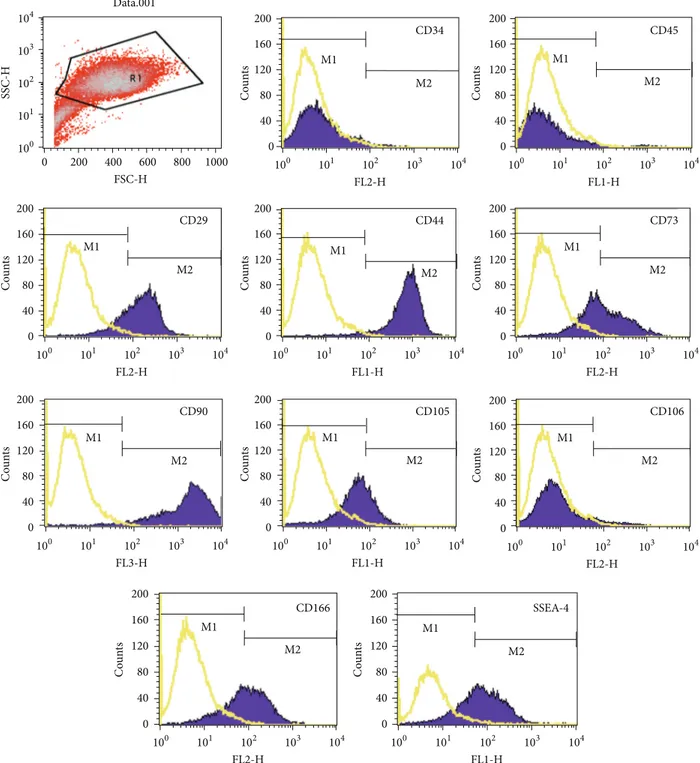


Documento similar
Figure 3 Effects of acute and allogenic intravenous (i.v.) administration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal (BM-MSC) and adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal (AD-MSC) cells on
(C) lncRNAs can represent a bridge between the many layers of epigenetic gene regulation, interacting with, for example, histone modifiers or serving as ceRNAs for miRNAs; (D)
human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow and adipose tissue under xeno-free conditions for cell therapy. Stem Cell
Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Safely Healed with Autologous, Expanded, Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in a Multicentric Trial with Minimum 5 Years
The expression of most of the genes comprised in lung AM-related module 296 was upregulated in VHL-deficient AMs compared to control WT cells, including its associated
Human cancer cells show predominant expression of NANOGP8, whereas pluripotent cells (embryonic stem cells and embryonal carcinoma cells) express the NANOG variant
In CTSB deficient cells, the HSV-1 infection in the absence or presence of X-XOD induced higher levels of lysosomal proteins than in non-deficient X-XOD treated cells (Figure
Cell viability after shipment was > 80% in all cases, enabling evaluation of (1) adhesion to plastic flasks and hydroxyapatite tricalcium phosphate osteoconductive
