Comparasion of road traffic emission models in Madrid (Spain)
Texto completo
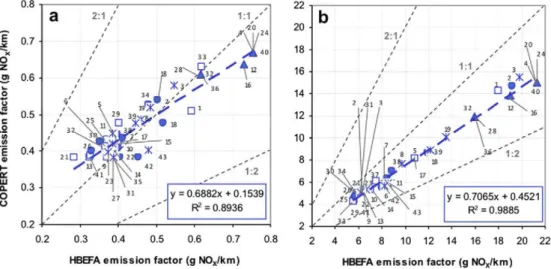
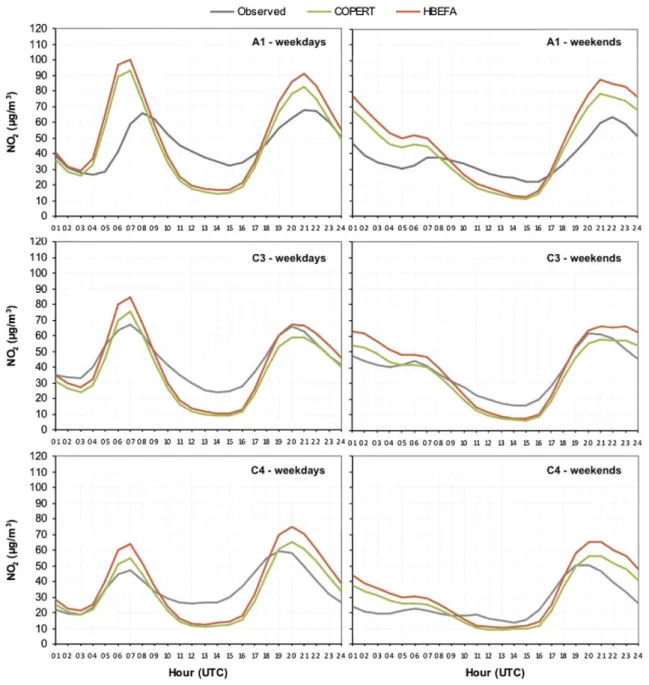
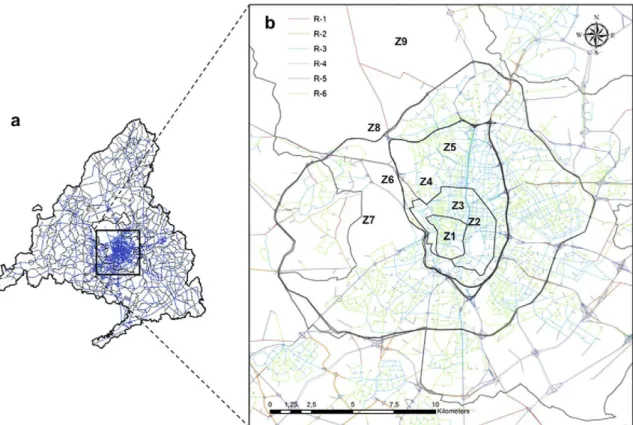
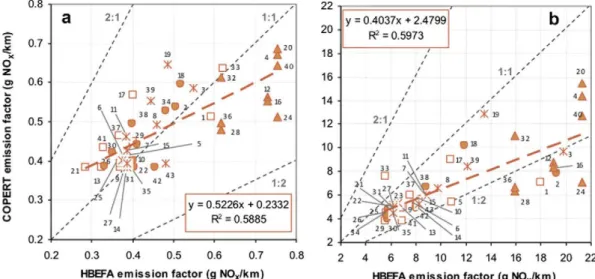
Figure

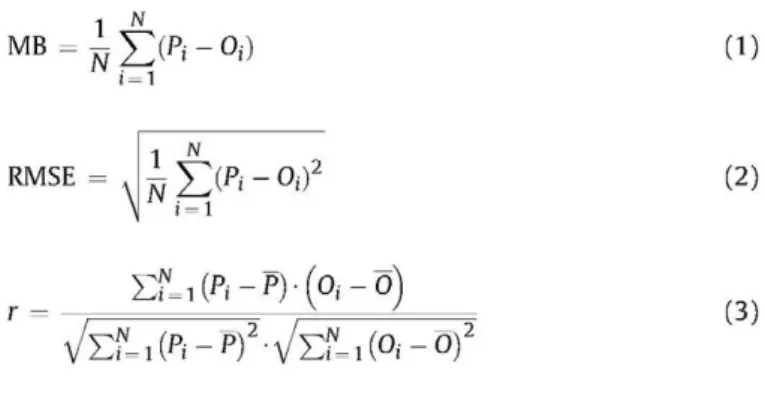
Documento similar
This article describes the current situation of desalinated seawater production and supply to agriculture in the southeast of Spain, and analyzes key questions such as its role
2) preserving correlations among multiple services, both in terms of structural similarity and percentage contribution to total traffic; 3) allowing traffic generation for target
1) We collected the firmware and traffic information from real-world devices using crowd-sourcing methods (§II). We obtained the firmware from 2,748 users spanning 1,742 device
Second, the performance of our proposal, in terms of throughput, shows that Skype traffic can be identified from a traffic aggregate of up to 1 Gbps with a single process
In addition to traffic and noise exposure data, the calculation method requires the following inputs: noise costs per day per person exposed to road traffic
In this sense, the present systematic review aims to examine the scientific articles in which a traffic and road safety campaign has been evaluated, whether they are adver-
The MTE manager is in charge of deciding where to send the traffic based on QoS information from the network. Layer 2 connections reduce the delay and traffic sent to the IP routers.
From a network planning perspective, the problem of finding the lightpaths to accommodate a given traffic demand is called the routing and wavelength assignment (RWA) problem