Selective carotid body ablation in experimental heart failure: a new therapeutic tool to improve cardiorespiratory control
Texto completo
Figure
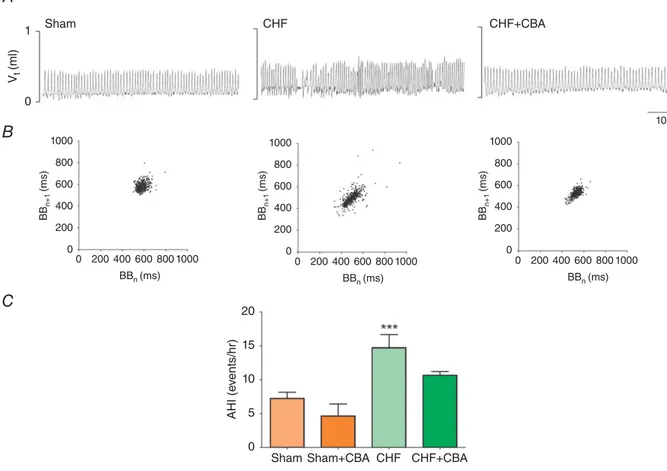
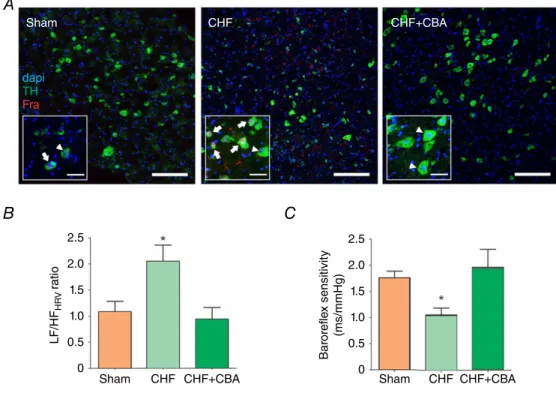
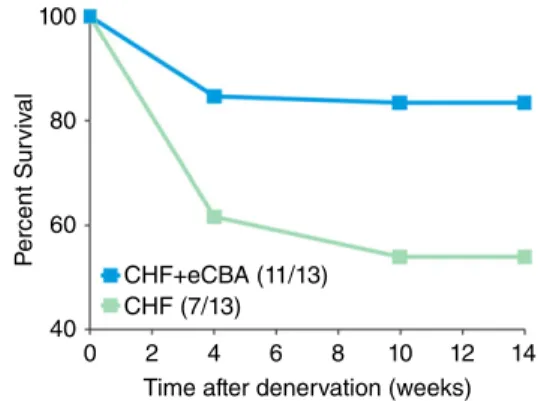
Documento similar
BMI: body mass index; CRF: cardiorespiratory fitness (i.e., peak VO 2 uptake); CRF BW : CRF relative to body weight (peak VO 2 uptake/kg of body weight); CRF FFM : CRF relative to
Beta-blocker improves survival, left ventricular function, and myocardial remodeling in hypertensive rats with diastolic heart failure. Induction of cardiac fibrosis by β- blocker
This study is part of a bigger and ambitious research project with the general aim to achieve a standardized and unique self-reported scale in Spanish-speaking population to
The cardiac regenerative response in zebrafish involves a substantial amount of cardiomyocyte proliferation, and zebrafish cardiomyocytes have a much higher degree of cell
Objectives: The aim of this study was to investigate the acute effect of water immersion (22.6 °C) on heart rate, heart rate variability, body temperature, oxygen saturation,
This study investigates the impact of the office workers' physical conditions described in body mass index (BMI) related to the Time to Recovery (TTR) and heart rate increase
Objectives: This study aimed to evaluate mid-term results of successful atrial fibrillation surgical ablation during valvular heart disease surgery, to explore left
This is the first case to be published in which acute Wernicke’s encephalopathy is triggered by the use of furosemide to treat heart failure in a patient with a probable prior