Low doses of insulin like growth factor I improve insulin resistance, lipid metabolism and oxidative damage in aging rats
Texto completo
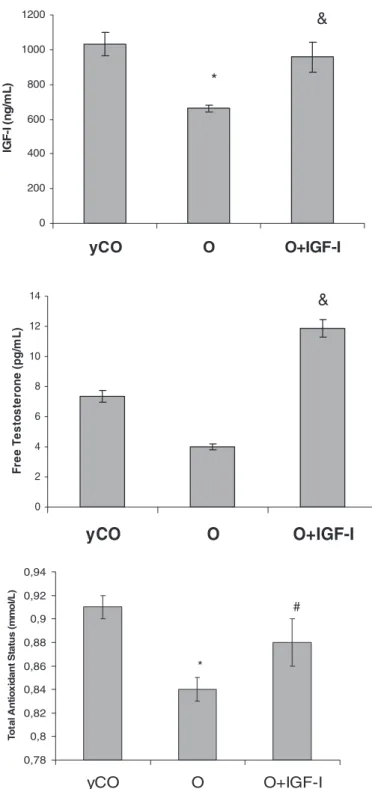
Figure



Documento similar
Recombinant human insulin‑like growth factor I has significant anabolic effects in adults with growth hormone receptor deficiency: studies on protein, glucose, and lipid
Evolution of insulin resistance measured by glucose tolerance test in CT, MtS and MtS-SYNB rats at the beginning of procedure (a), after 8 weeks of diet intervention (b) and after
(A) Relative GH receptor (GHR) protein levels in control rats (C); rats receiving acute central administration of insulin (CI); pair-fed rats (PF); pair-fed rats treated with
To investigate the effects of low- intensity resistance training on body fat, muscular strength, cardiovascular fitness and insulin sensitivity on overweight..
In support that this may be a cause for the insulin signalling defects, the replenishment of cholesterol to the hippocampus of old mice reduced PI3K/Akt activity, prevented
Methods Cross-sectional, multicentre, observational study conducted to determine the effectiveness—measured by control of serum insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) —of
Accordingly, the present study was devised to determine: (i) whether the PG become insulin resistant under obesity conditions in mice, for this may entail important
Treatment of the diabetic rats with RDE ameliorated hyperglycemia, improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, increased liver glycogen and alleviated the activity of