Functional and structural neural correlates of attention and memory during bimodal (auditory/visual) stimuli in children who play a musical instrument
Texto completo
Figure
Documento similar
It could maybe seem somehow insubstantial to consider an actual increase in computing power produced merely by a change in representation, consid- ering that computable functions
Here we can verify what we believe constitutes a paradox: the necessity of con- siderations of an ethical kind is imposed, but from that tradition of Economic Theory whose
Based on the aforementioned models proposing similar neural mechanisms for perception and memory and the studies showing recruitment of body-related cortices during
Alternatively, the allocation of attentional resources from a limited pool could occur at distinct points in time for target detection and perception of a blurry word, which
The present experiments study the effects of memory contents and memory load in RSVP speeded responses in two different situations: when memory and attentional tasks must be
The influence of puberty on vitamin D status in obese children and the possible relation between vitamin D deficiency and insulin
Conclusions: Very preterm infants who received formula with an ω-6/ω-3 ratio of 2/1 had higher blood levels of essential fatty acids during the first year of life, and
MCI participants performed at the same level as the control group in discrimination tasks, emotional labelling, prosody comprehension tasks, and immediate facial emotional memory
![Figure 4: Whole brain activation during encoding phase for the contrasts [ASA > P], [VSA > P] and [DA > P] in musically trained children (corrected p < 0.05)](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/7330196.454194/41.918.181.586.157.874/figure-activation-encoding-contrasts-musically-trained-children-corrected.webp)
![Figure 5: Whole brain activation during encoding phase for the contrast [VSA > P] in control children (corrected p < 0.05)](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/7330196.454194/42.918.204.727.146.445/figure-brain-activation-encoding-contrast-control-children-corrected.webp)
![Figure 6: Two-sample comparison of musically trained children over control children during encoding phase for the contrasts [ASA > P], [VSA > P] and [DA > P] (corrected p < 0.05)](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/7330196.454194/43.918.162.629.145.916/figure-comparison-musically-children-children-encoding-contrasts-corrected.webp)
![Figure 7: Conjunction analysis between the activation Musicians > Controls for the encoding phase of the contrasts [ASA > P], [VSA > P] and [DA > P]](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/7330196.454194/44.918.128.800.188.467/figure-conjunction-analysis-activation-musicians-controls-encoding-contrasts.webp)
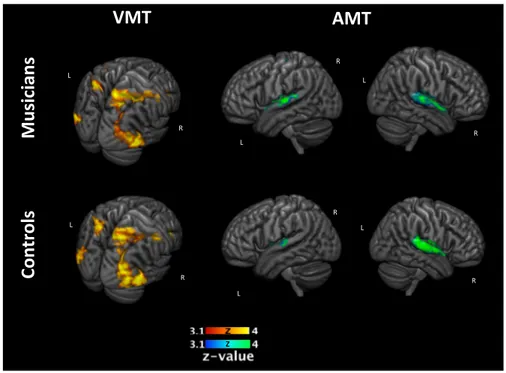
![Figure 9: Two-sample comparison of musically trained children over control children for the correlation between the activation in the encoding phase of the [VSA > P] with the correct responses of each subject in the auditory](https://thumb-us.123doks.com/thumbv2/123dok_es/7330196.454194/47.918.180.719.165.460/comparison-musically-children-children-correlation-activation-encoding-responses.webp)