Nanoscale effects on the thermal and mechanical properties of AlGaAs/GaAs quantum well laser diodes: influence on the catastrophic optical damage
Texto completo
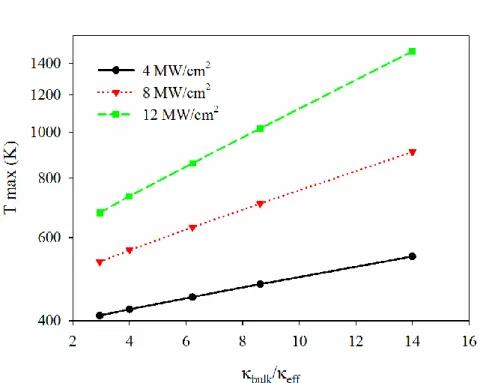
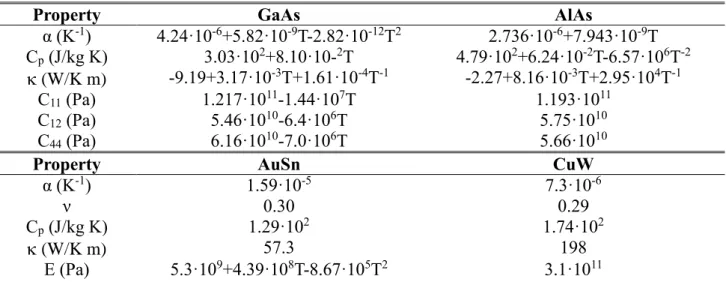
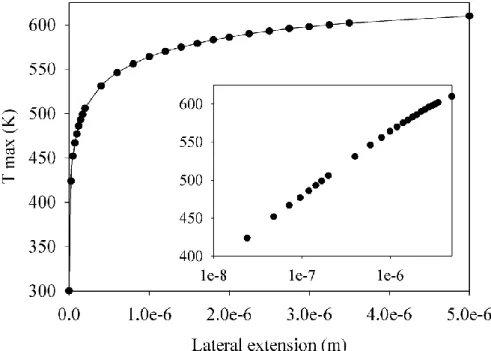
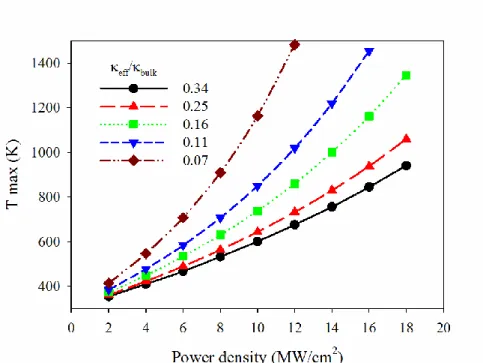
Figure

Documento similar
The scope of this Thesis is the investigation of the optical properties of two systems based on semiconductor nanostructures: InAs/GaAs quantum rings embedded in photonic
In the previous sections we have shown how astronomical alignments and solar hierophanies – with a common interest in the solstices − were substantiated in the
Li, Investigation on the flow and convective heat transfer characteristics of nanofluids in the plate heat exchanger, Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science 76
influence of these parameters on the size and distribution of Te inclusions, deep defects, optical and electrical properties of CdZnTe detectors. In the fourth chapter, the effect
Two cases are considered, the one for which the symplectic form on the torus is of integer cohomology class n (section 4.1), where full modular invariance is obtained only when the
CFD simulations for different Reynolds numbers provide a further insight into the relation of the flow structures with wall shear stress, and their role on the local heat
Next, in sections 7 and 8, the influence of the different elements/characteristics of the standard (termination, airline, thermal bead, level of liquid Nitrogen, etc.)
MD simulations in this and previous work has allowed us to propose a relation between the nature of the interactions at the interface and the observed properties of nanofluids: