Role of nitric oxide in placental vascular development and function
Texto completo
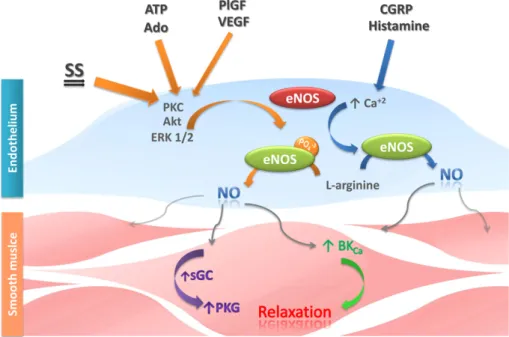
Figure

Documento similar
Keywords: nitrate assimilation, nitrate/nitrite uptake, green algae, nitric oxide, nitrogen metabolism,
the effect of NO donors was only abolished by the adenosine A 1 receptors antagonist; 2) in tail arteries, noradrenaline release was increased by NO donors and it was reduced by
Representative vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A) immunostaining of placenta sections (A) and Western blot VEGF-A protein analysis in placental lysed samples (B) for
Expression Pattern of Nitric Oxide Synthase during Development of the Marine Gastropod Mollusc, Crepidula fornicata.. Marta Truchado-Garcia 1,2 , Filomena Caccavale 3 , Cristina
Although R-Ras2/TC21 is expressed in tissues (ovary) and cells (vascular endothelial cells, adipo- cytes, and hematopoietic cells) that in- fluence mammary gland
This study analyzes whether the release of nitric oxide (NO) and thromboxane A 2 (TXA 2 ) depends on the time lapsed since gonadal function is lost, and their correlation with
Previous work has shown that VEGF up-regulates endothelial Adamts1 expression in a Protein Kinase C (PKC)-dependent manner and has involved the CN-NFAT pathway in Adamts1 gene
To evaluate quantitatively, the cytotoxicity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in a dose-dependent manner in control and hypertrophic cardiac cells.. To synthesize