TítuloGhrelin and lipid metabolism: key partners in energy balance
Texto completo
Figure

Documento similar
ApoAV reduces plasma triglycerides by inhibiting very low density lipoprotein-triglyceride (VLDL-TG) production and stimulating lipoprotein lipase-mediated VLDL-TG hydrolysis. 156)
Upon IS formation, mitochondria and peroxisomes are major organelles that mediate lipid metabolism changes and, in turn, T cell activation signaling pathways.. Mitochondria polarize
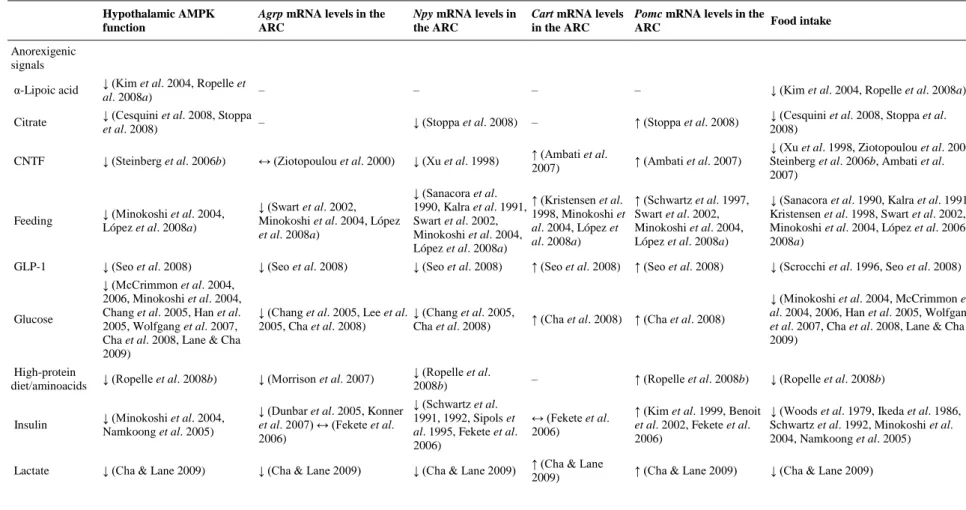
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway is an evolutionarily conserved nutrient-sensing protein kinase that regulates cell growth and metabolism
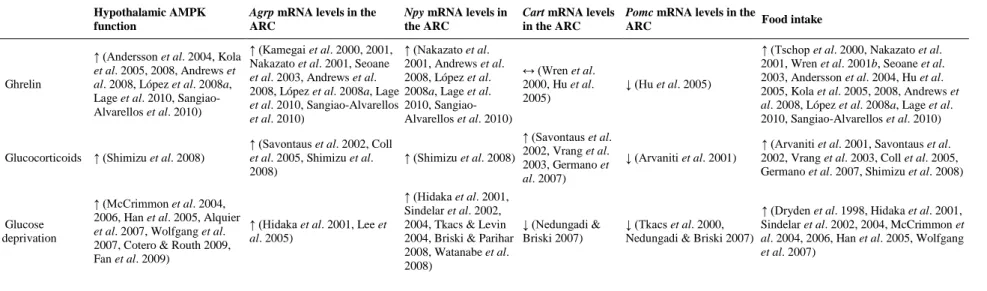
In agreement with the observed changes in hepatic SREBP-1c expression in liver, central leptin blunted the up- regulation of the mRNA levels of ACC, FAS, and SCD-1 elicited by the
In the context of lipid metabolism, we identified an expression signature: ColoLipidGene (ABCA1 (ATP- Binding Cassette Subfamily-A Member), ACSL1 (Acyl- CoA Synthetase
mRNA relative expression in human pancreatic cancer-derived cells (MIA PaCa-2) treated with two different concentrations of Yarrow extract (30 and 70 μg/mL) in comparison
This is consistent with the observation that acyl-ghrelin treatment rapidly decreased glucose uptake in primary astrocyte cultures that increased to control levels with 24 h
Background aims: After recent observations that intrathecal administration of autologous bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) increases cerebral metabolism in patients